Using Logstash for Data Migration
Logstash can be used to collect, transform, clean, and parse logs. This section offers an example of using a CSS Logstash cluster to migrate data between different Elasticsearch clusters. Through this example, you can learn how to use the Logstash service, including creating clusters, importing and exporting data, and configuring tasks.
Procedure
The following describes how to use a Logstash cluster to migrate data from one Elasticsearch cluster to another.
Before starting to migrate data, make the necessary preparations. For details, see Preparations.
- Step 1: Obtaining Elasticsearch Cluster Information: Obtain the addresses of the source and destination Elasticsearch clusters.
- Step 2: Creating a Logstash Cluster: Create a Logstash cluster for migrating data between Elasticsearch clusters.
- Step 3: Configuring a Data Migration Task: Configure an Elasticsearch cluster migration task for the Logstash cluster.
- Step 4: Starting the Migration Task: Start the migration task in the Logstash cluster.
- Step 5: Stopping the Task: After data migration is complete, stop the migration task.
Preparations
- You have registered with Huawei Cloud and performed real-name authentication. Make sure your account is not frozen or in arrears.
If you do not have a Huawei Cloud account, perform the following operations to create one:
- Visit the Huawei Cloud official website.
- In the upper-right corner of the page, click Register and complete the registration as prompted.
- Select the service agreement and click Enable.
- Perform real-name authentication.
- If your account is an individual account, see Individual Real-Name Authentication.
- If your account is an enterprise account, see Enterprise Real-Name Authentication.
- The source Elasticsearch cluster (Source-ES) and destination Elasticsearch cluster (Dest-ES) are ready. Both clusters are single-node non-security mode clusters.
- Confirm the indexes to be migrated in the source Elasticsearch cluster. In our example, the indexes whose name starts with index are to be migrated.
Step 1: Obtaining Elasticsearch Cluster Information
Obtain the addresses of the source and destination Elasticsearch clusters. For security-mode clusters, contact the administrator to obtain their usernames and passwords.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
- In the cluster list, obtain the IP address of the destination cluster from the Private Network Address column. Generally, the IP address format is <host>:<port> or <host>:<port>,<host>:<port>.
In this example, the address of the source Elasticsearch cluster (Source-ES) is 10.62.179.32:9200, and that of the destination Elasticsearch cluster (Dest-ES) is 10.62.179.33:9200.
Figure 1 Obtaining IP addresses
Step 2: Creating a Logstash Cluster
Create a Logstash cluster for migrating data between Elasticsearch clusters.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
- In the upper right corner, click Create Cluster. The new-version UI for creating a cluster is displayed by default.
Figure 2 Create Cluster (new version)

- Select the cluster type and version.
Table 1 Cluster configuration Parameter
Example
Description
Cluster Type
Logstash
Select Logstash.
Cluster Version
7.10.0
Select a cluster version from the drop-down list.
- Configure basic settings, including the region, billing mode, and AZs.
Table 2 Basic settings Parameter
Example
Description
Region
Hong Kong, China
Select the region where the cluster is located. A region is the location of a physical data center. Regions are defined based on their geographical location and network latency. For lower network latency and quicker resource access, select the nearest region.
AZ
AZ 1
Select AZs associated with the cluster region. An AZ is a physical region where resources use independent power supplies and networks. AZs are physically isolated but interconnected through an internal network.
A maximum of two AZs can be configured.
Billing Mode
Pay-per-use
Billing mode for the cluster, which can be Yearly/Monthly or Pay-per-use.
- Yearly/Monthly: You prepay for a yearly or monthly subscription.
- Pay-per-use (postpaid): You will be billed hourly by actual duration of use. Any partial hour of usage will be rounded up to one hour.
- Configure data nodes.
The data nodes in a Logstash cluster are used for processing and transmitting data.Figure 3 Configuring data nodes
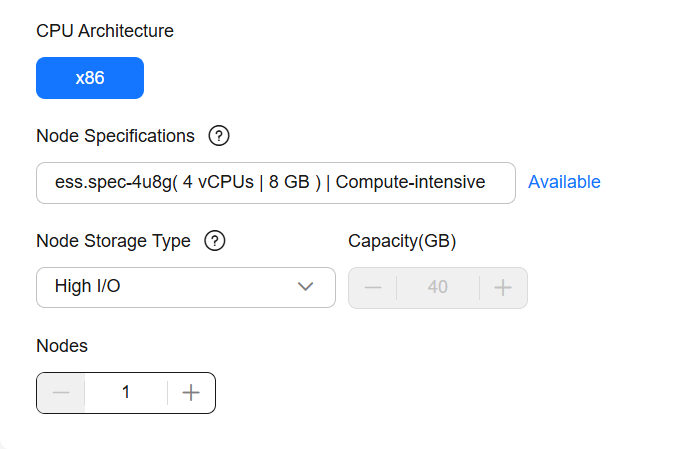
Table 3 Configuring data nodes Parameter
Example
Description
CPU Architecture
x86
Select the CPU architecture of the data nodes.
Node Specifications
ess.spec-4u8g
Select the specifications of the data nodes. Click Available. On the displayed page, select a flavor that suits your needs.
In the node flavor list, vCPUs | Memory indicate the number of vCPUs and memory capacity available for each flavor, and Recommended Storage indicates the supported storage capacity range.
The node flavors available may vary depending on the region you select.
Node Storage Type and Capacity
- High I/O
- 40GB
Select the storage type and capacity of the data nodes.
- Available EVS disk types vary depending on your region.
- The node storage capacity is fixed at 40 GB.
Nodes
1
Set the number of nodes in the cluster.
- Configure network settings for the cluster, including the VPC, IP address, and security group.
Figure 4 Configuring network settings
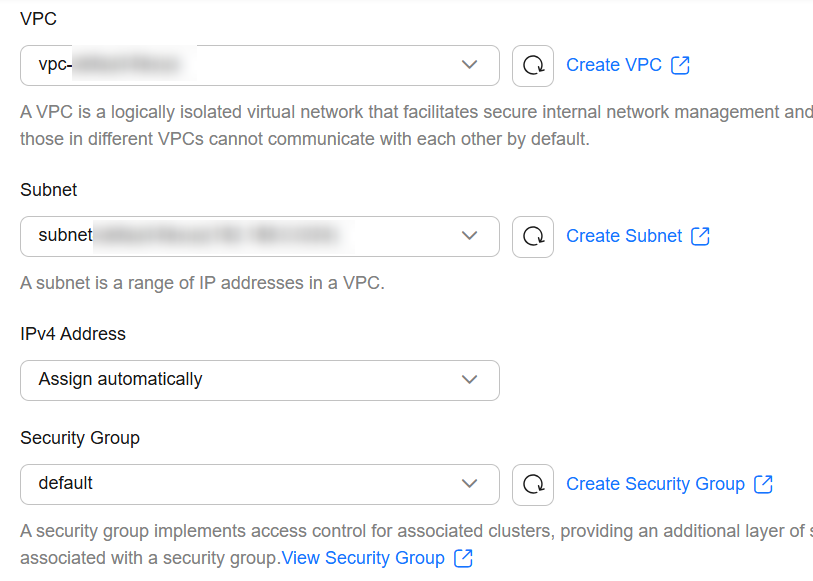
Table 4 Configuring network settings Parameter
Example
Description
VPC
vpc-default
Select a VPC for the cluster for proper network isolation.
Subnet
subnet-default
Select a subnet for the cluster. A subnet improves network security by providing exclusive network resources that are isolated from other networks.
Select a subnet in the current VPC.
IPv4 Address
Assign automatically
Assign IPv4 addresses to cluster nodes.
Security Group
default
Select a security group for the cluster. A security group serves as a virtual firewall that provides access control policies for clusters.
The selected security group must allow all ports or port 9200 in the inbound direction. Otherwise, the cluster may be inaccessible to external services.
- Configure cluster management settings, such as the cluster name and enterprise project.
Table 5 Cluster management Parameter
Example
Description
Cluster Name
Sample-Logstash
User-defined cluster name.
Add Description
Skip this setting.
Add a description for the cluster for easy recognition.
Enterprise Project
default
Associate the cluster with an enterprise project.
An enterprise project groups cloud resources, so you can manage resources and members by project. The default project is default.
If enterprise projects are enabled, you can select an enterprise project from the drop-down list.
Tags
None
Cluster tags help you identify and manage your cluster resources.
Each cluster can have a maximum of 20 tags.
- Click Create Now.
- Return to the cluster list and check the newly created cluster. If the cluster is created successfully, Cluster Status changes to Available.
Figure 5 Checking the cluster status

Step 3: Configuring a Data Migration Task
Configure an Elasticsearch cluster migration task for the Logstash cluster.
- In the Logstash cluster list, click Sample-Logstash to show the cluster information page.
- Click the Configuration Center tab.
- On the Configuration Center page, click Create in the upper-right corner. On the Create Configuration File page that is displayed, edit the configuration file.
Figure 6 Create Configuration File

Table 6 Parameters for creating a configuration file Parameter
Example
Description
Name
es-es
User-defined configuration file name.
It can contain only letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_), and must start with a letter. The minimum length is 4 characters.
Configuration File Content
See Table 7 for key configuration items. Use the default settings for others.
Expand System Templates, find elasticsearch, and click Apply in the Operation column. In the Configuration File Content area, configure the configuration file based on comments in the template.
Hidden Content
N/A
Configure the strings you want to hide.
For each string you enter, press Enter.
You can enter a maximum of 20 strings, each with a maximum length of 512 bytes.
Description
/
An additional description of the configuration file for easy identification.
Table 7 Configuration item description Configuration Item
Example
Description
hosts
input hosts: http://10.62.179.32:9200
output hosts: http://10.62.179.33:9200
Enter the addresses of the source and destination Elasticsearch clusters in input and output, respectively. For details about how to obtain the cluster addresses, see Step 1: Obtaining Elasticsearch Cluster Information.
user
Use # to comment it out.
Username for accessing the Elasticsearch cluster. This parameter is required for security-mode clusters. For non-security mode clusters, use # to comment out this parameter.
password
Use # to comment it out.
Password for accessing the Elasticsearch cluster. This parameter is required for security-mode clusters. For non-security mode clusters, use # to comment out this parameter.
index
index*
Specifies indexes that need to be migrated. You can use a wildcard.
- Click Next to configure Logstash pipeline parameters.
Figure 7 Configuring pipeline parameters

Table 8 Pipeline parameters Parameter
Example
Description
pipeline.workers
4
Number of worker threads that will execute the Filters and Outputs stages of the pipeline in parallel.
pipeline.batch.size
125
Maximum number of events that a worker thread collects from inputs before attempting to execute its filters and outputs. A larger value is more effective but increases memory overhead.
pipeline.batch.delay
50
Maximum amount of time (in milliseconds) that a pipeline worker waits for each new event while its current batch is not yet full.
query.type
memory
An internal queue model for event buffering.
- memory indicates a traditional memory-based queue.
- persisted indicates a disk-based ACKed persistent queue.
- Click Create. The system automatically verifies the configuration file. When the configuration file status changes to Available, the creation is successful.
Figure 8 Configuration file verification

Step 4: Starting the Migration Task
Start the configured migration task in the Logstash cluster.
- On the Configuration Center page, select the newly created configuration file, whose status is Available, and click Start. In the pipeline list, the Events column shows number of tasks processed by each stage of the pipeline.
Figure 9 Starting a task

- After the data migration is complete, check the data consistency between the source and destination Elasticsearch clusters. For example, run the GET _cat/indices command in the source and destination clusters, separately, to check whether their indexes are consistent.
- In the Elasticsearch cluster list, select the source Elasticsearch cluster Source-ES or the destination Elasticsearch cluster Dest-ES, and click Access Kibana in the Operation column to access the Kibana console.
- In the Kibana navigation pane on the left, choose Dev Tools.
The left part of the console is the command input box, and the triangle icon in its upper-right corner is the execution button. The right part shows the execution result.
- On the Console page, run the following command to view index information:
GET _cat/indices
Step 5: Stopping the Task
After data migration is complete, stop the migration task.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster. The cluster information page is displayed.
- Click the Configuration Center tab.
- In the cluster list, select the Sample-Logstash cluster, and click Configuration Center in the Operation column.
- On the Configuration Center page, select the name of the pipeline that has been started, and click Stop All to stop all running tasks. Wait until all pipeline tasks are stopped.
Figure 10 Stopping tasks

Follow-up Operations
After data migration is completed, you may delete clusters created earlier to reclaim resources. Before you start, make sure that all pipeline tasks are stopped.

To ensure data security, before deleting a cluster, stop all ongoing tasks, and back up the necessary files.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
- In the cluster list, locate the Sample-Logstash cluster, and choose More > Delete in the Operation column.
- In the confirmation dialog box, type in DELETE, and click OK.
- (Optional) Delete the source and destination Elasticsearch clusters following this same procedure if they are no longer needed.
Related Documents
Learn how to use Logstash to synchronize data to CSS's Elasticsearch:
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





