What Is WAF?
Web Application Firewall (WAF) is a tool used to protect web applications. WAF is deployed in front of web applications. It checks HTTP and HTTPS traffic between the Internet and web applications and identifies and blocks web attacks based on predefined protection rules. WAF can defend against many types of attacks, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), web shells, command/code injection, file inclusion, sensitive file access, third-party application vulnerability exploits, CC attacks, malicious crawler scanning, and cross-site request forgery (CSRF). You can use WAF to protect web servers, web applications, and sensitive data.
Video Tutorial
How WAF Works
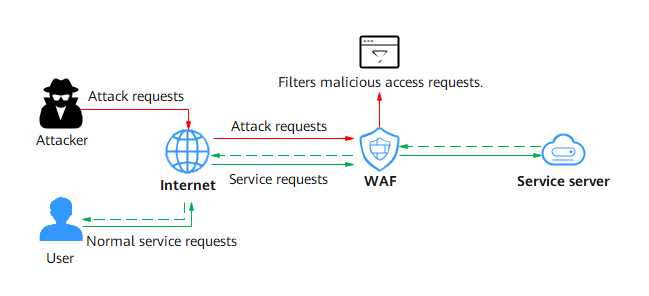
After a website is connected to WAF, all HTTP and HTTPS requests (including attack requests from attackers and normal service requests from users) are checked by WAF. WAF filters out attack requests and forwards normal service requests to the web server. The web server processes received requests and returns data to WAF. WAF filters the content (for example, masking part of the content) and returns the checked content to the website users.
Defense System
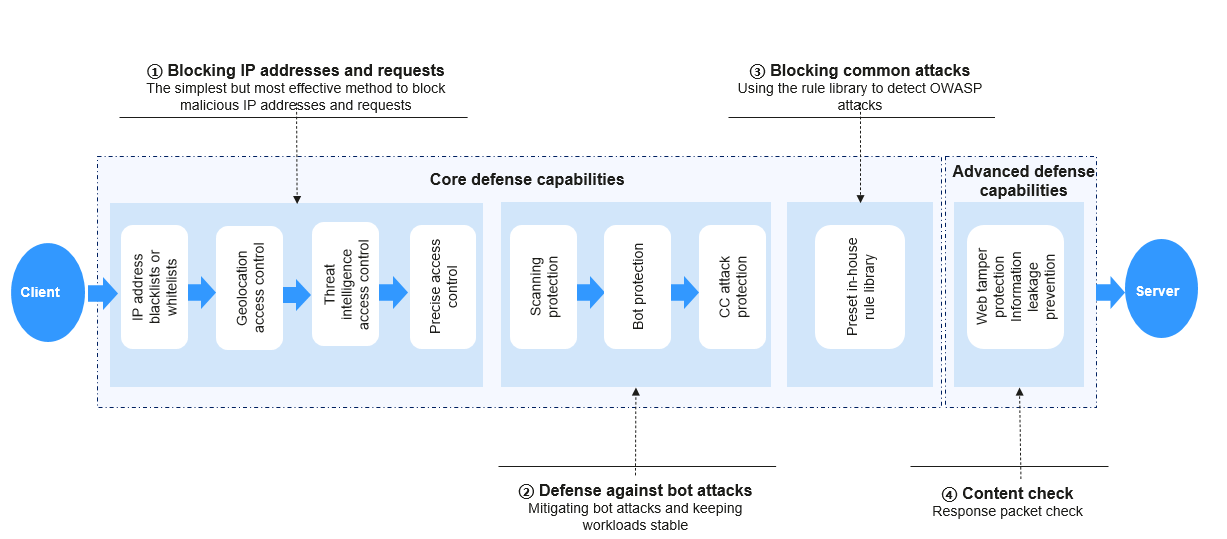
Huawei Cloud WAF uses layered detection to build an intelligent multi-layer defense system, providing all-around protection for your web applications.
WAF can:
- Filter malicious IP addresses to effectively block requests based on IP address blacklist/whitelist, geographical locations, and IDC reputation databases, and specific access requests.
- Protect your website from automated attacks, such as scanning attacks, bot attacks, and CC attacks.
- Detect OWASP attacks with a rule library and defend against common web attacks.
- Check response packets to protect website page content.
Protected Objects
- Cloud Mode - CNAME: protects your web applications that are accessible over domain names and are deployed on any clouds or in on-premises data centers.
- Cloud Mode - Load balancer: protects your web applications that are deployed on Huawei Cloud and accessible over domain names or IP addresses (public or private IP addresses).
- Dedicated Mode: protects your web applications that are deployed on Huawei Cloud and accessible over domain names or IP addresses (public or private IP addresses).
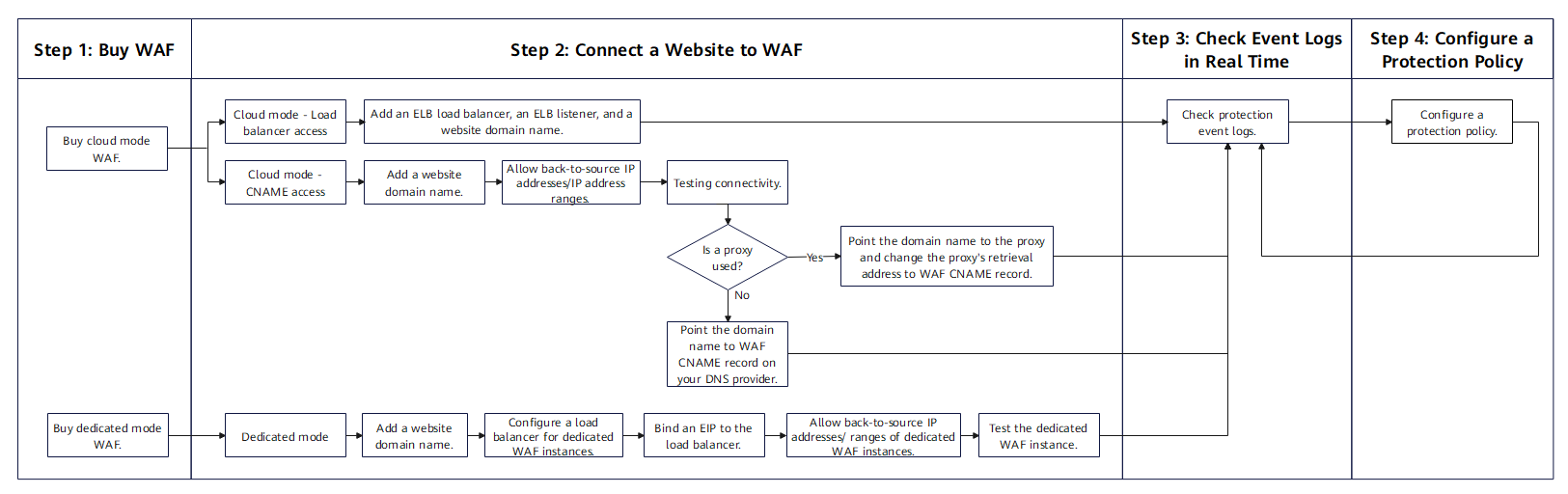
How to Use WAF
WAF offers the cloud and dedicated modes to protect websites. You can connect your website to WAF in either of the following ways: cloud mode CNAME access, cloud mode load balancer access, and dedicated mode access. You can quickly use WAF by referring to Figure 3. For more information, see Getting Started.
References
- Edition Differences: describes the access modes, service specifications, and function differences supported by WAF in cloud mode and dedicated mode.
- Functions: describes the service configurations, web application security capabilities, and other functions (such as protection event management, and alarm notifications) supported by WAF.
- Product Advantages: describes the advantages of WAF.
- Application Scenarios: describes the main application scenarios of WAF.
- Notes and Constraints: describes the constraints and limitations on using WAF.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot