CarbonData Basic Principles
CarbonData is a new Apache Hadoop native data-store format. CarbonData allows faster interactive queries over PetaBytes of data using advanced columnar storage, index, compression, and encoding techniques to improve computing efficiency. In addition, CarbonData is also a high-performance analysis engine that integrates data sources with Spark.
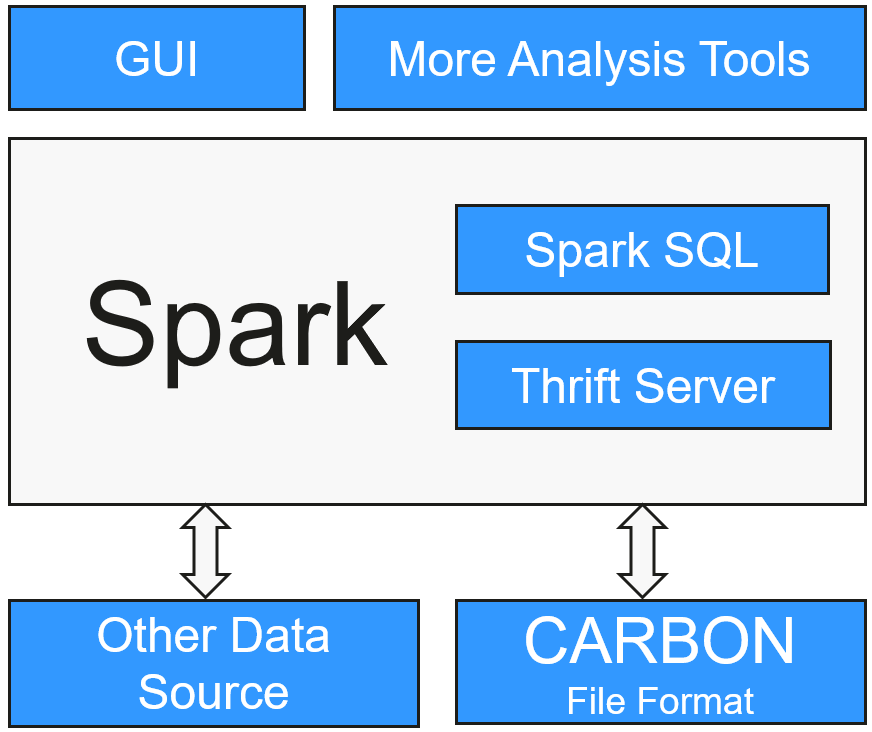
The purpose of using CarbonData is to provide quick response to ad hoc queries of big data. Essentially, CarbonData is an Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) engine, which stores data by using tables similar to those in Relational Database Management System (RDBMS). You can import more than 10 TB data to tables created in CarbonData format, and CarbonData automatically organizes and stores data using the compressed multi-dimensional indexes. After data is loaded to CarbonData, CarbonData responds to ad hoc queries in seconds.
CarbonData integrates data sources into the Spark ecosystem and you can query and analyze the data using Spark SQL. You can also use the third-party tool JDBCServer provided by Spark to connect to SparkSQL.
Topology of CarbonData
CarbonData runs as a data source inside Spark. Therefore, CarbonData does not start any additional processes on nodes in clusters. CarbonData engine runs inside the Spark executor.
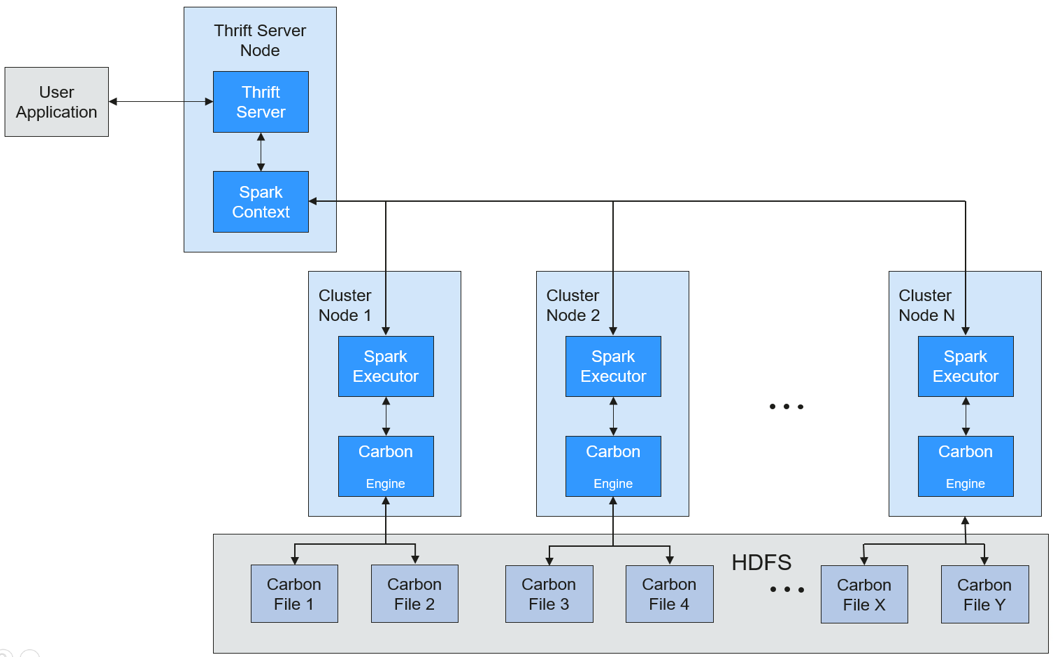
Data stored in CarbonData Table is divided into several CarbonData data files. Each time when data is queried, CarbonData Engine reads and filters data sets. CarbonData Engine runs as a part of the Spark Executor process and is responsible for handling a subset of data file blocks.
Table data is stored in HDFS. Nodes in the same Spark cluster can be used as HDFS data nodes.
CarbonData Features
- SQL: CarbonData is compatible with Spark SQL and supports SQL query operations performed on Spark SQL.
- Simple Table dataset definition: CarbonData allows you to define and create datasets by using user-friendly Data Definition Language (DDL) statements. CarbonData DDL is flexible and easy to use, and can define complex tables.
- Easy data management: CarbonData provides various data management functions for data loading and maintenance. CarbonData supports bulk loading of historical data and incremental loading of new data. Loaded data can be deleted based on load time and a specific loading operation can be undone.
- CarbonData file format is a columnar store in HDFS. This format has many new column-based file storage features, such as table splitting and data compression. CarbonData has the following characteristics:
- Stores data along with index: Significantly accelerates query performance and reduces the I/O scans and CPU resources, when there are filters in the query. CarbonData index consists of multiple levels of indices. A processing framework can leverage this index to reduce the task that needs to be schedules and processed, and it can also perform skip scan in more finer grain unit (called blocklet) in task side scanning instead of scanning the whole file.
- Operable encoded data: Through supporting efficient compression and global encoding schemes, CarbonData can query on compressed/encoded data. The data can be converted just before returning the results to the users, which is called late materialized.
- Supports various use cases with one single data format: like interactive OLAP-style query, sequential access (big scan), and random access (narrow scan).
Key Technologies and Advantages of CarbonData
- Quick query response: CarbonData features high-performance query. The query speed of CarbonData is 10 times of that of Spark SQL. It uses dedicated data formats and applies multiple index technologies, global dictionary code, and multiple push-down optimizations, providing quick response to TB-level data queries.
- Efficient data compression: CarbonData compresses data by combining the lightweight and heavyweight compression algorithms. This significantly saves 60% to 80% data storage space and the hardware storage cost.
CarbonData Index Cache Server
To solve the pressure and problems brought by the increasing data volume to the driver, an independent index cache server is introduced to separate the index from the Spark application side of Carbon query. All index content is managed by the index cache server. Spark applications obtain required index data in RPC mode. In this way, a large amount of memory on the service side is released so that services are not affected by the cluster scale and the performance or functions are not affected.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





