Hybrid Cloud Resolution
What is hybrid cloud resolution?
DNS Resolver answers DNS queries to and from your on-premises data center after your data center is connected to the cloud over Direct Connect or VPN.
Generally, on-premises data centers can access cloud resources over a Direct Connect or VPN connection. However, for security purposes, on-premises servers are not allowed to access the DNS service on the cloud directly. If your on-premises servers need to access private domain names used within VPCs, or your cloud servers use Huawei Cloud private DNS to access an on-premises domain name, you need to set up DNS on your cloud servers for forwarding DNS queries between the cloud DNS and on-premises DNS. This increases management and maintenance costs and causes reliability risks.
With Huawei Cloud DNS Resolver, on-premises servers and cloud servers can easily communicate with each other in hybrid cloud scenarios.
DNS Resolver is now available in CN North-Ulanqab1, CN Southwest-Guiyang1, AP-Bangkok, AP-Singapore, AP-Jakarta, AP-Manila, CN-Hong Kong, AF-Cairo, LA-Sao Paulo1, TR-Istanbul, AF-Johannesburg, ME-Riyadh, and LA-Mexico City2.
Video
This video introduces the main functions of Huawei Cloud DNS Resolver and how to use DNS Resolver to set up hybrid cloud DNS.
Where to Use
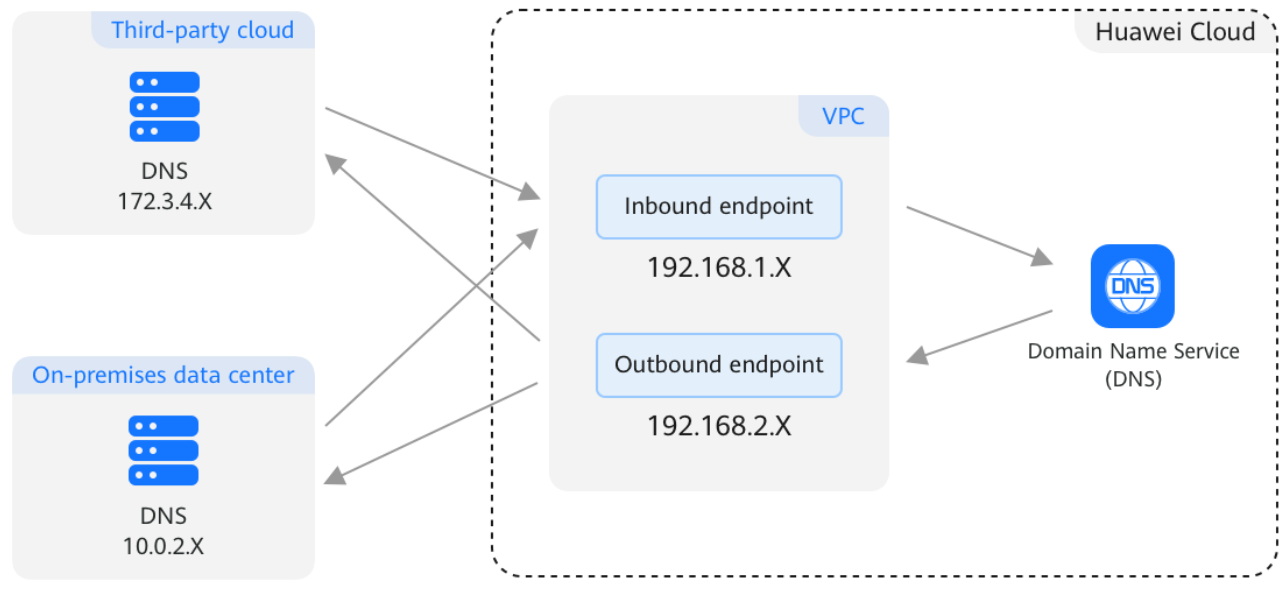
- Access to a Service Domain Name on the Cloud from an On-premises Server
To enable access, you need to create an inbound endpoint and configure forwarding rules on the on-premises DNS servers to forward the DNS queries for the cloud service domain name to the IP addresses specified in the inbound endpoint.
- Access to an On-Premises Service Domain Name from a Cloud Server
To enable access, you need to create an outbound endpoint and configure endpoint rules to specify the on-premises domain name to be accessed and the IP addresses of the on-premises DNS servers. Huawei Cloud private DNS then forwards the DNS queries for the on-premises domain name to the on-premises DNS servers based on the endpoint rules.
Advantages
- Simple networking
You do not need to worry about conflicts with IP addresses starting with 100 because DNS Resolver responds recursively to DNS queries within VPCs.
- Conditional forwarding
DNS queries for particular domain names and for top-level domains are forwarded to specific DNS servers for resolution.
Functions
|
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Inbound endpoint |
Create an inbound endpoint and configure forwarding rules on the on-premises DNS servers to forward the DNS queries for the cloud service domain name to the IP addresses specified in the inbound endpoint. You can create, modify, delete, and view inbound endpoints. For details, see Managing Inbound Endpoints. |
|
Outbound endpoint |
Create an outbound endpoint and configure endpoint rules to specify the on-premises domain name to be accessed and the IP addresses of the on-premises DNS servers. Huawei Cloud private DNS then forwards the DNS queries for the on-premises domain name to the on-premises DNS servers based on the endpoint rules. You can create, modify, delete, and view endpoints, and disassociate endpoints from VPCs. For details, see Managing Outbound Endpoints and Managing Endpoint Rules. |
|
Requirements |
Helpful Links
For details about how to configure DNS Resolver to enable communication between on-premises servers and the cloud, see Using DNS Resolver to Enable Communication Between On-premises Servers and the Cloud.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





