What Is CodeArts Repo?
What Is CodeArts Repo?
CodeArts Repo provides software developers with Git-based online code hosting services. It is a cloud code repository that supports security control, member and permission management, branch protection and merging, online editing, and statistics. The service aims to address cross-region collaboration, multi-branch concurrency, code version management, and security issues.
- Code can be read, modified, and committed online at any time from anywhere.
- Online branch management allows efficient concurrent development on multiple branches. You can create, change, and merge branches.
- Protected branches prevent pushes to the branches and prevent the branches from being incorrectly deleted.
- The Domain-level IP address whitelist and data transmissions via HTTPS block unauthorized code downloads to secure data.
- Passwords can be reset.
Introduction Video
Why CodeArts Repo?
CodeArts Repo provides efficient and secure code hosting for end-to-end code traceability.
- Innovative full-stack development
- Efficient collaborative code development
- Hierarchical protection
- Code-centered tracing
CodeArts Repo Working Mode
- CodeArts Repo uses GitFlow as the basic working mode.
- Following the rules suggested by GitFlow, small and medium-sized development teams can better manage their development.
- Concurrent development: Features and patches are developed concurrently.
- Teamwork: Developers are aware of the current work of other team members during collaboration.
- Flexibility: Emergency fixes are developed on the hotfix branch.
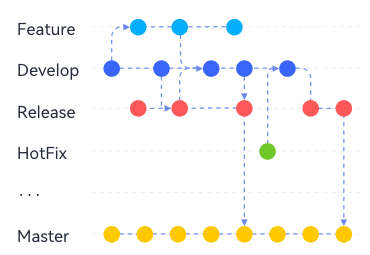
- Master branch: the most stable branch with complete features and code that can be released at any time.
- Develop branch: a permanent branch with the latest and most complete features. It contains all the code ready for the next release and is used to merge other branches.
- Feature branch: a branch for developing a new feature. Once the development is complete, the feature branch is merged into the develop branch for the next release after passing tests.
- Release branch: a dedicated branch for release preparation.
- Hotfix branch: a branch for fixing bugs in a live production version.
- All feature branches are pulled from the develop branch.
- All hotfix branches are pulled from the master branch.
- All commits to the master branch must have tags to facilitate rollback.
- Any changes that are merged to the master branch must be merged to the develop branch for synchronization.
- The master and develop branches are the main branches and they are unique. Other types of branches can have multiple derived branches.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





