Application Scenarios
APM is widely used. You can learn how to use APM based on the following typical application scenarios.
Diagnosis of Application Exceptions
Pain Points
In the distributed microservice architecture, enterprises can develop diverse complex applications efficiently. However, this architecture poses great challenges to traditional O&M and diagnosis technologies. In the example of an e-commerce application, problems are as follows:
- Difficult fault locating
After receiving the feedback from customers, customer service personnel submit problems to technical personnel for troubleshooting. In the distributed microservice architecture, a request usually undergoes multiple services/nodes before a result is returned. If a fault occurs, O&M personnel need to repeatedly view logs on multiple hosts to locate the fault. Even for simple problems, troubleshooting requires cooperation from multiple teams.
- Difficult architecture sort-out
When service logic becomes complex, it is difficult to find out the downstream services (databases, HTTP APIs, and caches) that an application depends on, and external services that depend on the application from the code perspective. It is also difficult to sort out the service logic, manage the architecture, and plan capacities. For example, enterprises find it hard to determine the number of hosts required for online promotions.
Service Implementation
APM can diagnose exceptions in large distributed applications. When an application breaks down or a request fails, you can locate faults in minutes through topologies and drill-downs.
- Visible topology: Abnormal application instances can be automatically discovered on the topology.
- Tracing: You can locate root causes in code through drill-downs after identifying abnormal applications on the topology.

- SQL analysis: APM displays graphs of key metrics (such as number of SQL statement calls, latency, and number of errors), and supports analysis of database performance problems caused by abnormal SQL statements.
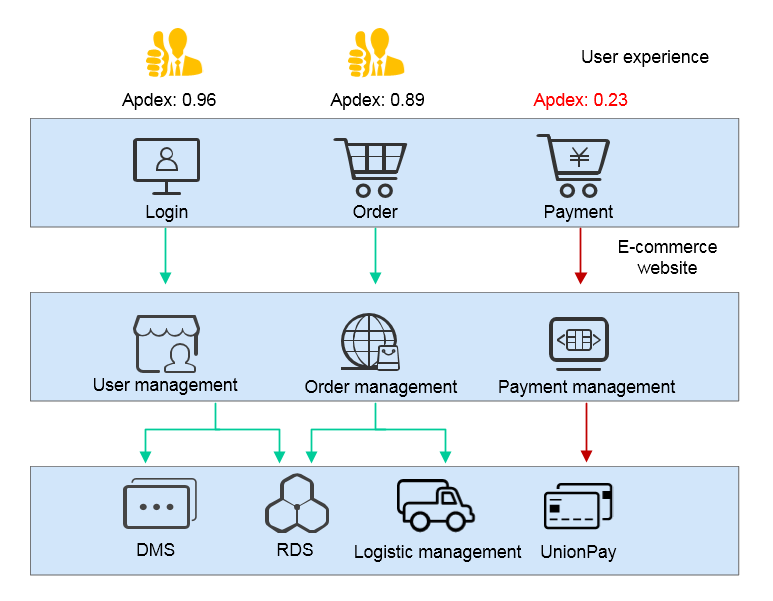
User Experience Management
Pain Points
In the Internet era where user experience is of crucial importance, you cannot obtain user access information even if backend services run stably. It is much more difficult to locate frontend problems that occur occasionally. After a system goes online, if users cannot access the system due to errors and you fail to obtain the information in time, you will lose lots of users. If users report page usage problems, how can these problems be reproduced immediately? How can error details be obtained for fast troubleshooting?
Service Implementation
APM provides experience management capabilities. Specifically, it analyzes the complete process (user request > server > database > server > user request) of application transactions in real time, and provides Apdex scores, enabling you to monitor comprehensive user experience in real time. For transactions with poor user experience, locate problems through topologies and tracing.
- Application KPI analysis: KPIs such as throughput, latency, and call success rate are displayed, so that you can monitor user experience easily.
- Full-link performance tracing: Web services, caches, and databases are traced, so that you can detect performance bottlenecks quickly.
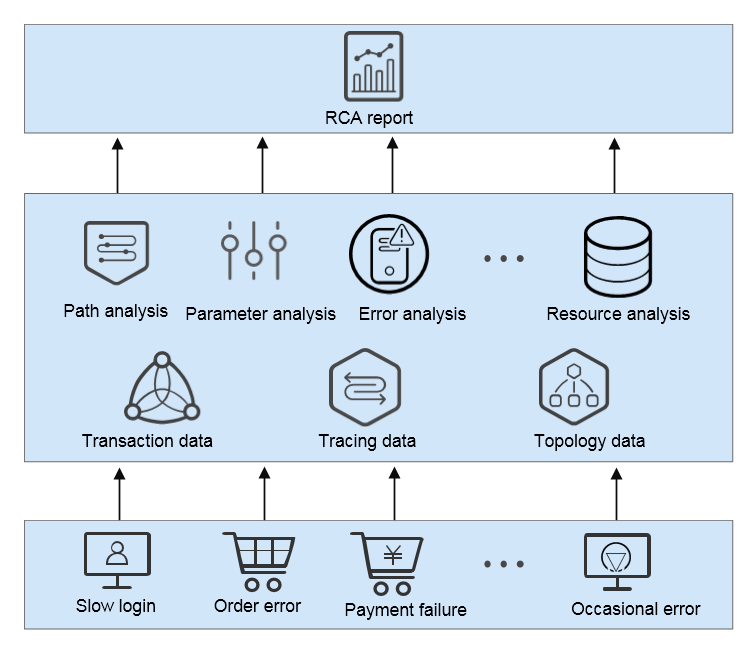
Intelligent Diagnosis
Pain Points
For massive quantities of services, there is rich but unassociated application O&M data, such as hundreds of monitoring metrics, KPI data, and tracing data. How can the system associate metric and alarm data from multiple perspectives (such as applications, services, instances, hosts, and transactions), and automatically complete RCA? How can intelligence analysis be made and possible causes be provided based on the learned historical data and O&M experience library?
Service Implementation
APM supports automatic detection of faults using machine learning algorithms, and intelligent diagnosis. When an exception occurs in a transaction, APM learns historical metric data based on intelligent algorithms, associates exception metrics for multi-dimensional analysis, extracts characteristics of context data (such as resources, parameters, and call structures) when services are normal and abnormal, and locate root causes through cluster analysis. APM can collect and compare the historical data about good and poor experience, and record the environment data that may cause application errors, including input and output parameters, tracing, resource data, and JVM parameters. Based on the Enterprise Intelligent (EI) engine, APM can train historical data online and make predictions.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot








