Functionality Partially Supported by Babelfish
Babelfish is extending its support for T-SQL functionality in each release to enhance compatibility. However, some functions and behaviors are still not fully supported. This section lists the differences between Babelfish and T-SQL and provide some suggestions on how to address them.
Views
Table 1 lists the SQL Server system views that cannot be found in Babelfish.
|
View |
Description |
|---|---|
|
sys.parameters |
Contains parameters of stored procedures, functions, and some other objects. |
|
sys.periods |
Stores definitions of the periods for temporal tables (history tables). |
|
sys.service_queues |
Contains configurations of Service Broker service queues. |
|
sys.sql_dependencies |
Records dependencies among database objects. |
|
sys.stats_columns |
Displays information about the columns involved in statistics objects. |
|
sys.masked_columns |
Contains columns that dynamic data masking is applied to. |
|
sys.memory_optimized_tables_internal_attributes |
Contains internal attributes of memory-optimized tables. |
|
sys.numbered_procedure_parameters |
Contains parameters of numbered stored procedures. |
|
sys.allocation_units |
Displays information about allocation units (storage structures) in a database. |
|
sys.event_notifications |
Contains configurations of event notifications. |
|
sys.extended_procedures |
Displays information about extended stored procedures. |
|
sys.function_order_columns |
Contains information about the sequence column in the common language runtime (CLR) table-valued function. |
|
sys.trigger_event_types |
Lists the type of each event that causes a trigger to fire. |
Differences in How a ROWVERSION/TIMESTAMP Value Is Assigned
SQL Server assigns a unique ROWVERSION/TIMESTAMP value to each row inserted (INSERT) or updated (UPDATE). Babelfish assigns the same ROWVERSION/TIMESTAMP value to all rows modified in a given statement.
For example, when an UPDATE or INSERT SELECT operation that affects multiple rows is executed:
- SQL Server generates different values for the ROWVERSION/TIMESTAMP column of each row.
- Babelfish (PostgreSQL) assigns the same value to all affected rows.
Limited Compatibility with the JSON Data Type
Babelfish does not directly support SQL Server's native JSON data type. Instead, it is stored as the NVARCHAR, VARCHAR, or TEXT data type. For more information, see JSON data in SQL Server and JSON data type.
Babelfish provides a set of JSON functions that can be used to handle JSON data. The functions are:
- JSON_VALUE
- JSON_QUERY
- OPENJSON
- JSON_MODIFY
- ISJSON
Identifier Differences
If an index named ix1 in T-SQL is on table t1, the index will internally be renamed ix1t1a5111d2a1767bc43a700e9f2162be019 (ix1t1 + hash value) by Babelfish.
- T-SQL transparency: Users still use the original identifiers to compile queries, and Babelfish automatically maps the identifiers to internal names.
- PostgreSQL visibility: The actual object name seen in PostgreSQL (using psql) contains a hash value.
Babelfish uses a hash algorithm to dynamically adjust identifiers. This approach is compatible with the lengthy names and flexible rules of SQL Server while also meeting the strict requirements of PostgreSQL. T-SQL users are unaware of this processing, but each object name seen in PostgreSQL has a hash suffix. For more information, see Babelfish identifiers.
Impact of identifier differences in Babelfish on system views:
- If an object name contains 64 or fewer characters, the identifier differences have no impact on accessing the object through SQL commands (such as USE and SELECT), and the original object name is stored in system views such as sys.databases, sys.indexes, and sys.tables.
- If an object name contains more than 64 characters, the identifier differences still have no impact on accessing the object through SQL commands (such as USE and SELECT), but the object name is stored in the format of partial prefix + hash value in system views such as sys.databases, sys.indexes, and sys.tables. The original object name cannot be restored through simple string processing.
Impact scenarios of identifier differences:
- In the migration link with a Babelfish instance as the destination, DRS pre-checks the destination Babelfish instance before the migration. During the pre-check, DRS queries sys.* system views to check whether objects exist. If any database objects in the source SQL Server instance have names exceeding 64 characters, the pre-check fails.
- When a user accesses sys.* system views, objects that contain more than 64 characters cannot be found.
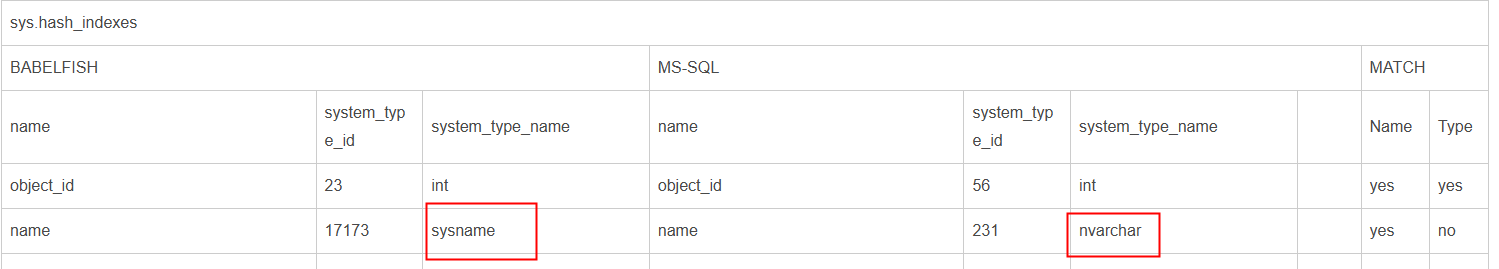
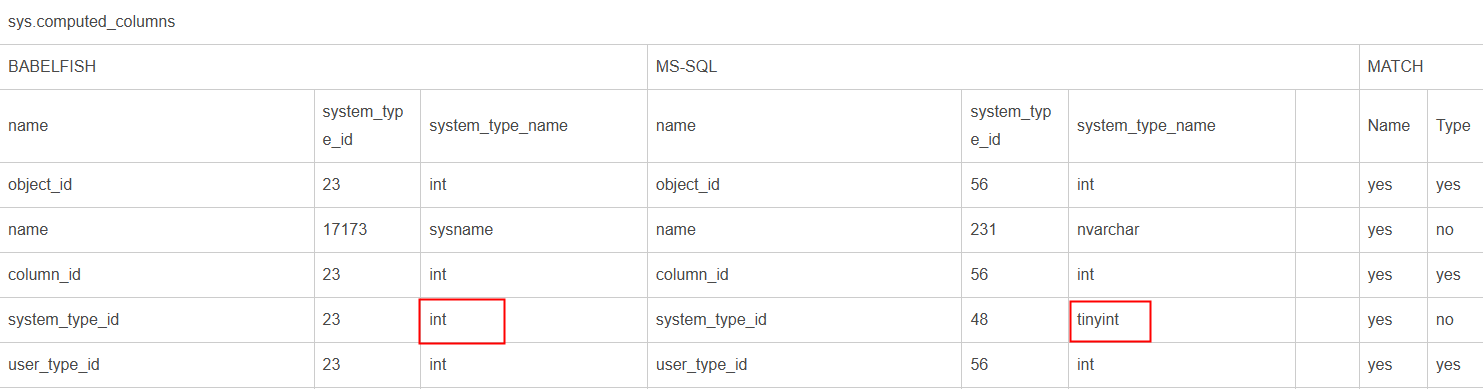
System View Differences
The following views differ.
Parameters
Babelfish does not support the following settings:
SET ANSI_NULL_DFLT_OFF ON
SET ANSI_NULL_DFLT_ON OFF
SET ANSI_PADDING OFF
SET ANSI_WARNINGS OFF
These server-side settings will prevent the SET ANSI_DEFAULTS command from working properly.
The following parameters cannot be modified.

For more information, see parameters that should not be modified in the official Babelfish documentation.
Cursors
Babelfish does not support SET CURSOR_Closed_ON_COMMIT ON. Also, Babelfish does not recognize cursors that are dynamically defined in stored procedures or functions. You can rewrite these cursors using temporary tables.
The following items are not supported:
- Updatable cursors
- Global cursors
- Cursor extraction behaviors: FETCH PRIOR, FIRST, LAST, ABSOLUTE, and RELATIVE
- Cursor output parameters (Variables and parameters of cursor types cannot be used as output parameters, or an error will be reported.)
- Cursor options: SCROLL, KEYSET, DYNAMIC, FAST_FORWARD, SCROLL_LOCKS, OPTIMISTIC, TYPE_WARNING, and FOR UPDATE
In addition, the Babelfish community documentation states: "When ANSI_DEFAULTS is turned on, it enables the following settings: ANSI_NULLS, ANSI_NULL_DFLT_ON, IMPLICIT_TRANSACTIONS, ANSI_PADDING, QUOTED_IDENTIFIER, ANSI_WARNINGS and CURSOR_CLOSE_ON_COMMIT. The driver and provider set CURSOR_CLOSE_ON_COMMIT and IMPLICIT_TRANSACTIONS to OFF (so CURSOR_CLOSE_ON_COMMIT is actually OFF at connect time, though ANSI_DEFAULTS is ON)."
Commands
- Babelfish does not support SET STATISTICS or SET STATISTICS_ALL, but provides the following alternatives:
- SET BABELFISH_STATISTICS PROFILE [ON|OFF]: Set this function to ON for the actual query execution plan. This function implements the functionality of EXPLAIN ANALYZE in PostgreSQL.
- SET BABELFISH_SHOWPLAN_ALL [ON|OFF]: Setting this function to ON will generate an estimated query execution plan. This function implements the functionality of EXPLAIN in PostgreSQL. Use this command to obtain the explanation plan of a given query.
In addition, the Babelfish community documentation states: "Starting with version 2.2.0, you can set the escape_hatch_showplan_all parameter to ignore in order to avoid the use of BABELFISH_ prefix in the SQL Server syntax for SHOWPLAN_ALL and STATISTICS PROFILE SET commands."
To use them as SET SHOWPLAN_ALL and SET STATISTICS PROFILE without the BABELFISH_ prefix, run:
EXEC sp_babelfish_configure 'babelfishpg_tsql.escape_hatch_showplan_all', 'ignore';
Or:
EXEC sp_babelfish_configure 'babelfishpg_tsql.escape_hatch_showplan_all', 'strict';
You can use sp_babelfish_configure to change parameter settings. Example:
execute sp_babelfish_configure 'explain_buffers', 'on';
- Babelfish does not support SET SHOWPLAN_XML.
Babelfish can output query plans in XML format. For details about how to check Babelfish query plans, see Reviewing a Query Plan.
Before running a query, you can visualize the statistics profile by executing SET BABELFISH_STATISTICS PROFILE ON.
- Run the following command to set explain_format:
execute sp_babelfish_configure 'explain_format', 'xml'
- Run the following commands to visualize the statistics profile:
select set_config('babelfishpg_tsql.explain_format', 'xml', false);SET BABELFISH_STATISTICS PROFILE ON;
- Run the following command to set explain_format:
- Babelfish does not support SET FORCEPLAN.
- Babelfish does not support SET SHOWPLAN_TEXT.
- Babelfish only supports OFF for SET NOEXEC. For details, see unsupported functionality in the Babelfish community documentation.
- Babelfish does not support SET TEXTSIZE, but provides the following alternative:
Babelfish sets the TEXTSIZE parameter to 4096 during session initialization. To change the value, perform the following operations.
If the value of -y is smaller than that of TEXTSIZE, the output text size cannot be adjusted. In this case, the value of -y is used.
- Use sqlcmd to connect to a Babelfish instance.
sqlcmd -U babelfish_user -P 12345678 -No -y <textsize_value>
- Set the TEXTSIZE parameter.
SET TEXTSIZE <textsize_value>
- Query the value of TEXTSIZE.
SELECT id, LEFT(name, CAST(current_setting('babelfishpg_tsql.textsize') as int )) AS name FROM <table_name>;SELECT * FROM <table_name>;
- Use sqlcmd to connect to a Babelfish instance.
Functions
The following functions differ:
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot