Function Overview
-
VPC
OBS 2.0 Supported
-
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) allows you to provision logically isolated virtual private networks for cloud resources, such as cloud servers, containers, and databases. You can create subnets, security groups, network ACLs, route tables, and more to manage cloud resources flexibly. You can also use EIPs to connect cloud resources in VPCs to the Internet, and use Direct Connect and VPN to connect on-premises data centers to VPCs to build a hybrid cloud network.

-
-
Subnet
OBS 2.0 Supported
-
A subnet is a unique CIDR block with a range of IP addresses in a VPC. All resources in a VPC must be deployed on subnets.
All instances in different subnets of the same VPC can communicate with each other by default, and the subnets can be located in different AZs. If you have a VPC with two subnets in it and they are located in different AZs, they can communicate with each other by default.

Availability: All regions
-
-
Route Table
OBS 2.0 Supported
-
A route table contains a set of routes that are used to control the traffic in and out of your subnets in a VPC. Each subnet must be associated with a route table. A subnet can only be associated with one route table, but you can associate multiple subnets with the same route table.
· Default route table: Each VPC comes with a default route table. If you create a subnet in the VPC, the subnet associates with the default route table. The default route table ensures that subnets in a VPC can communicate with each other. You can add routes to, delete routes from, and modify routes in the default route table, but cannot delete the table.
· Custom route table: If you do not want to use the default route table, you can create a custom route table and associate it with the subnet. Custom route tables can be deleted if they are no longer required.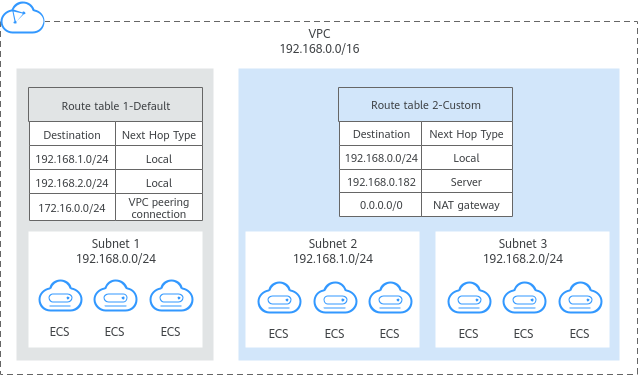

Availability: All regions
-
-
Virtual IP Address
OBS 2.0 Supported
-
A virtual IP address is a private IP address that can be independently assigned from and released to a VPC subnet. You can:
· Bind one or more virtual IP addresses to an ECS so that you can use either the virtual IP address or private IP address to access the ECS. If you have multiple services running on an ECS, you can use different virtual IP addresses to access them.
· Bind a virtual IP address to multiple ECSs. You can use a virtual IP address and an HA software (such as Keepalived) to set up a high-availability active/standby cluster. If you want to improve service availability and eliminate single points of failure, you can deploy ECSs in the active/standby pair or deploy one active ECS and multiple standby ECSs. In this case, the ECSs can use the same virtual IP address. If the active ECS goes down, the standby ECS becomes the active ECS and continues to provide services.
Generally, ECSs use private IP addresses for internal network communication. A virtual IP address has the same network access capabilities as a private IP address. You can use either of them to enable layer 2 and layer 3 communications in a VPC, access a different VPC using a peering connection, enable Internet access through EIPs, and connect the cloud and the on-premises servers using VPN connections and Direct Connect connections. The below figure shows how private IP addresses, the virtual IP address, and EIPs work together.
· Private IP addresses are used for internal network communication.
· The virtual IP address works with Keepalived to build an HA cluster. ECSs in this cluster can be accessed through one virtual IP address.
· EIPs are used for Internet communication.
-
-
Elastic Network Interface
OBS 2.0 Supported
-
An elastic network interface (referred to as a network interface in this documentation) is a virtual network card. You can create and configure network interfaces and attach them to your instances (ECSs and BMSs) to obtain flexible and highly available network configurations.
· A primary network interface is created together with an instance by default, and cannot be detached from the instance.
· An extended network interface is created on the Network Interfaces console, and can be attached to or detached from an instance.
Availability: CN North-Beijing1, CN North-Beijing4, CN North-Ulanqab1, CN East-Shanghai1, CN East-Shanghai2, CN East-Qingdao, CN East2, CN South-Guangzhou, CN Southwest-Guiyang1, CN-Hong Kong, AP-Bangkok, AP-Singapore, AP-Jakarta, ME-Riyadh, AF-Cairo, AF-Johannesburg, TR-Istanbul, LA-Mexico City2, LA-Sao Paulo1, and LA-Santiago
-
-
Security Group
OBS 2.0 Supported
-
A security group is a collection of access control rules for cloud resources, such as cloud servers, containers, and databases, that have the same security protection requirements and that are mutually trusted. After a security group is created, you can configure access rules that will apply to all cloud resources added to this security group.
Each security group can have both inbound and outbound rules. You need to specify the source, port, and protocol for each inbound rule and specify the destination, port, and protocol for each outbound rule to control the inbound and outbound traffic to and from the instances in the security group. As shown in the below figure, you have a VPC (VPC-A) with a subnet (Subnet-A) in region A. An ECS (ECS-A) is running in Subnet-A and associated with security group Sg-A.
· Security group Sg-A has a custom inbound rule to allow ICMP traffic to ECS-A from your PC over all ports. However, the security group does not have rules that allow SSH traffic to ECS-A so you cannot remotely log in to ECS-A from your PC.
· If ECS-A needs to access the Internet through an EIP, the outbound rule of Sg-A must allow all traffic from ECS-A to the Internet.

Availability: All regions
-
-
Network ACL
OBS 2.0 Supported
-
A network ACL is an optional layer of security for your subnets. After you add inbound and outbound rules to a network ACL and associate subnets with it, you can control traffic in and out of the subnets.
A network ACL is different from a security group. A security group protects the instances in it, such as ECSs, databases, and containers, while a network ACL protects the entire subnet. Security groups are a mandatory layer of protection but network ACLs are optional. Network ACLs and security groups can be used together for fine-grained access control.
You need to specify the protocol, source port and address, and destination port and address for each inbound and outbound rule of the network ACL. Suppose you have two subnets in region A, as shown in the below figure. Subnet-X01 is associated with network ACL Fw-A, and ECSs deployed in this subnet provide web services accessible from the Internet. Subnet-X02 is associated with network ACL Fw-B. Subnet-X02 and Subnet-Y01 are connected through a VPC peering connection. Now, you need to configure inbound and outbound rules to allow ECS-C01 in Subnet-Y01 to remotely log in to ECSs in Subnet-X02.
· Inbound and outbound rules on Fw-A: Custom inbound rule A01 allows any IP address to access the ECSs in Subnet-X01 through port 80 over TCP or HTTP. If the traffic does not match custom rule A01, the default rule is applied and the traffic is denied to flow into the subnet. Stateful network ACLs allow responses to inbound requests to leave the subnet without being controlled by rules. The responses from ECSs in Subnet-X01 can go out of the subnet. Other outbound traffic is not allowed to leave Subnet-X01, because the default rule is applied.
· Inbound and outbound rules on Fw-B: Custom inbound rule B01 allows ECS-C01 in Subnet-Y01 to use access the ECSs in Subnet-X02 through port 22 over TCP or SSH. Custom outbound rule B02 allows all ICMP traffic over any port. The ping traffic from ECSs in Subnet-X02 to ECS-C01 in Subnet-Y01 can be routed successfully to test the network connectivity.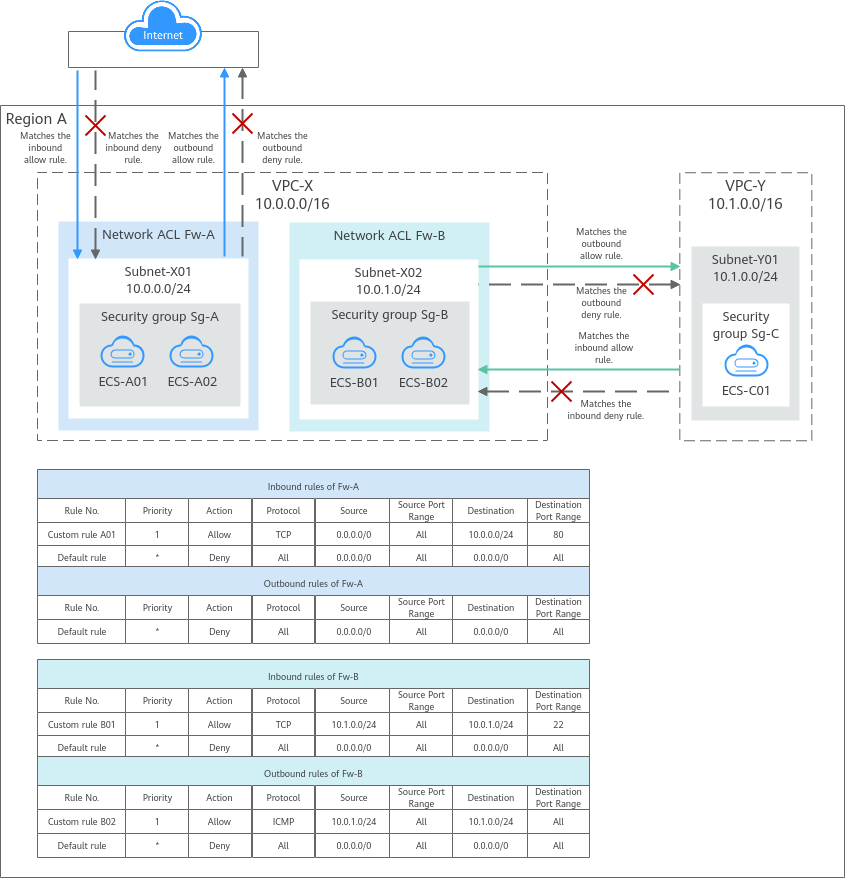

Availability: All regions
-
-
IP Address Group
OBS 2.0 Supported
-
An IP address group is a collection of IP addresses. It can be associated with security groups and network ACLs to simplify IP address configuration and management.
You can add IP address ranges and IP addresses that need to be managed in a unified manner to an IP address group. An IP address group can work together with different cloud resources.

Availability: All regions
-
-
VPC Peering Connection
OBS 2.0 Supported
-
A VPC peering connection enables two VPCs in the same region to communicate using private IP addresses. The VPCs to be connected can be from the same account or different accounts.
The below figure shows an application scenario of VPC peering connections.
· There are two VPCs (VPC-A and VPC-B) in region A that are not connected.
· Service servers (ECS-A01 and ECS-A02) are in VPC-A, and database servers (RDS-B01 and RDS-B02) are in VPC-B. The service servers and database servers cannot communicate with each other.
· You need to create a VPC peering connection (peering-AB) between VPC-A and VPC-B so the service servers and database servers can communicate with each other.
-
-
VPC Sharing
OBS 2.0 Supported
-
VPC sharing allows multiple accounts to create and manage cloud resources, such as ECSs, load balancers, and RDS instances, in one VPC. With Resource Access Manager (RAM), you can share subnets in a VPC with one or more accounts so you can centrally manage resources in multiple accounts, which improves resource management efficiency and reduces O&M costs.
The following describes how you can share subnets among several accounts, as shown in the below figure.
· Account A: IT management account of the enterprise and the owner of the VPC and subnets. Account A creates a VPC and four subnets and shares these subnets with other accounts. Account A creates resources in Subnet-01.
· Account B: service account of the enterprise and the principal of the shared subnet. Account B creates resources in Subnet-02.
· Account C: service account of the enterprise and the principal of the shared subnet. Account C creates resources in Subnet-03.
· Account D: service account of the enterprise and the principal of the shared subnet. Account D creates resources in Subnet-04.

Availability: All regions
-
-
IPv4 and IPv6 Dual-Stack Network
OBS 2.0 Supported
-
An IPv4 and IPv6 dual-stack network allows your resources, such as ECSs, to use both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses for private and public network communications.


Availability: CN North-Beijing4, CN North-Ulanqab1, CN East-Shanghai1, CN East-Qingdao, CN East2, CN South-Guangzhou, CN Southwest-Guiyang1, CN-Hong Kong, AP-Bangkok, AP-Singapore, AP-Jakarta, ME-Riyadh, AF-Cairo, TR-Istanbul, LA-Mexico City1, LA-Mexico City2, LA-Sao Paulo1, and LA-Santiago
-
-
VPC Flow Log
OBS 2.0 Supported
-
A VPC flow log records information about the traffic going to and from a VPC. VPC flow logs help you monitor network traffic, analyze network attacks, and determine whether security group and network ACL rules require modification.
VPC flow logs must be used together with the Log Tank Service (LTS). Before you create a VPC flow log, you need to create a log group and a log stream in LTS.
Availability: CN North-Beijing4, CN North-Ulanqab1, CN East-Shanghai1, CN East-Shanghai2, CN East-Qingdao, CN East2, CN South-Guangzhou, CN Southwest-Guiyang1, CN-Hong Kong, AP-Bangkok, AP-Singapore, AP-Jakarta, ME-Riyadh, AF-Johannesburg, TR-Istanbul, LA-Mexico City1, LA-Mexico City2, LA-Sao Paulo1, and LA-Santiago
-
-
Traffic Mirroring
OBS 2.0 Supported
-
Traffic Mirroring can be used to mirror traffic that meets a mirror filter from an elastic network interface. You can configure inbound and outbound rules for a mirror filter to determine which traffic from an elastic network interface will be mirrored to a network interface or load balancer. You can then send the traffic for inspection, audit analysis, and troubleshooting.
The following describes the working principles of traffic mirroring. As shown in the below figure, a mirror session is associated with two mirror sources, one mirror filter, and one mirror target.
· Mirror source 01 is network interface-B that is attached to ECS-B. To access ECS-A from ECS-B, the outbound and inbound traffic of network interface-B is mirrored.
· Mirror source 02 is network interface-C that is attached to ECS-C. To access ECS-C from the Internet, the outbound and inbound traffic of network interface-C is mirrored.
· The mirror filter contains both inbound and outbound rules.
· The mirror target is a load balancer that receives mirrored traffic.

Availability: CN North-Beijing4, CN East-Shanghai1, CN East2, CN South-Guangzhou, and AP-Singapore
-
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot






