Training a Model
After labeling the sound files, train a model. You can perform model training to obtain the required sound classification model. Training sound files must be classified into at least two classes, and each class must contain at least five sound files. Before training, ensure that the labeled sound files meet the requirements. Otherwise, the Train button is unavailable.
Procedure
Before starting the training, set the training parameters and then perform auto training.
- On the ExeML page, click the name of the project that is successfully created. The Label Data tab page is displayed.
Figure 1 Finding unlabeled files
- On the Label Data tab page, click Train in the upper right corner. In the displayed Training Configuration dialog box, set related parameters by referring to Table 1 and click OK to start model training.
Figure 2 Setting training parameters
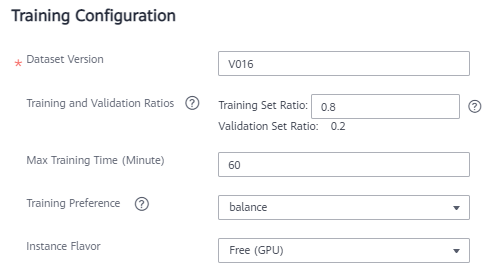
Table 1 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Default Value
Dataset Version
This version is the one when the dataset is published in Data Management. In an ExeML project, when a training job is started, the dataset is published as a version based on the previous data labeling.
The system automatically provides a version number. You can change it to the version number that you want.
Randomly provided by the system
Max. Training Duration (Minute)
If the training is not completed within the maximum training duration, the training is forcibly stopped. You are advised to enter a larger value to prevent forcible stop during training. The value ranges from 6 to 6000.
60
Instance Flavor
Select the resource specifications used for training. By default, the following types are supported:
- Compute-intensive 1 instance (GPU): This flavor is billed on a pay-per-use basis.
- Free (GPU): This flavor is free. However, if the flavor is used, the training job automatically stops after one hour. That is, the training job lasts for only one hour at a time. You are advised to evaluate the data size and ensure that the time of a training job does not exceed 1 hour. When there are a large number of users, they need to wait in a queue for this flavor.
ExeML (GPU)
- After configuring training parameters, click Next to go to the configuration page, confirm the specifications, and click Submit to start auto model training. The training takes a certain period of time. Wait until the training is complete. If you close or exit this page, the system still performs the training operation.
- On the Train Model tab page, wait until the training status changes from Running to Completed.
- View the training details, such as Accuracy, Evaluation Result, Training Parameters, and Classification Statistics.
Figure 3 Training details
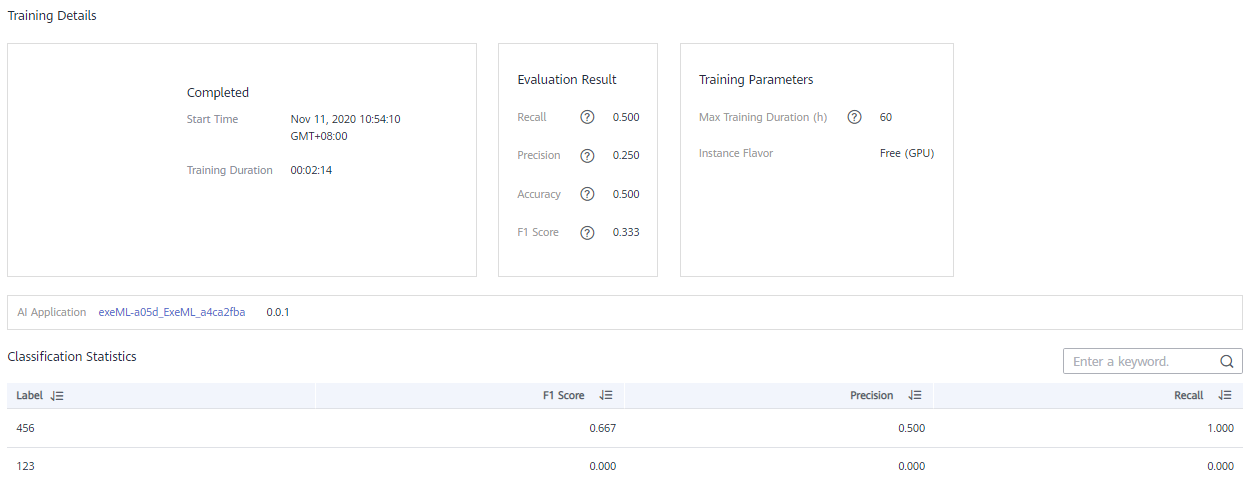
Table 2 Evaluation result parameters Parameter
Description
Recall
Fraction of correctly predicted samples over all samples predicted as a class. It shows the ability of a model to distinguish positive samples.
Precision
Fraction of correctly predicted samples over all samples predicted as a class. It shows the ability of a model to distinguish negative samples.
Accuracy
Fraction of correctly predicted samples over all samples. It shows the general ability of a model to recognize samples.
F1 Score
Harmonic average of the precision and recall of a model. It is used to evaluate the quality of a model. A high F1 score indicates a good model.
An ExeML project supports multiple rounds of training, and each round generates a version. For example, the first training version is V001 (xxx), and the next version is V002 (xxx). The trained models can be managed by training version. After the trained model meets your requirements, deploy the model as a service.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





