ECS Types
- General-Purpose ECSs
- Dedicated General-Purpose ECSs
- Memory-optimized ECSs
- Disk-intensive ECSs
- Ultra-high I/O ECSs
- GPU-accelerated ECSs
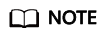
For details about the regions in which a flavor is available, see the information displayed on the management console.
ECS Flavor Naming Rules
ECS flavors are named in the "AB.C.D" format.
Example: s2.medium.4

The format is defined as follows:
- AB indicates the ECS type and type ID.
- A specifies the ECS type. For example, s indicates a general-computing ECS, c indicates a general computing-plus ECS, and m indicates a memory-optimized ECS.
- B specifies the type ID. For example, 1 in s1 indicates the first-generation general-computing ECS, and 2 in s2 indicates the second-generation general-computing ECS. Generally, a larger number indicates a newer generation, which is more cost-effective. For example, compared with s1 and s2, s6 is more cost-effective.
- C specifies the flavor size (the number of vCPUs), such as small, medium, large, xlarge, 2xlarge, 4xlarge, and 8xlarge.
- D specifies the ratio of memory to vCPUs and is expressed in a digit. For example, value 4 indicates that the ratio of memory to vCPUs is 4.
Table 1 Mapping between flavor and the number of vCPUs Flavor Size
vCPUs
small
1
medium
1
large
2
xlarge
4
Nxlarge
N × 4. A larger value of N indicates more vCPUs.
How Do I Know My ECS Flavor?
When creating an ECS, you can view the flavors in the flavor list.
vCPU
ECS supports hyper-threading, which enables two threads to run concurrently on a single CPU core. Each thread is represented as a virtual CPU (vCPU) and a CPU core contains two vCPUs (logical cores).
Hyper-threading is enabled for most ECS flavors by default. If hyper-threading is disabled during the ECS creation or flavor change, the number of vCPUs queried from the ECS is half of the number of vCPUs defined by the ECS flavor.
For example, a 2-core physical CPU contains 4 vCPUs (threads).
Network QoS
Network QoS uses basic technologies to improve the quality of network communication. A network with QoS enabled offers predictable network performance and effectively allocates network bandwidth to use network resources.
To obtain the QoS data of an ECS flavor, including the maximum/assured bandwidth, maximum intranet PPS, NIC multi-queues, and maximum NICs, see A Summary List of ECS Specifications.
- Assured intranet bandwidth: indicates the guaranteed bandwidth allocated to an ECS when there is a network bandwidth contention in the entire network.
- Maximum intranet bandwidth: indicates the maximum bandwidth that can be allocated to an ECS when the ECS does not compete for network bandwidth (other ECSs on the host do not have high requirements on network bandwidth).
- Maximum intranet PPS: indicates the maximum ECS capability in sending and receiving packets.
PPS: packets per second, indicates the number of packets received and sent per second. It is usually used to measure the network performance.
- NIC multi-queues: allocates NIC interruptions to multiple vCPUs for higher PPS performance and bandwidth
- Maximum NICs: indicates the maximum number of NICs that can be attached to an ECS.
- Maximum supplementary NICs: indicates the maximum number of supplementary NICs that can be attached to an ECS.
- For instructions about how to test packet transmit and receive, see How Can I Test the Network Performance of Linux ECSs?
- For instructions about how to enable NIC multi-queue, see Enabling NIC Multi-Queue.
- The maximum bandwidth is the total bandwidth allocated to an ECS. If an ECS has multiple NICs, the sum of the maximum bandwidths allocated to all NICs cannot exceed the maximum bandwidth allocated to the ECS.
Dedicated and Shared ECSs
|
Dimension |
Dedicated ECS |
Shared ECS |
|---|---|---|
|
CPU Allocation |
CPUs are exclusively used and there is no CPU contention. |
CPUs are shared and CPU contention may occur. |
|
Feature |
|
|
|
Application Scenario |
For enterprises that have high requirements on service stability |
For small- and medium-sized websites or individuals that have requirements on cost-effectiveness |
|
ECS Specifications |
Specifications except general-purpose |
x86 computing: |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





