Configuring Java Environment Variables (Windows OS)
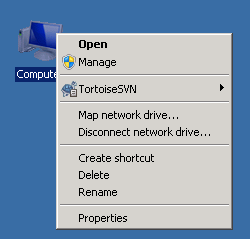
- Right-click Computer and choose Properties.
Figure 1 Properties
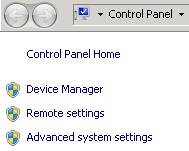
- Select Advanced system settings.
Figure 2 System
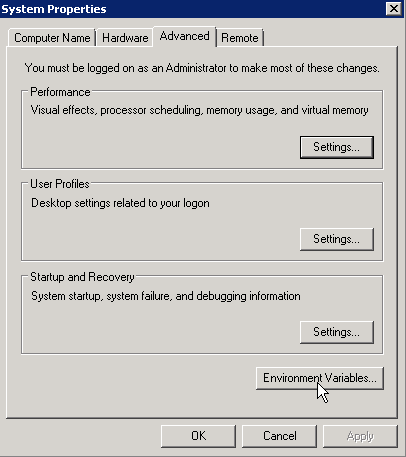
- In the System Properties dialog box, choose .
Figure 3 System Properties dialog box
- Configure the system variables. Configure the following three variables: JAVA_HOME, Path, and CLASSPATH (where the variable names are case-insensitive). If a variable name exits, click Edit. If a variable name does not exist, click New to create one. Generally, the Path variable exists, and the JAVA_HOME and CLASSPATH variables need to be added.
Figure 4 Environment Variables dialog box

JAVA_HOME indicates the JDK installation path and is set to C:\ProgramFiles\Java\jdk1.8.0_45. This path contains the lib and bin files.
Figure 5 Creating JAVA_HOME
Path enables the system to recognize a Java command in any path. If the Path variable exists, add a path at the end of the variable value. Configuration example: ;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_45\bin;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_45\jre\bin
Two paths need to be separated by using a semicolon (;).
Figure 6 Setting Path
CLASSPATH specifies the path of loaded Java classes (class or lib). Java commands can be identified only if they are contained in the class path. Configuration example: .;%JAVA_HOME%\lib\dt.jar;%JAVA_HOME%\lib\tools.jar
 NOTE:
NOTE:
The path starts with a dot (.), indicating the current path.
Figure 7 Setting CLASSPATH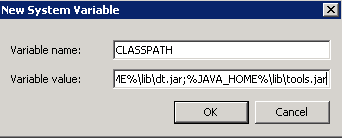
- Restart the OS for the environment variables to take effect.
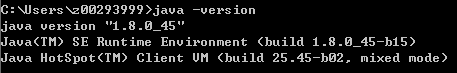
- Choose , enter cmd, and run the following commands: Java -version, java, and javac. If the commands can be run, the environment variables are set successfully.
Figure 8 Verifying environment variables
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





