Basic Syntax Examples of GeminiDB Cassandra Instances
This section describes the basic syntax of GeminiDB Cassandra instances.
- Keyspace syntax
- Create a keyspace.
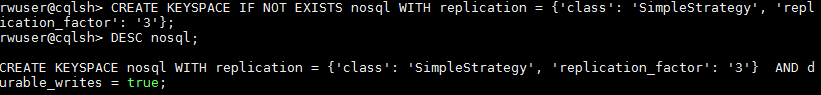
CREATE KEYSPACE IF NOT EXISTS nosql WITH replication = {'class': 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor': '3'};
In this example, the keyspace name is set to nosql and class to SimpleStrategy. replication_factor indicates the number of copies. A GeminiDB Cassandra instance provides strong consistency, three-copy storage by default.
- Run DESC <keyspace_name> to verify the creation results.
Figure 1 Verifying the creation results
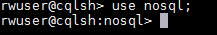
- Run use <keyspace_name> to switch to the created keyspace.
Figure 2 Switching the keyspace
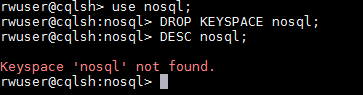
- Run DROP KEYSPACE <keyspace_name> to delete the created keyspace.
Figure 3 Deleting the keyspace
- Create a keyspace.
- Table syntax
- Create a table.
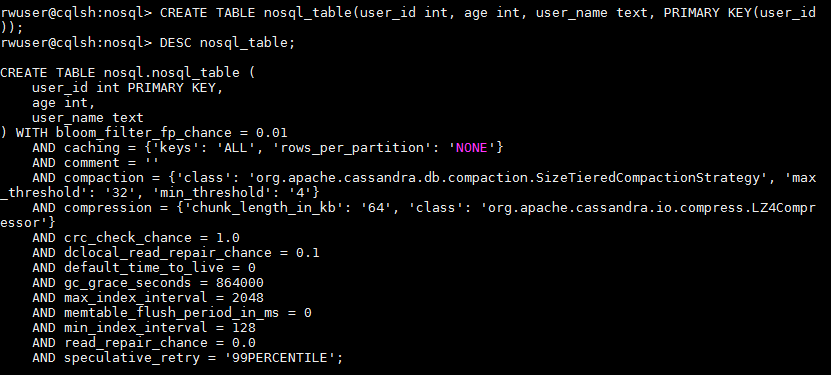
CREATE TABLE nosql_table(user_id int, age int, user_name text, PRIMARY KEY(user_id));
nosql_table is a table name defined by the following three columns: user_id, age, and user_name. user_id indicates a user ID of the INT data type. age indicates user age of the INT data type. user_name indicates a username of the TEXT data type. The primary key is user_id.
- Run DESC <table_name> to verify the creation results.
Figure 4 Verifying the creation results
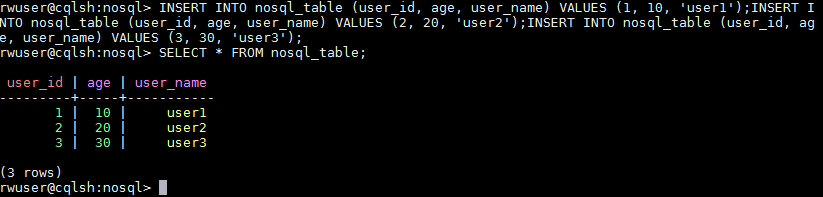
- Insert data into the table, for example,
INSERT INTO nosql_table (user_id, age, user_name) VALUES (1, 10, 'user1');
INSERT INTO nosql_table (user_id, age, user_name) VALUES (2, 20, 'user2');
INSERT INTO nosql_table (user_id, age, user_name) VALUES (3, 30, 'user3');
- Run SELECT * FROM <table_name> to query table data.
Figure 5 Querying table data
- Add a column to the table, for example:
- Update data in a table of a keyspace, for example:
UPDATE nosql.nosql_table SET gender = 'male' WHERE user_id = 1;
UPDATE nosql.nosql_table SET gender = 'male' WHERE user_id = 2;
UPDATE nosql.nosql_table SET gender = 'female' WHERE user_id = 3;
Figure 6 Viewing the update results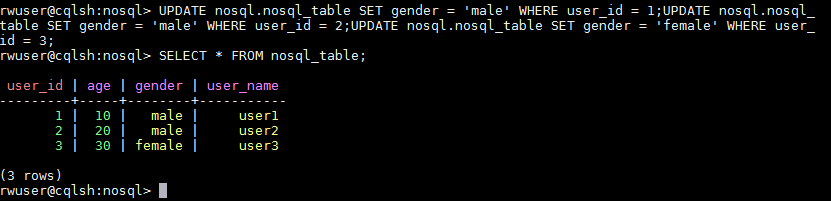
- Delete data from a table in a keyspace, for example:
Delete age data of the user whose ID is 1.
DELETE age FROM nosql.nosql_table WHERE user_id=1;
Figure 7 Deleting a data record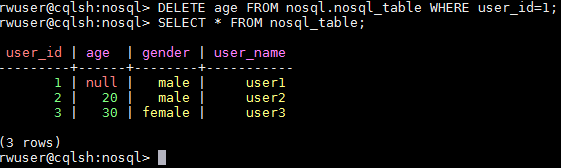
Delete the entire record of the user whose ID is 2.
DELETE FROM nosql.nosql_table WHERE user_id=2;
Figure 8 Deleting the entire record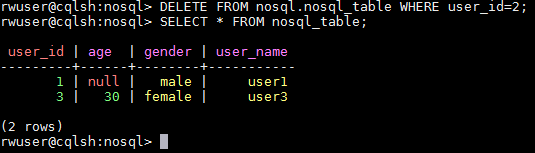
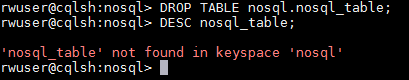
- Delete an entire table, for example:
Figure 9 Deleting an entire table
- Create a table.
- HELP command
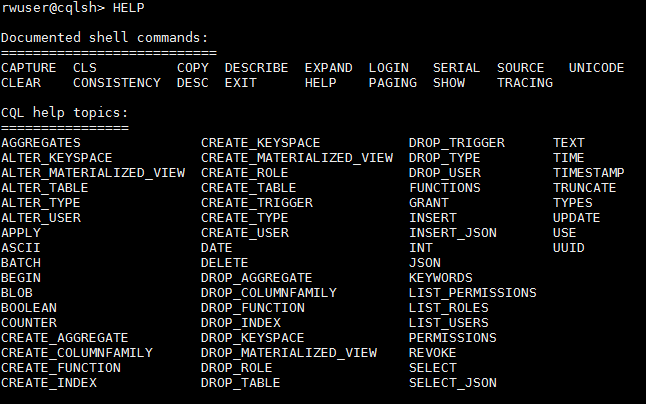
- Run HELP to view all supported commands.
Figure 10 Viewing all supported commands
- Run HELP <COMMAND> to query the usage of a command.
Example: HELP DESC
- Run HELP to view all supported commands.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





