Overview
Scenarios
You have servers both in VPCs and your on-premises data center and want to use load balancers to distribute incoming traffic across these servers.
This section describes how you can use a dedicated load balancer to route incoming traffic across cloud and on-premises servers.

Solution
You can enable IP as a Backend when creating a dedicated load balancer and associate cloud and on-premises servers with this dedicated load balancer using their IP addresses.
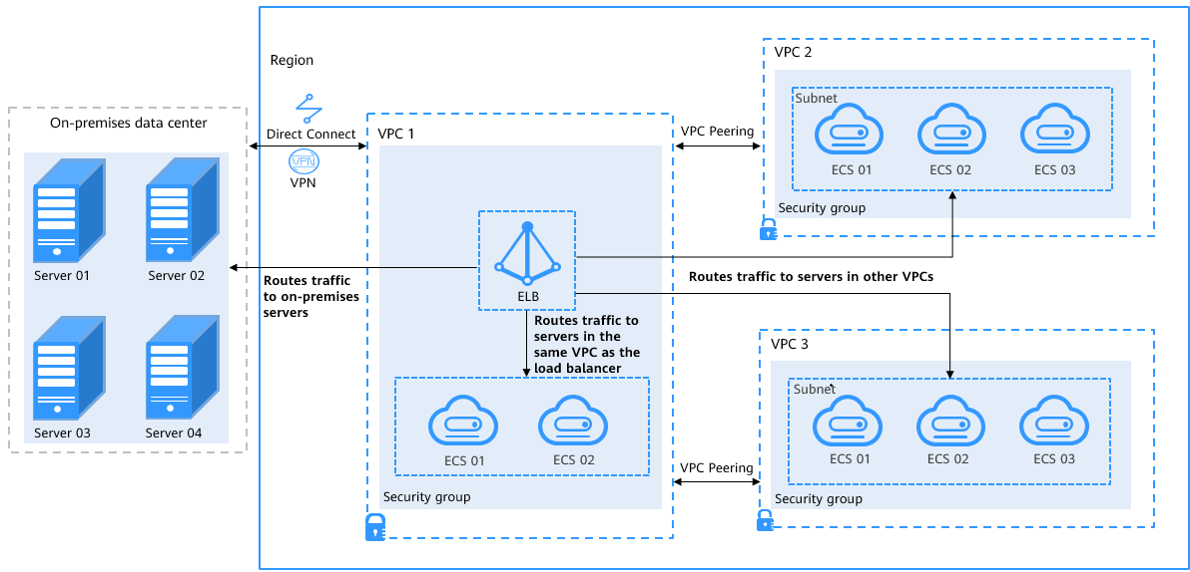
As shown in Figure 2, ELB can realize hybrid load balancing.
- You can associate the servers in the same VPC as the load balancer no matter whether you enable IP as a Backend.
- If you enable IP as a Backend:
- You can associate on-premises servers with the load balancer after the on-premises data center is connected to the cloud through Direct Connect or VPN.
- You can also associate the servers in other VPCs different from the load balancer after the VPCs are connected to the VPC where the load balancer is running over VPC peering connections.
- You can associate the servers in the same VPC as the load balancer.
Advantages
You can add servers in the VPC where the load balancer is created, in a different VPC, or in an on-premises data center, by using private IP addresses of the servers to the backend server group of the load balancer. In this way, incoming traffic can be flexibly distributed to cloud servers and on-premises servers for hybrid load balancing.
- You can add backend servers in the same VPC as the load balancer.
- You can add servers in other VPCs different from the load balancer by establishing a VPC peering connection between the two VPCs.
- You can add on-premises servers by connecting your on-premises data center to the cloud through Direct Connect or VPN.
Notes and Constraints
When you add IP as backend servers, note the following:
- Enable IP as a Backend first on the Summary page of the load balancer.
- IP as backend servers must use IPv4 addresses.
- To ensure requests are properly routed, IP as backend servers cannot use public IP addresses.
- To add IP as backend servers, the subnet where the load balancer works must have at least 16 available IP addresses. You can add more subnets for more IP addresses on the Summary page of the load balancer.
- To ensure normal health checks, security group rules configured for IP as backend servers must allow traffic from the backend subnet of the load balancer.
- IP as a Backend cannot be disabled after it is enabled.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot