Deploying WordPress Using the CCI Console
Cloud Container Instance (CCI) provides a serverless container engine, eliminating the need to manage clusters or servers. CCI delivers container agility and high performance with only three steps. CCI enables you to create Deployments. It enhances container security isolation and supports fast workload deployment, elastic load balancing, and auto scaling based on the Kubernetes workload model.
Creating a Namespace
- Log in to the CCI 2.0 console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Namespaces.
- On the Namespaces page, click Create Namespace in the upper right corner.
- Configure basic information.
Parameter
Description
Namespace Name
You can create different namespaces for environment isolation.
- The name of each namespace must be unique.
- Enter 1 to 63 characters starting and ending with a lowercase letter or digit. Only lowercase letters, digits, and hyphens (-) are allowed.
Enterprise Project
Select or create an enterprise project. This parameter is available only for enterprise users who have enabled an enterprise project. After an enterprise project is selected, the security group for the namespace will be created in that project. You can manage namespaces and other resources through the Enterprise Project Management Service (EPS). For more details, see Enterprise Management.
- (Optional) Specify monitoring settings.
Parameter
Description
AOM (Optional)
If this option is enabled, you need to select an AOM instance.
- Configure the network plane.
Table 1 Network plane settings Parameter
Description
IPv6
If this option is enabled, IPv4/IPv6 dual stack is supported.
VPC
Select the VPC where the workloads are running. If no VPC is available, create one first. The VPC cannot be changed once selected.
Recommended CIDR blocks: 10.0.0.0/8-22, 172.16.0.0/12-22, and 192.168.0.0/16-22
NOTICE:- You cannot set the VPC CIDR block and subnet CIDR block to 10.247.0.0/16, because this CIDR block is reserved for workloads. If you select this CIDR block, there may be IP address conflicts, which may result in workload creation failure or service unavailability. If you do not need to access pods through workloads, you can select this CIDR block.
- After the namespace is created, you can choose Namespaces in the navigation pane and view the VPC and subnet in the Subnet column.
Subnet
Select the subnet where the workloads are running. If no subnet is available, create one first. The subnet cannot be changed once selected.
- A certain number of IP addresses (10 by default) in the subnet will be warmed up for the namespace.
- You can set the number of IP addresses to be warmed up in Advanced Settings.
- If warming up IP addresses for the namespace is enabled, the VPC and subnet can only be deleted after the namespace is deleted.
NOTE:Ensure that there are sufficient available IP addresses in the subnet. If IP addresses are insufficient, workload creation will fail.
Security Group
Select a security group. If no security group is available, create one first. The security group cannot be changed once selected.
- (Optional) Specify advanced settings.
Each namespace provides an IP pool. You can specify the pool size to reduce the duration for assigning IP addresses and speed up the workload creation.
For example, 200 pods are running routinely, and 200 IP addresses are required in the IP pool. During peak hours, the IP pool instantly scales out to provide 65,535 IP addresses. After a specified interval (for example, 23 hours), the IP addresses that exceed the pool size (65535 – 200 = 65335) will be recycled.
Table 2 (Optional) Advanced namespace settings Parameter
Description
IP Pool Warm-up for Namespace
- An IP pool is provided for each namespace, with the number of IP addresses you specify here. IP addresses will be assigned in advance to accelerate workload creation.
- An IP pool can contain a maximum of 65,535 IP addresses.
- When using general-computing pods, you are advised to configure an appropriate size for the IP pool based on service requirements to accelerate workload startup.
- Configure the number of IP addresses to be assigned properly. If the number of IP addresses exceeds the number of available IP addresses in the subnet, other services will be affected.
IP Address Recycling Interval (h)
Pre-assigned IP addresses that become idle can be recycled within the duration you specify here.
NOTE:Recycling mechanism:
- Recycling time: The yangtse.io/warm-pool-recycle-interval field configured on the network determines when the IP addresses can be recycled. If yangtse.io/warm-pool-recycle-interval is set to 24, the IP addresses can only be recycled 24 hours later.
- Recycling rate: A maximum of 50 IP addresses can be recycled at a time. This prevents IP addresses from being repeatedly assigned or released due to fast or frequent recycling.
- Click OK.
You can view the VPC and subnet on the namespace details page.
By default, CCI creates an agency for users to access peripheral services in the namespace. This agency is encrypted and stored in aksk-secret. The encryption and decryption material is stored in system-preset-aeskey. The two resources are used by CCI and have been hidden on the console. You can call APIs to view them, and you are advised not to configure them.
Creating a Deployment Using YAML
- Log in to the CCI 2.0 console. In the navigation pane, choose Workloads. On the Deployments tab, click Create from YAML.
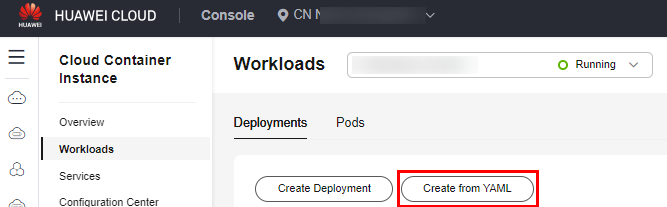
- Specify basic information. The following is an example YAML file:
kind: Deployment apiVersion: cci/v2 metadata: name: wordpress spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: wordpress template: metadata: labels: app: wordpress spec: containers: - name: wordpress image: wordpress:latest ports: - containerPort: 80 resources: limits: cpu: 500m memory: 1Gi requests: cpu: 500m memory: 1Gi dnsPolicy: Default - Create a Service of the LoadBalancer type. The load balancer associated with the Service must have an EIP bound. For details, see Public Network Access. The following is an example YAML file:
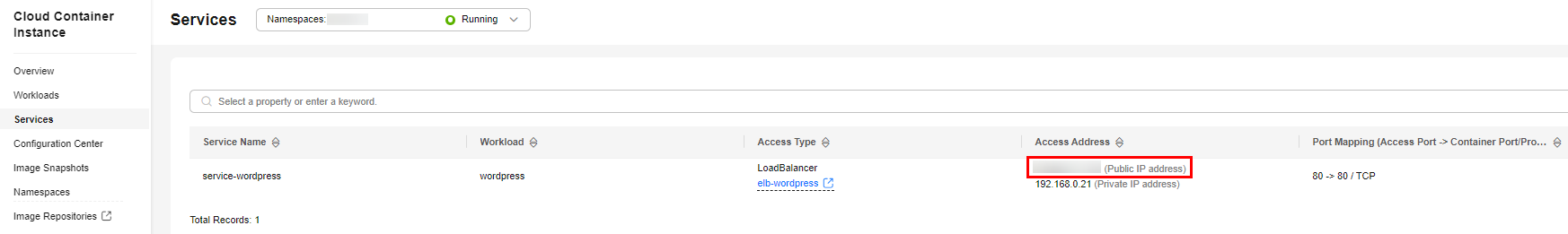
kind: Service apiVersion: cci/v2 metadata: name: service-wordpress annotations: kubernetes.io/elb.class: elb kubernetes.io/elb.id: '${elb_id}' spec: ports: - name: service-wordpress-port protocol: TCP port: 80 targetPort: 80 selector: app: wordpress type: LoadBalancer - Use a browser to access the EIP in the access address.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





