VPC Function
Function Description
The VPC module provides the following functions:
- Cropping: Crops a required area out of the input image.
- Resizing
- In the VPC, image resizing can be classified into 8K image resizing and non-8K image resizing modes based on resolution:
- 8K image resizing: used to process the input image whose width or height is within the range of 4096–8192 pixels
- Non-8K image resizing: used to process the input image whose resolution is within the range of 32 x 6 pixels to 4096 x 4096 pixels
- Single-image cropping/resizing (supporting uncompressed format and HFBC compressed format) and single-image multi-ROI cropping/resizing (supporting uncompressed format and HFBC compressed format):
HFBC is a compressed image format for the VDEC output. In this format, the VDEC has better processing performance.
- Other resizing modes: for example, original image resizing and proportional image resizing.
- In the VPC, image resizing can be classified into 8K image resizing and non-8K image resizing modes based on resolution:
- Overlaying: Crops an image out of an input image, resizes the cropped image, and places it in a specified area of the output image. The output image may be a blank image (when the output buffer allocated by the user is empty) or an existing image (when an image has been read into the output buffer allocated by the user). Note that the overlaying concept here refers only to the case when the output image is an existing image.
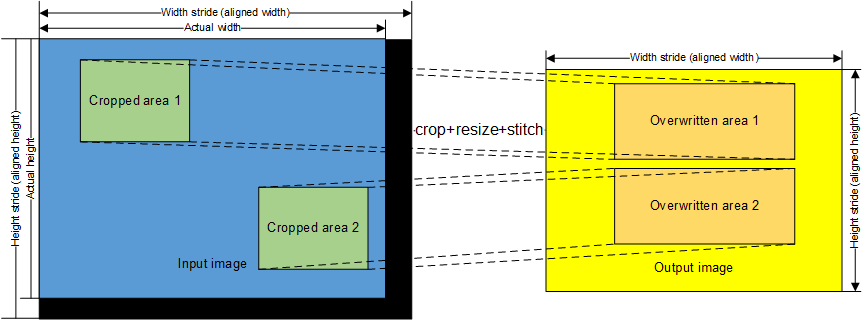
- Stitching: Crops multiple images out of an input image, resizes the cropped images, and place them in a specified area of the output image.
- Format conversion
- Converts an RGB, YUV422, or YUV444 image to a YUV420 image.
- Converts a color image to a grayscale image. For the output image, only the data of the Y component is used.
Restriction
- The following table describes the 8K image resizing and non-8K image resizing modes in the VPC based on resolution.
Input Image Resolution
Input Image Format
Width Stride x Height Stride Alignment for the Input Image
VPC Function
Output Image Resolution
Output Image Format
Width Stride x Height Stride Alignment for the Output Image
Width or height within the range of 4096–8192 pixels (excluding 4096)
YUV420SP (NV12 and NV21)
2 x 2 alignment
8K image resizing
16 x 16 to 4096 x 4096
For details, see the outputFormat parameter in Table 1.
2 x 2 alignment
32 x 6 to 4096 x 4096 pixels (including 4096)
For details, see the inputFormat parameter in Table 1.
- For details about the width stride alignment, see the widthStride parameter in Table 1.
- The height stride is 2-pixel aligned.
Non-8K image resizing
32 x 6 to 4096 x 4096
For details, see the outputFormat parameter in Table 1.
16 x 2 alignment
- Resizing ratio of the width or height: [1/32, 16]
- 8K image resizing: Resizing is supported, the format conversion between YUV420SP NV12 and YUV420SP NV21 is supported, but cropping is not supported.
- Buffer restrictions:
- The start address of the buffer must be 16-byte aligned.
- In the same task, the virtual addresses of the input and output buffers must be in the same 4 GB space.
VPC Function Diagram
|
Concept |
Description |
|---|---|
|
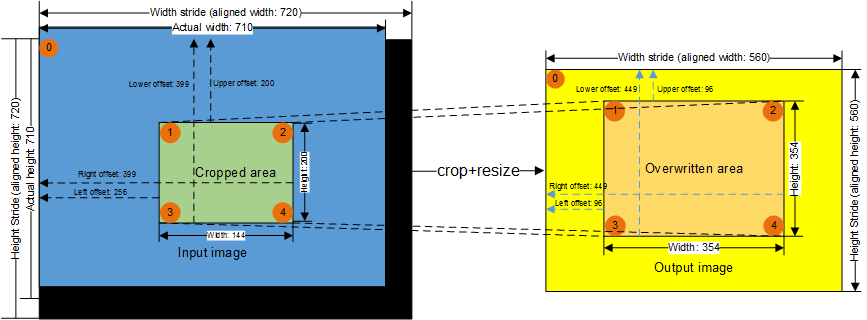
Width stride |
Step for a row of pixels, indicating the width of the input image after alignment. The width stride calculation of an RGB image is different from that of a YUV image. The minimum width stride is 32, and the maximum width stride is 4096 x 4 (the image width is 4096 and the image format is ARGB).
|
|
Height stride |
Number of lines in the buffer of an image, indicating the height of the input image after alignment. Value: The height of the input image must be 2-pixel aligned. The minimum height stride is 6, and the maximum height stride is 4096. |
|
Top/Bottom/Left/Right offset |
You can configure the top offset, bottom offset, left offset, and right offset to implement the following functions: (1) Specify the position of the cropped area or overwritten area. (2) Control the width and height of the cropped area or overwritten area by using the following formulas: Right offset – Left offset + 1 = Width; Bottom offset – Top offset + 1 = Height.
|
|
Cropped area |
Image area to be cropped. The minimum resolution is 10 x 6, and the maximum resolution is 4096 x 4096. |
|
Overwritten area |
Area specified by the user in the output image. The minimum resolution is 10 x 6, and the maximum resolution is 4096 x 4096.
Restrictions:
|
Performance Specifications
- For non-8K image resizing, the VPC performance involves different scenarios such as image cropping and resizing. When the resolution changes during image processing, the performance is calculated based on the larger resolution. For example, if the resolution of the image after resizing is greater than that before resizing, the former is used to calculate the performance specifications. If the resolution of the overwritten area is greater than that of the cropped area, the former is used to calculate the performance specifications. For YUV420 SP images, the performance specifications in typical scenarios are as follows:
Scenario
Total Frame Rate
1080p x n channels (n < 4, one channel corresponds to one thread)
n x 360 fps
1080p x n channels (n ≥ 4, one channel corresponds to one thread)
1440 fps
4K x n channels (n < 4, one channel corresponds to one thread)
n x 90 fps
4K x n channels (n ≥ 4, one channel corresponds to one thread)
360 fps
- For 8K image resizing, the VPC performance is closely related to the output resolution. A higher output resolution indicates longer processing time and lower performance. The following table lists the performance specifications in typical scenarios (output resolution of 1080p or 4K and image format of YUV420 SP).
Scenario
Total Frame Rate
1080p x n channels (n = 1, one channel corresponds to one thread)
4 fps
1080p x n channels (n ≥ 4, one channel corresponds to one thread)
16 fps
4K x n channels (n = 1, one channel corresponds to one thread)
1 fps
4K x n channels (n ≥ 4, one channel corresponds to one thread)
4 fps
Reference
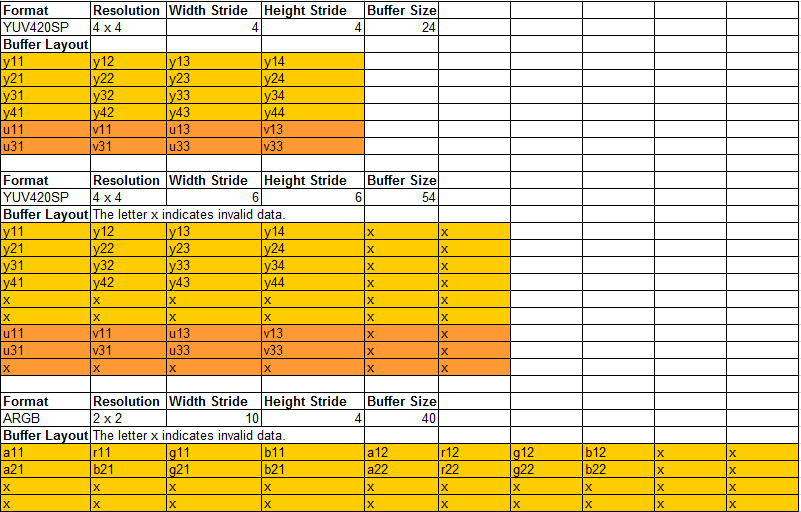
The following figure shows the component layout of the RBG and YUV images. Two YUV420SP images are used as examples for SP format images and an ARGB image is used as an example for packed and RGB images.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





