Index Settings
An index is a storage structure used to query and analyze logs. Different index settings will generate different query and analysis results. Configure the index settings as required.
Log Example
The following is a typical log. The value of the content field is the original log text. Use commas (,) to parse the original log into three fields: level, status, and message.
In the example log, hostName, hostIP, and pathFile are common built-in reserved fields. For details about the built-in fields, see Built-in Reserved Fields.
{
"hostName":"epstest-xx518",
"hostIP":"192.168.0.31",
"pathFile":"stdout.log",
"content":"error,400,I Know XX",
"level":"error",
"status":400,
"message":"I Know XX"
}
Index Types
The following table lists the index types supported by LTS.
|
Index Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Index Whole Text |
LTS splits all field values of an entire log into multiple words when this function is enabled.
NOTE:
|
|
Index Fields |
Query logs by specified field names and values (Key:Value).
NOTE:
Here are two examples:
|
Precautions
- Either whole text indexing or index fields must be configured.
- Index settings (such as adding, editing, and deleting fields and modifying items) take effect only for new log data but not for historical log data. Currently, indexes cannot be recreated for historical logs.
- After the index function is disabled, the storage space of historical indexes is automatically cleared after the data storage period of the current log stream expires.
- By default, LTS creates index fields for some built-in reserved fields. For details, see Built-in Reserved Fields.
- Different index settings will generate different query and analysis results. Configure the index settings as required. Full-text indexes and index fields do not affect each other.
- After the index configuration is modified, the modification takes effect only for newly written log data.
Configuring Whole Text Indexing
- Log in to the LTS console and choose Log Management.
- In the log group list, click
 on the left of a log group, and click a log stream to go to the details page.
on the left of a log group, and click a log stream to go to the details page. - Click
 in the upper right corner to go to the Index Settings page.
in the upper right corner to go to the Index Settings page. - Index Whole Text is enabled by default.

- For automatic configuration, the intersection of the raw logs and built-in fields in the last 15 minutes is obtained by default. LTS automatically combines the intersection of the raw logs and built-in fields, current structured fields, and tag fields to form the table data below the field index.
- If no raw log is generated within 15 minutes, obtain the hostIP, hostName, pathFile, structured field, and tag field to form the table data below the field index.
- When Log Structuring is configured for ECS ingestion, the category, hostName, hostId, hostIP, hostIPv6 and pathFile fields are automatically added on the Index Settings page. A field will not be added if the same one already exists.
- When Log Structuring is configured for CCE ingestion, the category, clusterId, clusterName, nameSpace, podName, containerName, appName, hostName, hostId, hostIP, hostIPv6 and pathFile fields are automatically added to Index Settings page. A Field will not be added if the same one already exists.
- Set parameters as described in Table 2.
Table 2 Whole text indexing parameters Parameter
Description
Index Whole Text
If Index Whole Text is enabled, a full-text index is created.
Case-Sensitive
Indicates whether letters are case-sensitive during query.
- If this function is enabled, the query result is case-sensitive. For example, if the example log contains Know, you can query the log only with Know.
- If this function is disabled, the query result is case-insensitive. For example, if the example log contains Know, you can also query the log with KNOW or know.
Include Chinese
Indicates whether to distinguish between Chinese and English during query.
- After the function is enabled, if the log contains Chinese characters, the Chinese content is split based on unigram segmentation and the English content is split based on delimiters.
NOTE:
- Unigram segmentation is to split a Chinese string into Chinese characters.
- The advantage of unigram segmentation is efficient word segmentation of massive logs, and other Chinese segmentation methods have great impact on the write speed.
- After this function is disabled, all content is split based on delimiters.
For example, assume that the log content is:
error,400,I Know TodayIsMonday.
- After this function is disabled, the English content is split based on delimiters. The log is split into error, 400, I, Know, and TodayIsMonday. You can search for the log by error or TodayIsMonday.
- After this function is enabled, the background analyzer of LTS splits the log into error, 400, I, Know, Today, Is, and Monday. You can search for the log by error or Today.
Delimiters
Splits the log content into multiple words based on the specified delimiter. Default delimiters include ,'";=()[]{}@&<>/:\n\t\r and spaces. If the default settings cannot meet your requirements, you can customize delimiters. All ASCII codes can be defined as delimiters.
If the delimiter is set to null, the field value is regarded as a whole. You can search for the corresponding log only through the complete character string or fuzzy search.
For example, assume that the log content is:
error,400,I Know TodayIsMonday.
- If no delimiter is set, the entire log is regarded as a string error,400,I Know TodayIsMonday. You can search for the log only by the complete string error,400,I Know TodayIsMonday or by fuzzy search error,400,I K*.
- If the delimiter is set to a comma (,), the raw log is split into: error, 400, and I Know TodayIsMonday. You can find the log by fuzzy search or exact words, for example, error, 400, Kn*, and TodayIs*.
- If the delimiter is set to a comma (,) and space, the raw log is split into: error, 400, I, Know, TodayIsMonday. You can find the log by fuzzy search or exact words, for example, Know, and TodayIs*.
ASCII Delimiters
Click Add ASCII Delimiter and enter the ASCII value by referring to ASCII Table.
- Click OK.
Configuring Index Fields
When creating a field index, you can add a maximum of 500 fields. A maximum of 100 subfields can be added for JSON fields.

Custom and special delimiters of field indexes are available only to whitelisted users. To use them, .
- Click Add Field under Index Fields and set field information by referring to Table 3.
- Alternatively, select fields and click Batch configuration. On the displayed page, configure parameters.
Figure 1 Batch configuration
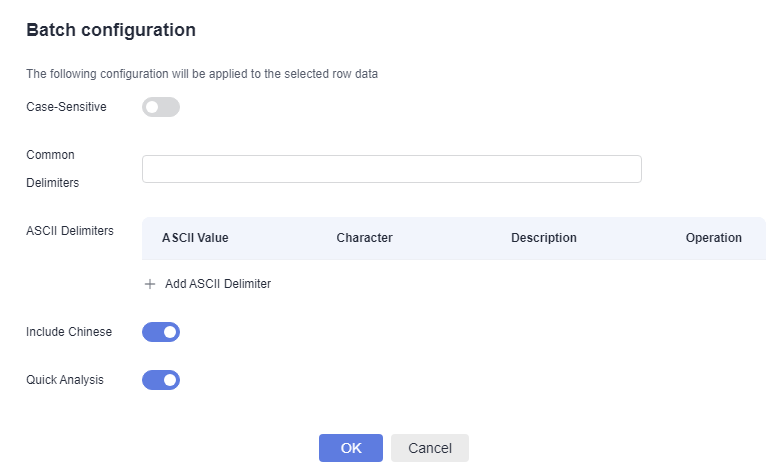
- Configure the index field by referring to Table 3.

- The preceding indexing parameters take effect only for the current field.
- Index fields that do not exist in log content are invalid.
Table 3 Index field parameters Parameter
Description
Field Name
Log field name, including level in the example log.
The field name can contain only letters, digits, and underscores (_), and must start with a letter or underscore (_). The field name cannot contain double underscores (__).
NOTE:- Double underscores (__) are used in built-in reserved fields that are not displayed to users in LTS. Double underscores (__) cannot be used in custom log field names. Otherwise, field index names cannot be configured.
- By default, LTS creates index fields for some built-in reserved fields. For details, see Built-in Reserved Fields.
Type
- Data type of the log field value. The options are string, long, and float.
- Fields of long and float types do not support Case-Sensitivity, Include Chinese and Delimiters.
Case-Sensitive
Indicates whether letters are case-sensitive during query.
- If this function is enabled, the query result is case-sensitive. For example, if the message field in the example log contains Know, you can query the log only with message:Know.
- If this function is disabled, the query result is case-insensitive. For example, if the message field in the example log contains Know, you can also query the log with message:KNOW or message:know.
Common Delimiters
Splits the log content into multiple words based on the specified delimiter. Default delimiters include ,'";=()[]{}@&<>/:\n\t\r and spaces. If the default settings cannot meet your requirements, you can customize delimiters. All ASCII codes can be defined as delimiters.
If the delimiter is set to null, the field value is regarded as a whole. You can search for the corresponding log only through the complete character string or fuzzy search.
For example, the content of the message field in the example log is I Know TodayIsMonday.
- If no delimiter is set, the entire log is regarded as a string I Know TodayIsMonday. You can search for the log only by the complete string message:I Know TodayIsMonday or by fuzzy search message:I Know TodayIs*.
- If the delimiter is set to a space, the raw log is split into: I, Know, and TodayIsMonday. You can find the log by fuzzy search or exact words, for example, message:Know, or message: TodayIsMonday.
ASCII Delimiters
Click Add ASCII Delimiter and enter the ASCII value by referring to ASCII Table.
Include Chinese
Indicates whether to distinguish between Chinese and English during query.
- After the function is enabled, if the log contains Chinese characters, the Chinese content is split based on unigram segmentation and the English content is split based on delimiters.
NOTE:
- Unigram segmentation is to split a Chinese string into Chinese characters.
- The advantage of unigram segmentation is efficient word segmentation of massive logs, and other Chinese segmentation methods have great impact on the write speed.
- After this function is disabled, all content is split based on delimiters.
For example, the content of the message field in the example log is I Know TodayIsMonday.
- After this function is disabled, the English content is split based on delimiters. The log is split into I, Know, and TodayIsMonday. You can search for the log by message:Know or message:TodayIsMonday.
- After this function is enabled, the background analyzer of LTS splits the log into I, Know, Today, Is, and Monday. You can search for the log by message:Know or message:Today.
Quick Analysis
By default, this option is enabled, indicating that this field will be sampled and collected. For details, see Quick Analysis.
NOTE:- The principle of quick analysis is to collect statistics on 100,000 logs that match the search criteria, not all logs.
- The maximum length of a field for quick analysis is 2000 bytes.
- The quick analysis field area displays the first 100 records.
Operation
Click
 to delete the target field.
to delete the target field. - Click OK.
Auto Index Field Configuration
When creating an index field, you can click Auto Config. The log service automatically adds some index fields. You can add or delete fields as required.
- The log service automatically generates an index field based on the first content in the preview data during collection.
- The log service selects several common built-in reserved fields (such as hostIP, hostName, and pathFile) and adds them to the index field.
ASCII Table
|
ASCII Value |
Character |
ASCII Value |
Character |
ASCII Value |
Character |
ASCII Value |
Character |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
NUL (Null) |
32 |
Space |
64 |
@ |
96 |
` |
|
1 |
SOH (Start of heading) |
33 |
! |
65 |
A |
97 |
a |
|
2 |
STX (Start of text) |
34 |
" |
66 |
B |
98 |
b |
|
3 |
ETX (End of text) |
35 |
# |
67 |
C |
99 |
c |
|
4 |
EOT (End of transmission) |
36 |
$ |
68 |
D |
100 |
d |
|
5 |
ENQ (Enquiry) |
37 |
% |
69 |
E |
101 |
e |
|
6 |
ACK (Acknowledge) |
38 |
& |
70 |
F |
102 |
f |
|
7 |
BEL (Bell) |
39 |
' |
71 |
G |
103 |
g |
|
8 |
BS (Backspace) |
40 |
( |
72 |
H |
104 |
h |
|
9 |
HT (Horizontal tab) |
41 |
) |
73 |
I |
105 |
i |
|
10 |
LF (Line feed) |
42 |
* |
74 |
J |
106 |
j |
|
11 |
VT (Vertical tab) |
43 |
+ |
75 |
K |
107 |
k |
|
12 |
FF (Form feed) |
44 |
, |
76 |
L |
108 |
l |
|
13 |
CR (Carriage return) |
45 |
- |
77 |
M |
109 |
m |
|
14 |
SO (Shift out) |
46 |
. |
78 |
N |
110 |
n |
|
15 |
SI (Shift in) |
47 |
/ |
79 |
O |
111 |
o |
|
16 |
DLE (Data link escape) |
48 |
0 |
80 |
P |
112 |
p |
|
17 |
DC1 (Device control 1) |
49 |
1 |
81 |
Q |
113 |
q |
|
18 |
DC2 (Device control 2) |
50 |
2 |
82 |
R |
114 |
r |
|
19 |
DC3 (Device control 3) |
51 |
3 |
83 |
S |
115 |
s |
|
20 |
DC4 (Device control 4) |
52 |
4 |
84 |
T |
116 |
t |
|
21 |
NAK (Negative acknowledge) |
53 |
5 |
85 |
U |
117 |
u |
|
22 |
SYN (Synchronous idle) |
54 |
6 |
86 |
V |
118 |
v |
|
23 |
ETB (End of transmission block) |
55 |
7 |
87 |
W |
119 |
w |
|
24 |
CAN (Cancel) |
56 |
8 |
88 |
X |
120 |
x |
|
25 |
EM (End of medium) |
57 |
9 |
89 |
Y |
121 |
y |
|
26 |
SUB (Substitute) |
58 |
: |
90 |
Z |
122 |
z |
|
27 |
ESC (Escape) |
59 |
; |
91 |
[ |
123 |
{ |
|
28 |
FS (File separator) |
60 |
< |
92 |
\ |
124 |
| |
|
29 |
GS (Group separator) |
61 |
= |
93 |
] |
125 |
} |
|
30 |
RS (Record separator) |
62 |
> |
94 |
^ |
126 |
~ |
|
31 |
US (Unit separator) |
63 |
? |
95 |
_ |
127 |
DEL (Delete) |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





