Healthcare
BCS helps healthcare institutions, third-party organizations, and supervision departments to form a collaboration consortium. Healthcare information silos are broken down using electronic medical records that cannot be tampered with to protect privacy. This builds trust between doctors and patients and provides comprehensive health and medical care information for telemedicine and referral.
Industry Status Quo and Pain Points
- Insecure data
Most healthcare data is stored in the data center. If a natural disaster or hacking occurs, patients' electronic medical records stored in the data center may be lost.
- Information silos
There is no appropriate mechanism for mutual trust and data sharing between healthcare institutions, which leads to information silos and makes it difficult to obtain complete and comprehensive data. Data may be modified casually when shared and therefore, is considered unreliable.
- Repeated medical treatment
Data is not shared between healthcare institutions. Performing repetitive health checks and creating new medical records are required when patients go to the different institutions, wasting time, money, and medical resources.
- No access to personal medical data
Patients' medical data is stored in the hospital systems, however, patients cannot access to or manage it.
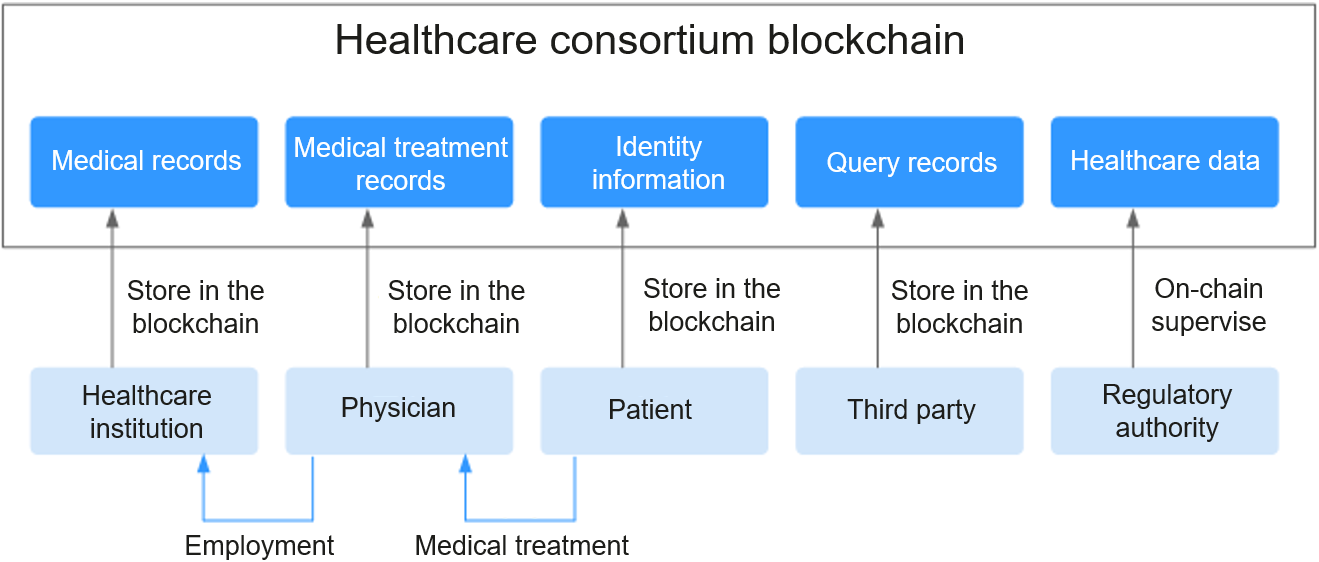
Solution Architecture
A healthcare consortium blockchain is built, comprising healthcare institutions, third parties, physicians, patients, and regulators based on electronic medical records (EMRs). The medical and healthcare data is stored in the blockchain and offered for queries or scientific research, with security and privacy protected by using encryption and smart contract-based authorization mechanisms.
Solution Highlights
- Information silos broken down
The healthcare consortium blockchain connects information systems of healthcare institutions, so that regional inspection as well as ultrasound and radiological examination results can be securely exchanged for online healthcare, two-way referral, and remote consultation.
- Immutable medical data
The EMRs, physicians' diagnosis process and results, medical record query histories, and patient identity information are transparently stored in blockchains to ensure that they cannot be tampered with. This reduces medical disputes and constructs a harmonious healthcare environment.
- Protected privacy and right to know
Encryption and smart contract-based authorization mechanisms offer patients access to their own healthcare data while protecting their privacy. Others can access the data only when authorized.
- Quick and effective supervision
Regulatory authorities can use the data on blockchains to effectively prevent healthcare treatment that violates regulations, reducing medical disputes.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





