Binary Division Operation
Function Name
$divide(intA, intB, intC)
Function Description
Implements the division operation between parameter A and parameter B. C is the precision value. Parameters A, B, and C support the following types:
- Numbers
- Local parameters
- Binary operations
- Division operation without precision: For exact division, the value is the number of reserved digits. For inexact division, the value is rounded off with six decimal places by default.
- Division operation with precision: The precision value is an integer ranging from 1 to 6. For exact division, the reserved decimal places must be in the precision range. For inexact division, the value is rounded off with the specified number of decimal places.
Application Scenarios
The binary division function can be used in the following scenarios for API automation:
- Request URL
- Request header
- Request body
- Checkpoint property
- if condition
- for loop interrupt condition
Example
- Request URL
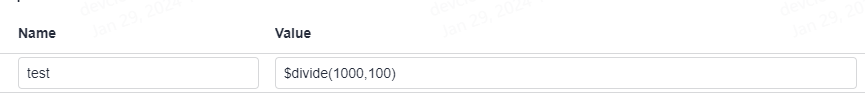
As shown in the following figure, the value of test in the request URL is the binary division function. Parameter A in the function is 1000 and parameter B is 100.
- As shown in the following figure, the value of test in the request URL is the binary division function with a precision value. Parameter A in the function is 1, parameter B is 3, and the precision value is 5.

- Request header
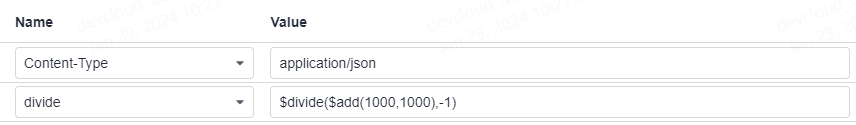
As shown in the following figure, the value of divide in the request header is the binary division function. Parameter A in the function is the binary addition operation $add(1000,1000), and parameter B is -1.
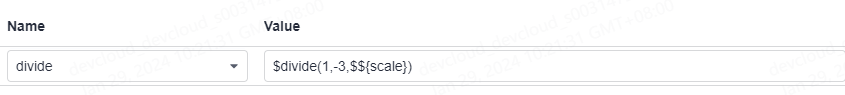
As shown in the following figure, the value of divide in the request header is the binary division function with a precision value. Parameter A in the function is 1, parameter B is –3, and parameter C is the global environment parameter $${scale}.
- Request body
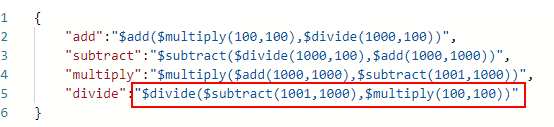
As shown in the following figure, the binary division function is used in the request body. Parameter A in the function is the binary subtraction operation $subtract(1001,1000), and parameter B is the binary multiplication operation $multiply(100,100).
As shown in the following figure, the binary division function with a precision value is used in the request body. Parameter A in the function is 1, parameter B is 3, and parameter C is the global environment parameter $${scale}.

- Checkpoint property
As shown in the following figure, the target value of the checkpoint property result is the binary division function. Parameter A in the function is the local parameter test, and parameter B is 1. For details about how to set local parameters, see Local Parameters.

As shown in the following figure, the target value of the checkpoint property result is the binary division function with a precision value. Parameter A in the function is the local parameter test, parameter B is 2, and parameter C is 5. For details about how to set local parameters, see Local Parameters.

- if condition
As shown in the following figure, the target value of the if condition is the binary division function. Parameter A in the function is 1, and parameter B is the environment variable status. Parameter C is the local parameter localScale. For details about how to set local parameters, see Local Parameters.

As shown in the following figure, the target value of the if condition is the binary division function with a precision value. Parameter A in the function is 1 and parameter B is 3. For details about how to set environment parameters, see Setting Environment Parameters of an API Script.

- for loop interrupt condition
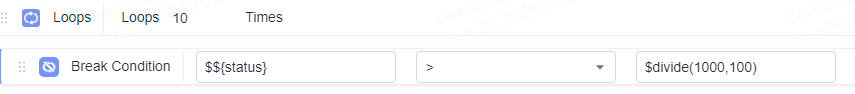
As shown in the following figure, the target value of the for loop interrupt condition is the binary division function. Parameter A in the function is 1000, and parameter B is 100.
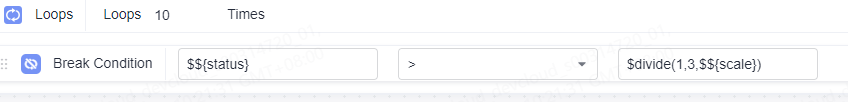
As shown in the following figure, the target value of the for loop interrupt condition is the binary division function with a precision value. Parameter A in the function is 1, parameter B is 3, and parameter C is the global environment parameter $${scale}.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





