Interconnecting Spark with OBS Using an IAM Agency
After configuring decoupled storage and compute for a cluster by referring to Interconnecting an MRS Cluster with OBS Using an IAM Agency, you can create tables with OBS paths as their location on the Spark client.
Interconnecting with OBS Using Spark Beeline
- Log in to the MRS Manager and choose Cluster > Services > Spark2x > Configurations > All Configurations. For how to log in to MRS Manager, see Accessing MRS Manager.
In the left navigation pane, choose JDBCServer2x > Customization. Add the configuration item dfs.namenode.acls.enabled to the spark.hdfs-site.customized.configs parameter and set the value to false to disable the HDFS ACL function.
Figure 1 Adding Spark custom parameters
- Search for the spark.sql.statistics.fallBackToHdfs parameter and set its value to false.
Figure 2 Setting spark.sql.statistics.fallBackToHdfs

- Save the configurations and restart the JDBCServer2x instance.
- Log in to the client installation node as the client installation user.
For details about how to download and install the cluster client, see Installing an MRS Cluster Client.
- Run the following commands to configure environment variables:
source Client installation directory/bigdata_env - Authenticate the user of the cluster with Kerberos authentication enabled. Skip this step for the user of the cluster with Kerberos authentication disabled.
kinit Username - Access OBS using Spark beeline. The following example creates a table named test in the obs://mrs-word001/table/ directory.
Access spark-beeline.
spark-beeline
Create the test table.
create table test(id int) location 'obs://mrs-word001/table/'; - Run the following command to query all tables. If table test is returned, OBS access is successful.
show tables;
Figure 3 Returned table names
- Press Ctrl+C to exit Spark beeline.
Interconnecting with OBS Using Spark SQL
- Log in to the client installation node as the client installation user.
For details about how to download and install the cluster client, see Installing an MRS Cluster Client.
- Run the following commands to configure environment variables:
source Client installation directory/bigdata_env - Modify the configuration file:
vim Client installation directory/Spark2x/spark/conf/hdfs-site.xmlModify the following content, where the dfs.namenode.acls.enabled parameter specifies whether to enable the HDFS ACL function.
<property> <name>dfs.namenode.acls.enabled</name> <value>false</value> </property>
- Authenticate the user of the cluster with Kerberos authentication enabled. Skip this step for the user of the cluster with Kerberos authentication disabled.
kinit Username - Access OBS using Spark SQL CLI. For example, create a table named test in the obs://mrs-word001/table/ directory.
- Check whether the table exists.
show tables;
- Run exit; to exit the Spark SQL CLI.
If a large number of logs are printed in the OBS file system, the read and write performance may be affected. You can adjust the log level of the OBS client as follows:
- Go to the conf directory.
cd Client installation directory/Spark2x/spark/conf - Edit the file log4j.properties.
vi log4j.properties
- Add the OBS log level configuration to the file.
log4j.logger.org.apache.hadoop.fs.obs=WARN log4j.logger.com.obs=WARN
Figure 4 Adding an OBS log level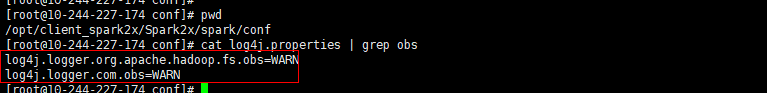
- Go to the conf directory.
Using Spark Shell to Read OBS Files
- Log in to the client installation node as the client installation user.
For details about how to download and install the cluster client, see Installing an MRS Cluster Client.
- Run the following commands to configure environment variables:
source Client installation directory/bigdata_env - Modify the configuration file:
vim Client installation directory/Spark2x/spark/conf/hdfs-site.xmlModify the following content, where the dfs.namenode.acls.enabled parameter specifies whether to enable the HDFS ACL function.
<property> <name>dfs.namenode.acls.enabled</name> <value>false</value> </property>
- Authenticate the user of the cluster with Kerberos authentication enabled. Skip this step for the user of the cluster with Kerberos authentication disabled.
kinit Username - Run the following commands to log in to the Spark SQL CLI:
Go to the bin directory.
cd Client installation directory/Spark2x/spark/binLog in to the Spark SQL CLI.
./spark-sql
- Create a table in OBS and import data to the table.
- Create a database.
create database test location "obs://Parallel file system path/test";
- Switch to the new database.
use test; - Create a table.
create table test1(a int,b int) using parquet; - Insert data into the table.
insert into test1 values(1,2); - View table details.
desc formatted test1;The Location of the table shown in Figure 5 is an OBS path.
- Run exit; to exit the Spark SQL CLI.
- Create a database.
- Run the following command to go to the Spark bin directory:
cd Client installation directory/Spark2x/spark/bin - Log in to the Spark SQL CLI.
./spark-shell
- In the Spark Shell CLI, run the following command to query the table created in 5.c:
spark.read.format("parquet").load("obs://Parallel file system path/test1").show();The table data is displayed, as shown below.
Figure 6 Viewing table data
- Run the :quit command to exit the Spark Shell CLI.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot






