Cloud Delivering Messages to Edge Nodes
Scenario
IEF can deliver messages from SystemREST in the cloud to SystemEventBus (MQTT broker) on edge nodes.
To be specific, IEF calls the open REST gateway interface to send messages to SystemEventBus on an edge node based on the node ID and custom topic. Your end devices can receive messages from the cloud by subscribing to custom topics.
The procedure is as follows:
Creating a Route
SystemREST and SystemEventBus are default endpoints and do not need to be created. SystemREST indicates the REST gateway interface of IEF in the region. SystemEventBus indicates the MQTT broker of an edge node.
- Log in to the IEF console, and click Switch Instance on the Dashboard page to select a platinum service instance.
- In the navigation pane, choose Edge-Cloud Messages > Routes.
- Click Create Route in the upper right corner.
- Set parameters.
Figure 1 Creating a route
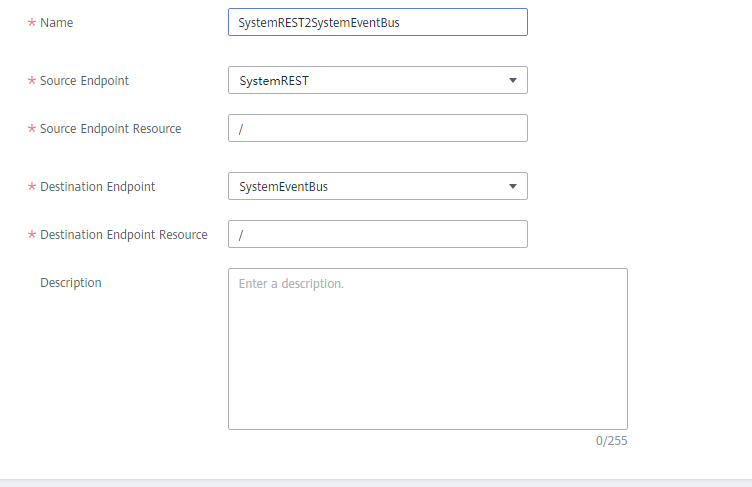
- Name: Enter a route name, for example, SystemREST2SystemEventBus.

Message routes and system subscriptions are of the same resource type. Their names cannot conflict with each other.
- Source Endpoint: Select SystemREST.
- Source Endpoint Resource: Enter a URL path starting with a slash (/). You can use {} for fuzzy match. For example, /aaa/{any-str}/bbb can match /aaa/ccc/bbb or /aaa/ddd/bbb. The specified source resource is used as a matching field for calling the REST interface.
- Destination Endpoint: Select SystemEventBus.
- Destination Endpoint Resource: Enter the topic name prefix used when the message is forwarded to the MQTT broker.
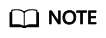
If both Source Endpoint Resource and Destination Endpoint Resource are set to /, IEF will forward all messages sent to the REST interface to the MQTT broker of the corresponding edge nodes. The topic name contained in the messages is the same as the request URL.
- Name: Enter a route name, for example, SystemREST2SystemEventBus.
- Click Create.
The created route is displayed in the message route list.
Figure 2 Routes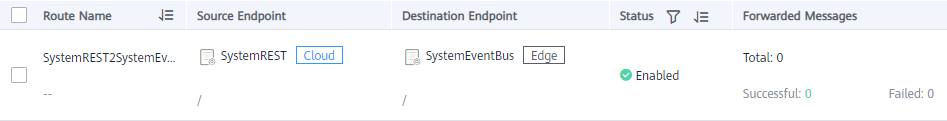
Sending a Message
To deliver a message from SystemREST in the cloud to SystemEventBus on an edge node, obtain the SystemREST endpoint property, construct a request, and send the request to SystemEventBus through a route.
- Obtain the SystemREST endpoint property.
- Log in to the IEF console, and click Switch Instance on the Dashboard page to select a platinum service instance.
- In the navigation pane, choose Edge-Cloud Messages > Endpoints. In the row where SystemREST is located, the value of public in the Property column is the endpoint of SystemREST, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 3 SystemREST endpoint property
- Construct a request and send it.
An HTTPS request needs to be constructed and sent to SystemREST. The details are as follows:
- Method: POST
- URL: https://{rest_endpoint}/{node_id}/{topic}. In the URL, {rest_endpoint} is the endpoint obtained in 1, {node_id} is the edge node ID, and {topic} is the message topic, that is, the source endpoint resource defined in Creating a Route.
- Body: content of the message to be sent, which is user-defined.
- Header: X-Auth-Token, which is a valid token obtained from IAM. For details on how to obtain a token, see Obtaining a User Token.
For example, use Postman to send the following message:
Figure 4 Sending a message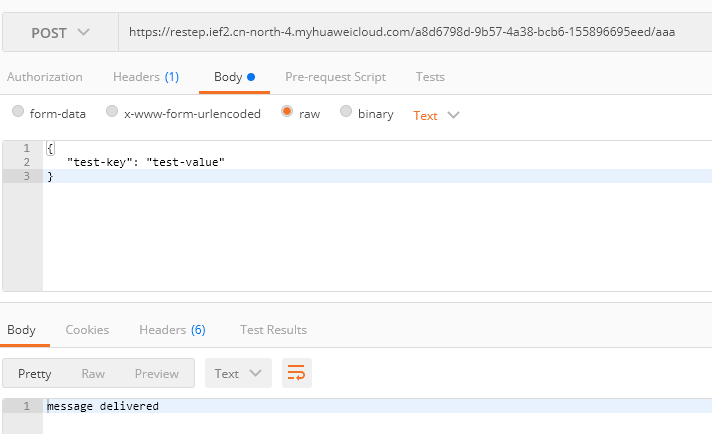
Receiving a Message
- Log in to the edge node.
- Use the MQTT client to receive messages.
Currently, edge nodes support two types of MQTT brokers.
- Built-in MQTT broker (using port 8883): To use this type of MQTT broker, edge nodes must pass certificate authentication and subscribe to corresponding topics. For details about certificate authentication, see Performing Security Authentication Using Certificate.
- External MQTT broker (using port 1883): To use this type of MQTT broker, install a third-party MQTT broker on edge nodes and enable edge nodes to subscribe to corresponding topics.
This section describes how to use an external MQTT broker, for example, Mosquitto, to receive messages. The procedure is as follows:
- In the Ubuntu OS, run the following commands to install Mosquitto:
apt-get install mosquitto systemctl start mosquitto systemctl enable mosquitto
- In the CentOS OS, run the following commands to install Mosquitto:
yum install epel-release yum install mosquitto systemctl start mosquitto systemctl enable mosquitto
After the installation is complete, run the topic subscription command. If a message is sent after the subscription, the edge node will receive the message. In the following command, # indicates that any topic is subscribed to. You can replace # with a specified topic, for example, /aaa or /bbb.
[root@ief-node ~]# mosquitto_sub -t '#' -d Client mosq-m02iwjsp4j2ISMw6rw sending CONNECT Client mosq-m02iwjsp4j2ISMw6rw received CONNACK (0) Client mosq-m02iwjsp4j2ISMw6rw sending SUBSCRIBE (Mid: 1, Topic: #, QoS: 0, Options: 0x00) Client mosq-m02iwjsp4j2ISMw6rw received SUBACK Subscribed (mid: 1): 0 Client mosq-m02iwjsp4j2ISMw6rw received PUBLISH (d0, q0, rQ, mQ, '/aaa', ... (31 bytes)) { "test-key": "test-value" }
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





