Policy Baseline Overview
The policy baseline is a comprehensive data security policy framework that incorporates data security management regulations, data classification and grading standards, cross-border data transfer management regulations, and critical and core data requirements. DSC offers pre-configured policy templates grounded in Huawei Cloud's extensive data security governance expertise, as well as support for policy creation, deletion, modification, querying, structured presentation, and filtered query functionality.
Enterprises can configure and implement unified data security protection policies to establish integrated collaborative protection measures, covering sensitive data discovery, identification, protection, supervision, and governance. This approach meets data security and personal information protection compliance requirements, simplifies data security management, and enhances the security and efficiency of enterprise data.
Application Scenarios
During the initialization phase, the enterprise administrator navigates to the DSC policy center page to establish the enterprise's data security protection policy baseline. Policies can be configured for the entire data lifecycle.
- Go to the Asset Map page and click an asset name. On the displayed page, click the Bucket Protection Policy Analysis or Protection Policy Analysis tab. On this page, you can view the security configurations (such as encryption, backup, and audit) and their policy baseline requirements. You can click View or Modify to go to the management console of the corresponding data source and configure related permissions based on policy requirements.
Figure 1 Protection policy analysis
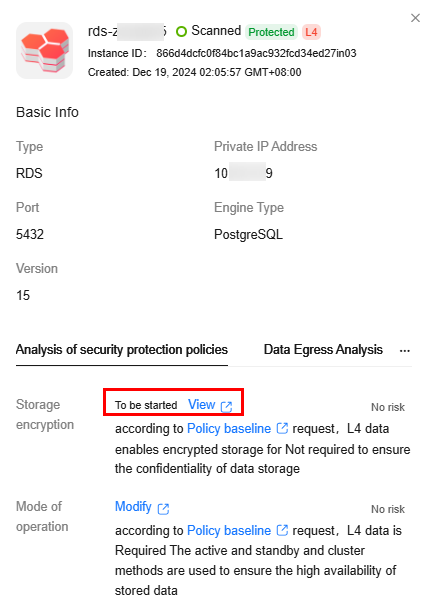
- Go to the Asset Map page and click Rating Details to view the security configurations (such as encryption, backup, and audit) of all assets and the policy baseline requirements. You can click View, Enable, or Modify to go to the management console of the corresponding data source and configure related permissions based on the policy requirements.
Figure 2 Protection policy analysis
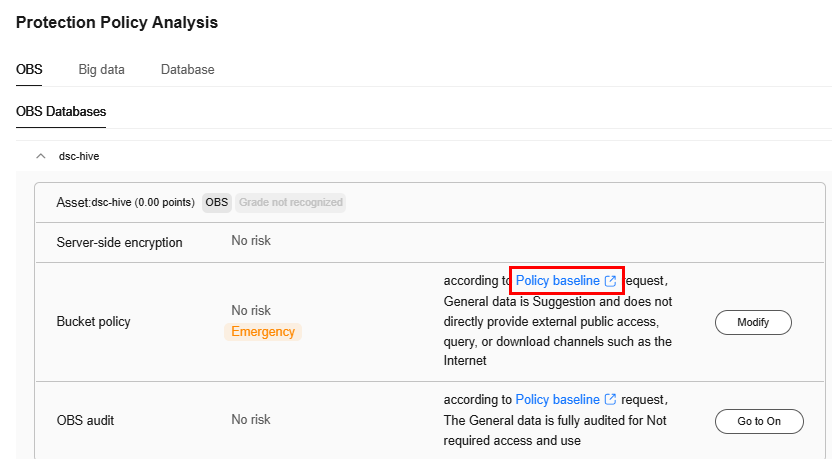
- Classification and grading: Classify and grade data, and implement corresponding security policies and assurance measures based on the data security level.
- Trace record: Trace and record the data collection process, including source, time, type, and quantity.
- Data source security authentication: Verify the security of data collection devices or systems using factors such as passwords, certificates, physical locations, and network access modes.
- Encryption: Encrypt the collected data.
- Integrity check: Verify data integrity during transmission.
- Availability assurance: Implement measures like device redundancy and line redundancy to ensure data transmission availability.
- Identity authentication and authorization: Perform identity authentication and authorization on both communication parties to ensure trustworthiness during transmission.
- Encryption: Use data encryption, secure transmission channels, or secure transmission protocols for data transmission.
- Approval and audit: Secure approval and authorization in advance, and retain data transfer logs for audit purposes.
- Classification and grading: Classify and grade the statically stored data, and implement corresponding security policies and assurance measures based on the data security level.
- Storage isolation: Store data of different levels separately, and use physical or logical isolation mechanisms to control data flow between regions.
- Integrity protection: Ensure data integrity using measures such as cryptographic technologies and integrity monitoring.
- Reliability assurance: Use active/standby and cluster modes to ensure high availability of stored data.
- Security management: Perform necessary security management on data storage devices and systems, including authentication mechanisms for operation terminals, system access control, and security baselines for system configurations.
- Backup and restoration: Establish a data backup and restoration mechanism and prepare a data DR emergency plan to detect and restore data promptly if lost or damaged.
- Encryption: Use data encryption and disk encryption to ensure storage confidentiality.
- Identity authentication and access control: Authenticate the identity of visitors and assign data access permissions to the identities or roles of the actual visitors to prevent unauthorized data access.
- Audit: Retain operation logs during data access for real-time or post-event audit.
- Review and secondary authorization: Establish an access permission application, review, and approval mechanism; verify actual operations and application operations; and establish multi-factor authentication or secondary authorization mechanisms.
- Masking: Implement technical measures such as masking and anonymization during data access, display, processing, development, and testing to prevent sensitive information leakage.
- Blocking: Use technical measures such as database firewalls to monitor and block malicious attacks, including SQL injection and vulnerability exploitation, in real-time.
- Public network protection: Prohibit external query and download channels, such as the Internet.
- Security audit: Record logs during data sharing to audit the security of shared data.
- Blocking: Establish an emergency response mechanism or technical means to cut off data sharing in a timely manner if necessary.
- Masking: Mask data containing sensitive fields.
- Encryption: If masking is not possible due to service requirements, encrypt the data, use secure and reliable transmission protocols, or share the data in a secure and controllable environment.
- Watermarking: Add watermarks to shared data and establish a watermark source tracing mechanism to determine responsibility in case of data leakage.
- Review and supervision: Establish a data sharing approval mechanism and adopt a pre-sharing approval policy. Obtain the approval of the data owner or authorized approver. Perform routine security supervision and review of shared data.
- Review and supervision: Establish a destruction approval and supervision process. Adopt a pre-destruction approval mechanism. Obtain the approval of the data owner or authorized approver. Supervise the destruction implementation process.
- Destruction evidence retention: Record data destruction operations so administrators can view, track, confirm, and collect evidence of the destruction.
- Physical destruction: Physically destroy storage media using methods such as degaussing, magnetic media destruction, crushing, and melting.
- Copy destruction: Destroy data on storage media that stores data copies to ensure the data cannot be restored.
Procedure
- Log in to the DSC console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project.
in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project. - In the navigation tree on the left, choose . The Policy Baseline page is displayed.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





