Overview
What Is Public DNS Resolution?
Public DNS resolution translates domain names (for example, www.example.com) and their subdomains into IP addresses like 1.2.3.4 for routing traffic over the Internet. Public DNS resolution is implemented by public DNS servers, including authoritative and non-authoritative DNS servers.
Authoritative DNS services are typically provided by either domain name registrars or cloud service providers. Authoritative DNS servers store various DNS records, including A, CNAME, and MX records, and provide accurate responses to DNS queries. DNS provides highly available and scalable authoritative DNS resolution services and domain name management services.
If you host domain names on the Huawei Cloud DNS service, authoritative DNS servers will be provided for public domain name resolution for your website and email server. Visitors can access your website, mailbox, or web application by entering your domain name in the address box of their browser.
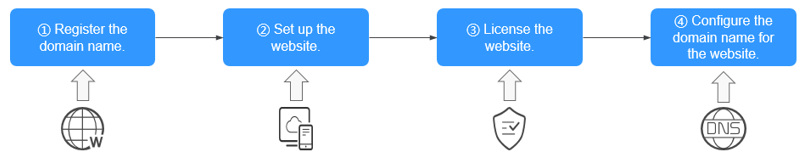
Public Zones
A domain name is registered and purchased through a domain name registrar, for example, Huawei Cloud. DNS service providers like Huawei Cloud Domain Name Service (DNS) are responsible for resolving domain names. You can use DNS to create a public zone for your domain name, which can work for access to portal websites, enterprise emails, and web applications.
Unlike private zones, public zones are designed for external users and prioritize higher security and robust management to handle internet-facing traffic. Private zones are used for internal network services and emphasize limited access scope.
The domain name resolution involves a hierarchical structure and often uses recursive queries.
The following uses example.com as an example to describe the structure and levels of a domain name.
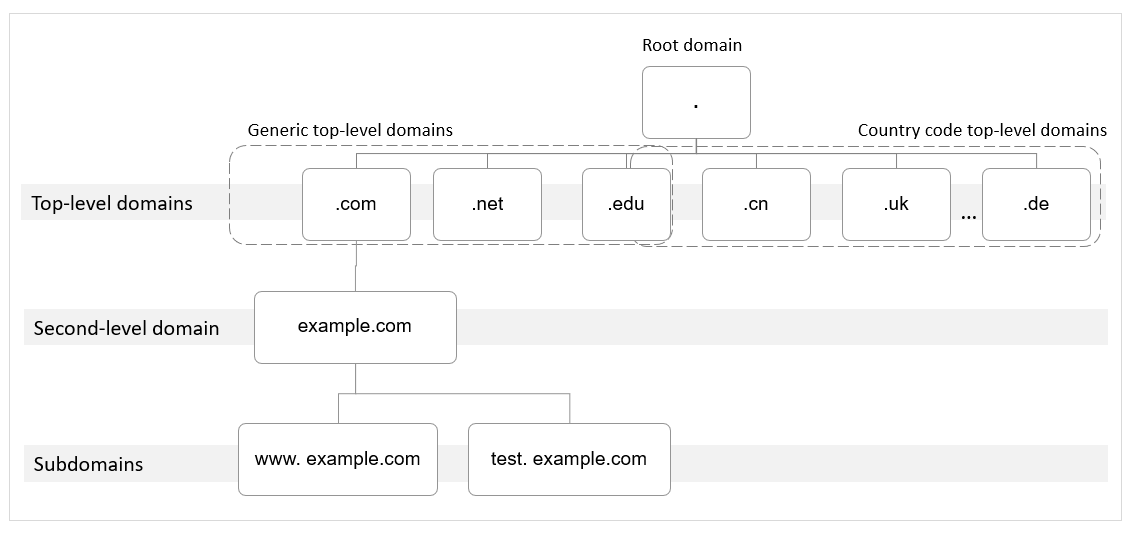
- Root domain
A period (.) is the designation for the root domain.
A fully qualified domain name (FQDN) ends with a period (example.com.). When you enter a domain name (example.com) in the browser, the DNS system will automatically add a period in the end.
Root domain names are resolved by root name servers that hold the addresses of top-level domain servers.
- Top-level domain
Below the root domain are top-level domains, which are categorized into two types:
- Generic top-level domain (gTLD), such as .com, .net, .org, and .top
- Country code top-level domain (ccTLD), such as .cn, .uk, and .de
Top-level domains are resolved by top-level domain servers that hold the addresses of second-level DNS servers. For example, the top-level domain server of .com saves the addresses of all DNS servers of second-level domains that end with .com.
- Second-level domain
Second-level domains (such as example.com) are subdomains of top-level domains and are resolved by second-level DNS servers, which provide authoritative domain name resolution services.
For example, if you purchase example.com from a domain name registrar and set a DNS server for the domain name, the DNS server will provide authoritative resolution for example.com, and its address will be recorded by all top-level domain servers.
If you host domain names on the Huawei Cloud DNS service, authoritative DNS servers will provide authoritative resolution services for your domain names.
- Subdomain
Second-level domains can be further divided into subdomains (such as www.example.com) to indicate specific servers or services.
Resolution Process
The figure below shows the process for accessing a website using the domain name www.example.com.
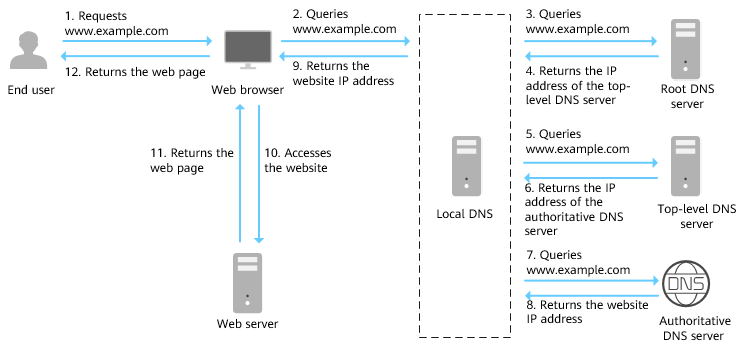
- An end user enters www.example.com in the address box of a browser.
- The query for www.example.com is routed to the local DNS server.
Local DNS servers are usually provided by the Internet service provider to cache domain name information and perform recursive lookup.
- If the local DNS server does not find any records in the cache, it routes the request for www.example.com to the root name server.
- The root name server returns the address of the top-level domain server of .com to the local DNS server.
- The local DNS server sends the request to the top-level domain server of .com.
- The top-level domain server of .com returns the address of the authoritative DNS server which provides authoritative records for example.com.
- The local DNS server sends the request to the authoritative DNS server of example.com.
If you have hosted www.example.com on the DNS service and configured Huawei Cloud DNS name servers, these name servers will provide authoritative DNS for the domain name.
- The authoritative DNS server returns the IP address mapped to www.example.com to the local DNS server.
- The local DNS server returns the IP address to the web browser.
- The web browser accesses the web server with the IP address.
- The web server returns the web page to the browser.
- The end user views the web page using the browser.
Related Operations
|
Category |
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Public zones |
Create a zone for your domain name. |
|
|
Create a subdomain. |
||
|
Create public zones for domain names registered with a third-party domain name registrar on the DNS console. Constraints:
|
||
|
View and change the DNS servers of the public domain name. |
||
|
Reclaim your own zone that has been created by another Huawei Cloud account. |
||
|
Modify, transfer, delete, batch delete, disable, enable, view, and batch export public zones. Constraints:
|
||
|
Transfer record sets configured on Huawei Cloud DNS from one account to another account. |
||
|
DNS rules |
Learn about types, scenarios, and configuration rules of record sets supported by public zones. |
|
|
Learn about rules of record set conflicts of public zones and how to handle the conflicts. |
||
|
Record sets |
Configure record sets for public zones. |
|
|
Modify a record set, delete a record set, batch delete record sets in a single zone, and view record set details. |
||
|
Add, modify, and delete record sets in batches. |
||
|
Check the record sets of website or email domains quickly and rectify the fault following the suggestions. |
||
|
Disable or enable record sets for a domain name. SOA and NS record sets are automatically generated and cannot be disabled. |
||
|
Map all subdomains of a domain name to the same value. SOA and NS record sets are automatically generated and cannot be disabled. |
||
|
Associate the record set of a domain name with a Huawei Cloud resource.
|
||
|
Use DNSSEC to ensure the integrity and authenticity of DNS queries and responses, thereby defending against attacks such as DNS spoofing and cache pollution. |
||
|
Intelligent resolution management |
Configure ISP lines when you create record sets. |
|
|
Configure region lines when you create record sets. |
||
|
Configure custom lines based on specific IP address ranges. |
||
|
Set weights for different record sets for load balancing, failover, and leveraging geographical location benefits.
|
||
|
Public zone configuration examples |
Configure a public zone for a website. |
|
|
Configure a public zone for an email domain. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





