Creating an HBase Cluster
You can centrally manage clusters with CloudTable. A cluster is necessary for using CloudTable. This section describes how to create a cluster on the CloudTable console.
HBase clusters support two billing modes: pay-per-use and yearly/monthly. By default, the cluster creation page is set to the pay-per-use mode, which provides flexibility by allowing you to enable or disable clusters as needed and pay only for the actual usage time. Alternatively, you can opt for the yearly/monthly billing mode, which is a prepaid option offering significant discounts compared to the pay-per-use mode. This option is particularly suitable for long-term users. You can also customize a CloudTable HBase cluster with specified computing capabilities and storage space to meet your business needs.
Created HBase clusters can be accessed without passing Kerberos authentication. If you have requirements on cluster access security, you are advised to use the HBase component on MRS.
Prerequisites
- The VPC and security group of the cluster to be created must be the same as those of the ECS on the public network. Otherwise, the client cannot access the cluster.
- Before creating a cluster, you must configure inbound security group rules for the host. For details, see Configuring Security Group Rules. For details about the security group port, see HBase Security Group Rules.
- Before creating a cluster, you must add the ICMP protocol to the security group rules so that you can view the status of each node by pinging the node IP address on the management plane. For details, see Configuring Security Group Rules.
Creating a Cluster
- Log in to the CloudTable console.
- Select a region in the upper left corner.
- Click Create Cluster. The Create Cluster page is displayed.
- Configure basic cluster information by referring to the following table.
Table 1 Region parameters Parameter
Description
Region
Region of the cluster.
For more information about regions, see Regions and Endpoints.
AZ
AZ associated with the cluster's region.
For more information, see Regions and AZs.
Billing Mode
Select Pay-per-use or Yearly/Monthly.
Required Duration
This option is available only when Billing Mode is set to Yearly/Monthly. Configure this parameter based on your service requirements.
Auto-renew
If you select Auto-renew when creating a cluster, the system will automatically renew your subscription before it expires.
Table 2 Network configuration parameters Parameter
Description
Name
Name of a cluster.
The cluster name must consist of 4 to 32 characters and must begin with a letter. It may include only letters, digits, and hyphens (-) but must not contain any other special characters. Additionally, the cluster name is case-insensitive.
VPC
A VPC is a secure, isolated, and logical network environment.
You can select an existing VPC or click View VPC to create a new one.
For details about how to create a VPC, see in Virtual Private Cloud.
Subnet
A subnet provides dedicated network resources that are logically isolated from other networks, improving network security.
A subnet is automatically created when a VPC is created. If you want to create a subnet, you can refer to in Virtual Private Cloud.
Security Group
A security group is used to control ECS access within a security group or between security groups by defining access rules. You can define different access control rules for a security group. These rules can specify which ECS ports or protocols are accessible and can be used to control inbound and outbound network traffic of VMs. After an ECS is added to the security group, it is protected by these access control rules. ECSs that do not belong to the security group cannot communicate with ECSs in the security group.
The underlying compute unit of a CloudTable cluster is ECS. In terms of security and stable service running, the ECSs must be added to the same security group in the same VPC. VPCs isolate networks and security groups specify which ports and protocols can be opened in the VPC.
You can use an existing security group or click View Security Group to create a new one.
For more information about security groups, see Security Group in the Virtual Private Cloud User Guide.
Database Engine
Select the type of cluster to be created.
Figure 1 Master/Core nodes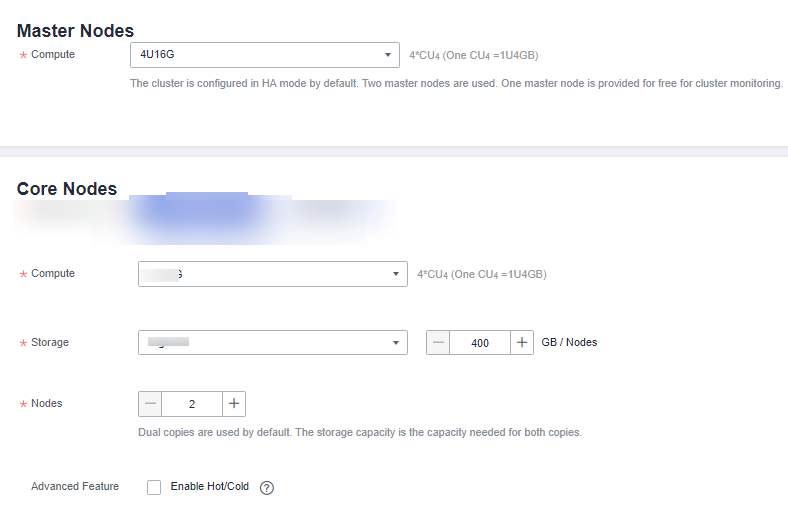
Table 3 Master node configuration Parameter
Description
Compute
Select proper compute specifications based on service requirements. Each specification displays the CPU, memory, and recommended application scenarios of a single node.
NOTE:- Available compute specifications:
- 4U16G
- 8U16G
- 8U32G
- 16U32G
- 16U64G
- 32U64G
Storage
Ultra-high I/O is recommended.
Nodes
Use the default value 2.
Table 4 Core node configuration Parameter
Description
Compute
Select proper compute specifications based on service requirements. Each specification displays the CPU, memory, and recommended application scenarios of a single node.
NOTE:- Available compute specifications:
- 4U16G
- 8U16G
- 8U32G
- 16U32G
- 16U64G
- 32U64G
- 32U128G
- 64U128G
Storage
Select the disk specifications and capacity of the HBase compute node.
NOTE:- Available storage specifications:
- Common I/O
- High I/O
- Ultra-high I/O
- The capacity ranges from 400 GB to 30,000 GB per node.
Nodes
Set the number of nodes in a cluster. The value ranges from 2 to 20.
Advanced Feature
Cold and hot data separation: It classifies data based on access frequency and stores data on different media to save storage costs. This feature is available only in HBase 2.4.14 and later versions. You can toggle it on to enable this feature.
Enable Security Channel
This is enabled by default. Enabling security channel may cause performance deterioration in a cluster.
Enable Thrift Server
This is disabled by default. You can enable this to ensure that HBase supports multi-language access.
Enterprise Project
You can group related cloud resources (for example, resources used for the same purpose) and manage them by enterprise project.
NOTE:- You can delete a user that was authorized to manage an enterprise project if the enterprise's business has changed and the user should not have the permissions to manage the enterprise project.
- You can delete a user or multiple users.
- After a user that was authorized to manage an enterprise project is deleted, the user cannot manage the enterprise project. If the user needs to manage the enterprise project, authorize the user to manage the enterprise project again.
- Available compute specifications:
- Click Next.
- Confirm the details of the order and click Submit. The cluster creation task is submitted successfully.
- Click Back to Cluster List to view the cluster status.
The cluster creation task takes some time. The initial status of the cluster is Creating. After the cluster is created, the cluster status changes to In service.
- Submit the creation task of a yearly/monthly cluster.
Click Pay. On the displayed purchase page, confirm the information, select a proper payment method, and confirm the payment.
Return to the console and check the cluster status. Cluster creation takes some time. The initial status of the cluster is Creating. After the cluster is created, the cluster status changes to In service.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





