Network Types (Dedicated Load Balancers)
Description
Load balancers work on both public and private networks.
Dedicated load balancers support three network types as described in Table 1.
|
Network Type |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Public IPv4 network |
Each load balancer has an IPv4 EIP bound to route requests from the Internet to backend servers. |
|
|
Private IPv4 network |
Each load balancer has only a private IPv4 address and routes requests from the same VPC to backend servers. |
|
|
IPv6 network |
Each load balancer has an IPv6 address bound.
NOTE:
|
|
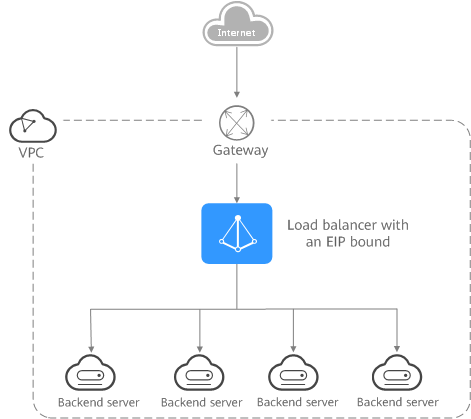
Load Balancing on a Public Network
You can bind an EIP to a load balancer so that it can receive requests from the Internet and route the requests to backend servers.
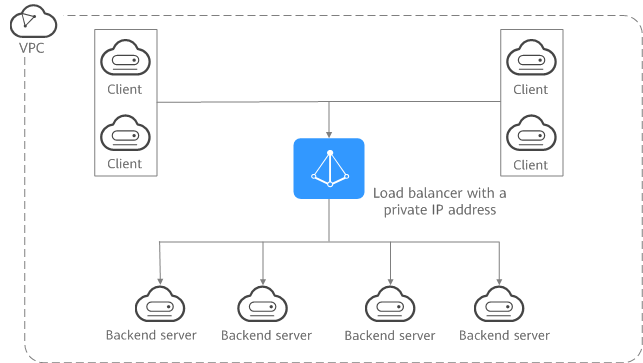
Load Balancing on a Private Network
A load balancer has only a private IP address to receive requests from clients in a VPC and routes the requests to backend servers in the same VPC. This type of load balancers can only be accessed in a VPC.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





