How Many Domain Name Levels Does DNS Support?
When you create a public zone, a maximum of 16 levels of domain names (including top-level domains) are supported.
Take example as an example.
- DNS supports the following levels for domain names with the .com suffix:
- Primary domain name: example.com, which is considered as a level-2 domain name (including the top-level domain).
- Subdomain: A maximum of 14 prefixes can be added before the primary domain name, for example, 1.example.com, 1.2.example.com, 1.2.3.example.com,...,1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.example.com.
- DNS supports the following levels for domain names with the .com.cn suffix:
- Primary domain name: example.com.cn, which is considered as a level-2 domain name (including the top-level domain).
- Subdomain: A maximum of 14 prefixes can be added before the primary domain name, for example, 1.example.com.cn, 1.2.example.com.cn, 1.2.3.example.com.cn,...,1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.example.com.cn.
Domain Name Hierarchy
The domain name resolution involves a hierarchical structure and often uses recursive queries.
The following uses example.com as an example to describe the structure and levels of a domain name.
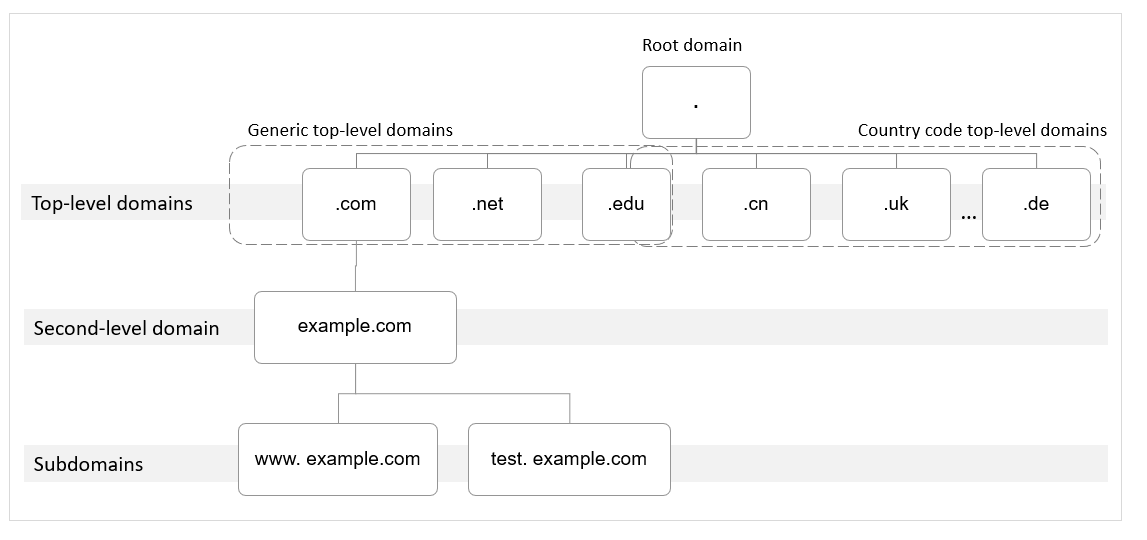
- Root domain
A period (.) is the designation for the root domain.
A fully qualified domain name (FQDN) ends with a period (example.com.). When you enter a domain name (example.com) in the browser, the DNS system will automatically add a period in the end.
Root domain names are resolved by root name servers that hold the addresses of top-level domain servers.
- Top-level domain
Below the root domain are top-level domains, which are categorized into two types:
- Generic top-level domain (gTLD), such as .com, .net, .org, and .top
- Country code top-level domain (ccTLD), such as .cn, .uk, and .de
Top-level domains are resolved by top-level domain servers that hold the addresses of second-level DNS servers. For example, the top-level domain server of .com saves the addresses of all DNS servers of second-level domains that end with .com.
- Second-level domain
Second-level domains (such as example.com) are subdomains of top-level domains and are resolved by second-level DNS servers, which provide authoritative domain name resolution services.
For example, if you purchase example.com from a domain name registrar and set a DNS server for the domain name, the DNS server will provide authoritative resolution for example.com, and its address will be recorded by all top-level domain servers.
If you host domain names on the Huawei Cloud DNS service, authoritative DNS servers will provide authoritative resolution services for your domain names.
- Subdomain
Second-level domains can be further divided into subdomains (such as www.example.com) to indicate specific servers or services.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





