Codec for Containing Command Execution Results
Scenarios
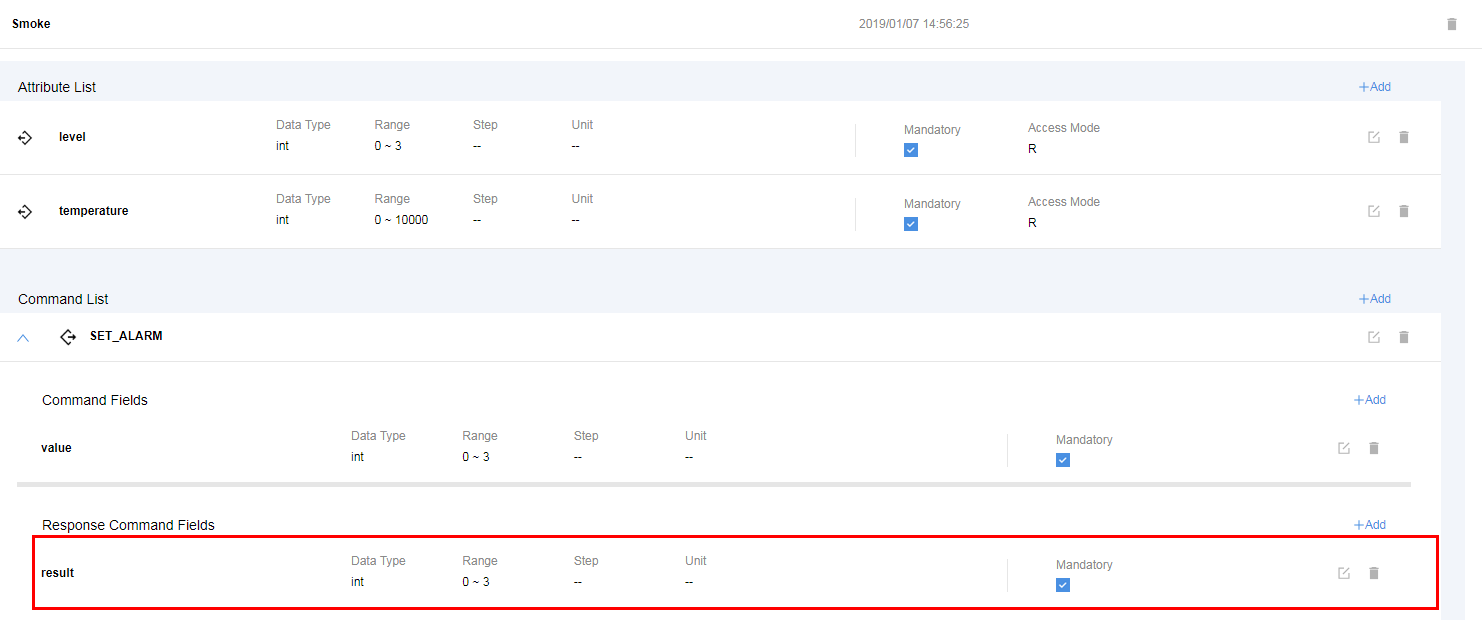
A smoke detector provides the following functions:
- Reporting smoke alarms (fire severity) and temperature
- Remote command, which can enable the alarm function remotely
For example, the smoke detector can report the temperature on the fire scene and remotely trigger the smoke alarm for evacuation.
- Reporting command execution results
Defining the Profile File
Define the profile file in the development space of the smoke sensor.
Developing a Codec
- In the development space of the smoke sensor, click Codec Development.

- Configure a data reporting message to report the fire severity and temperature.
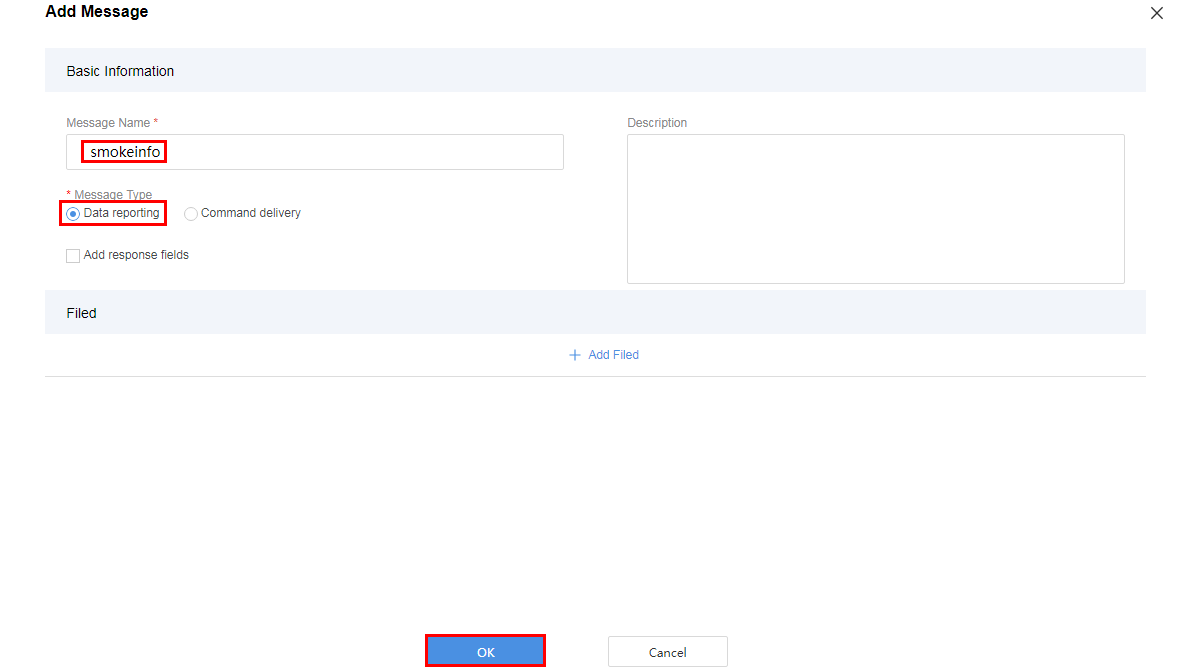
Add the messageId field to indicate the message type.
- In this scenario, there are two types of data reporting messages. Therefore, the messageId field must be defined to identify the message type.
- Data Type is configured based on the number of data reporting message types. In this scenario, only two types of data reporting messages are available. Therefore, the value int8u will suffice.
- Default Value can be changed but must be in hexadecimal format. In addition, the corresponding field in data reporting messages must be the same as the default value. In this scenario, the value 0x0 is used to identify the message that reports the fire severity and temperature.
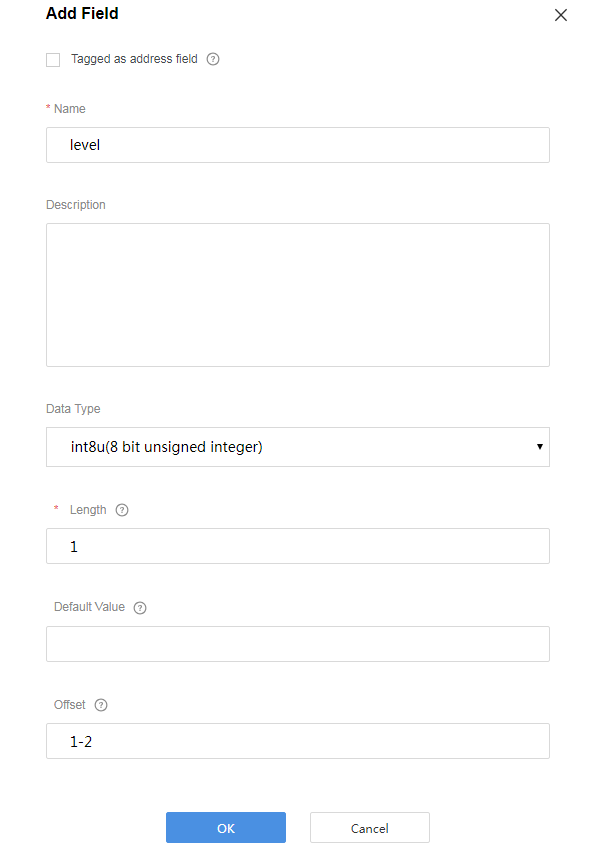
 Add a level field to indicate the fire severity.
Add a level field to indicate the fire severity.- Name can contain only letters, digits, underscores (_), and dollar signs ($) and cannot start with a digit.
- Data Type is configured based on the data reported by the device and must match the type defined in the profile file.
- The values of Length and Offset are automatically filled based on Data Type.
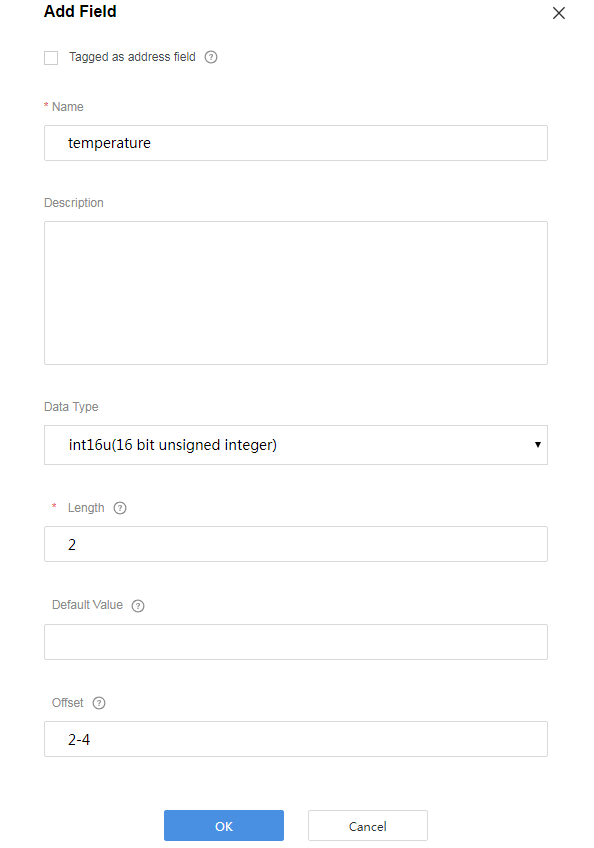
Add the temperature field to indicate the temperature at the fire scene. In the profile file, the maximum value of temperature is 1000. Therefore, set the data type of the temperature field to int16u in the codec to meet the value range requirement of temperature.
- Configure a command delivery message.
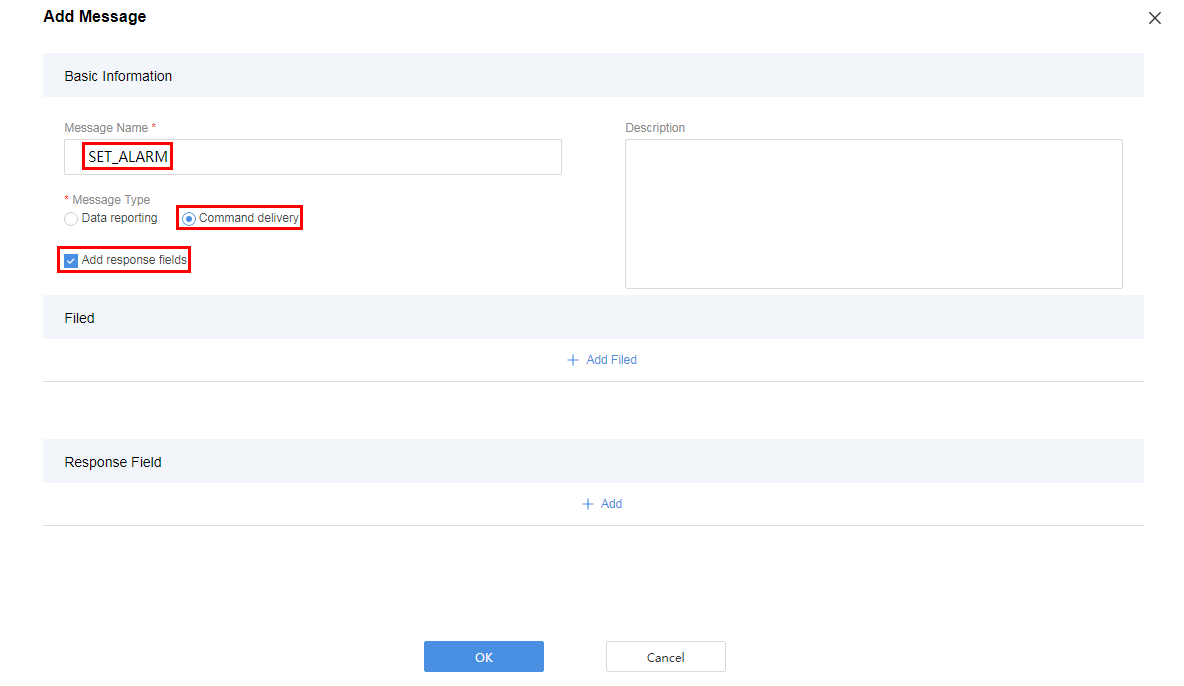
Add the messageId field to indicate the message type. If there is only one type of command delivery message, this parameter does not need to be set.
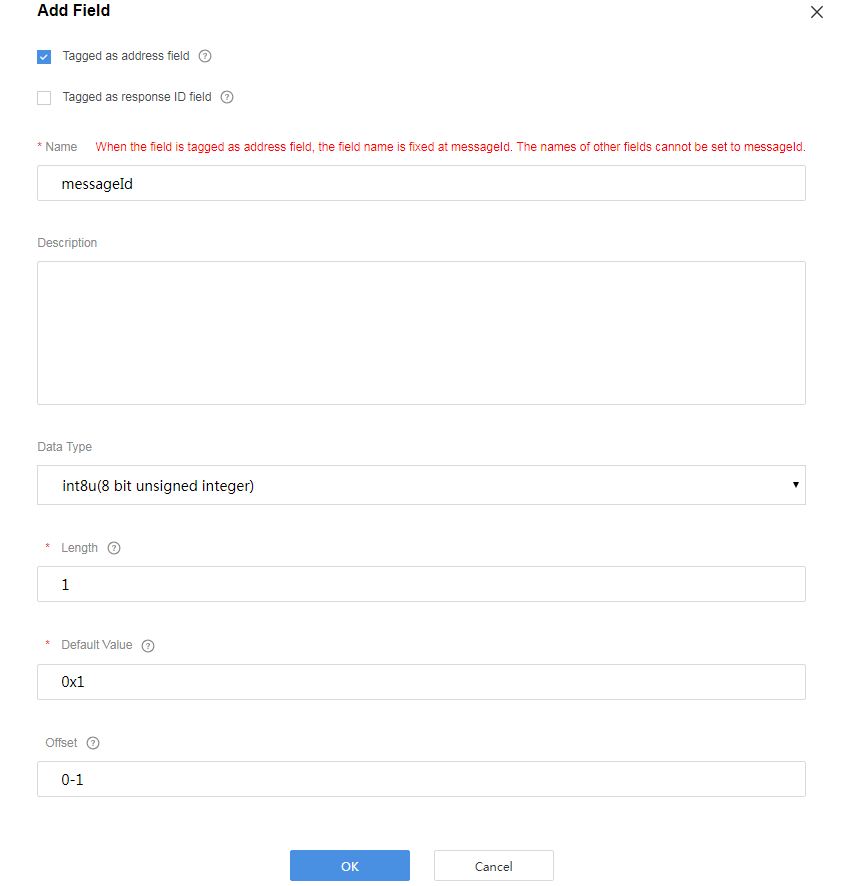
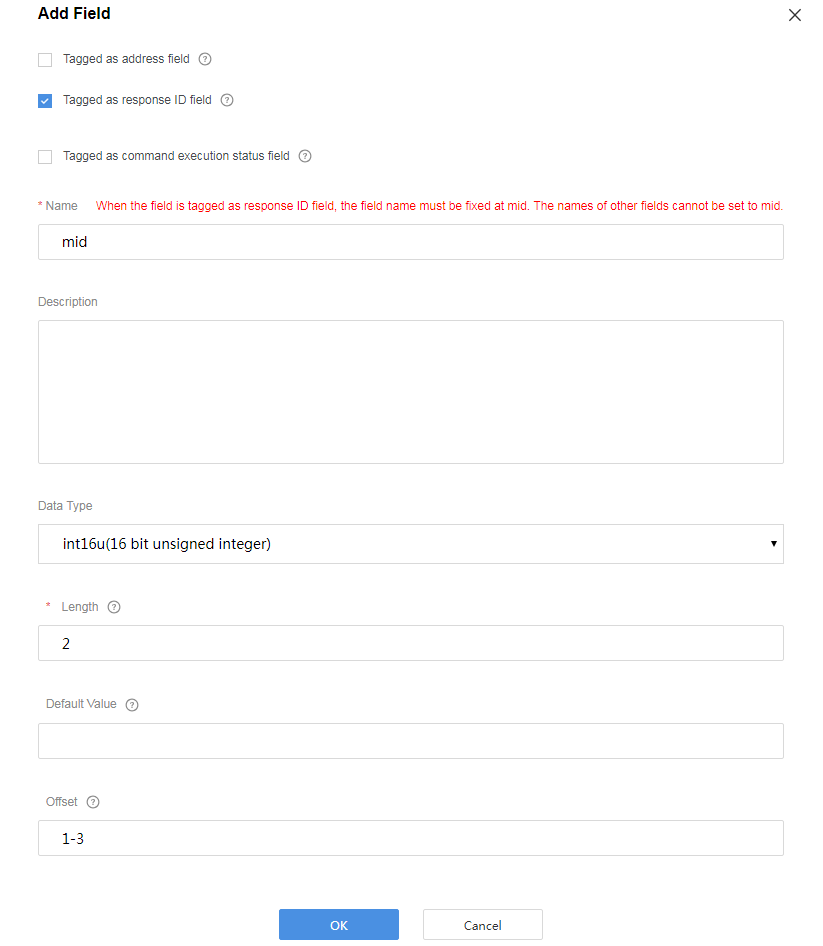
Add the mid field to associate the delivered command with the command execution result.
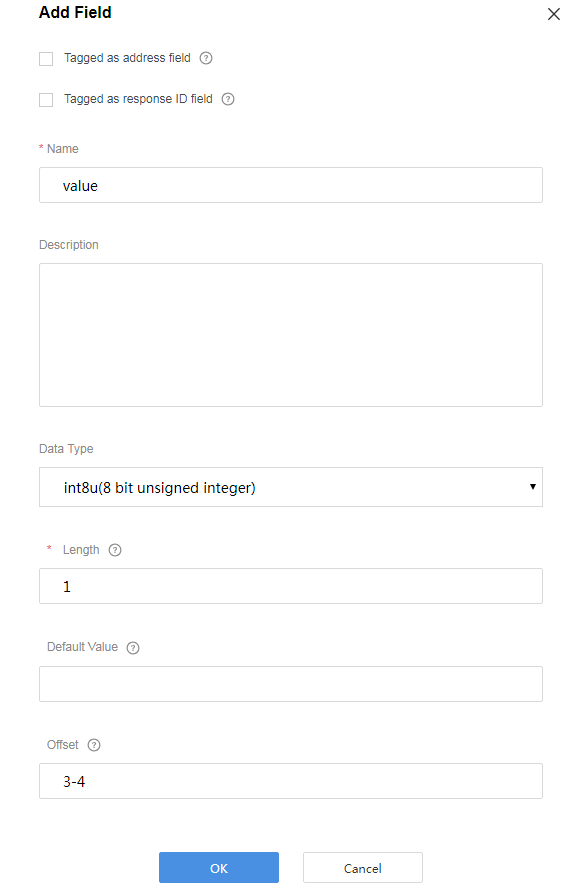
Add the value field to indicate the parameter value of the delivered command.
- Configure a command response.
Add the messageId field to indicate the message type. The command execution result is an upstream message, which is differentiated from the data reporting message by the messageId field.
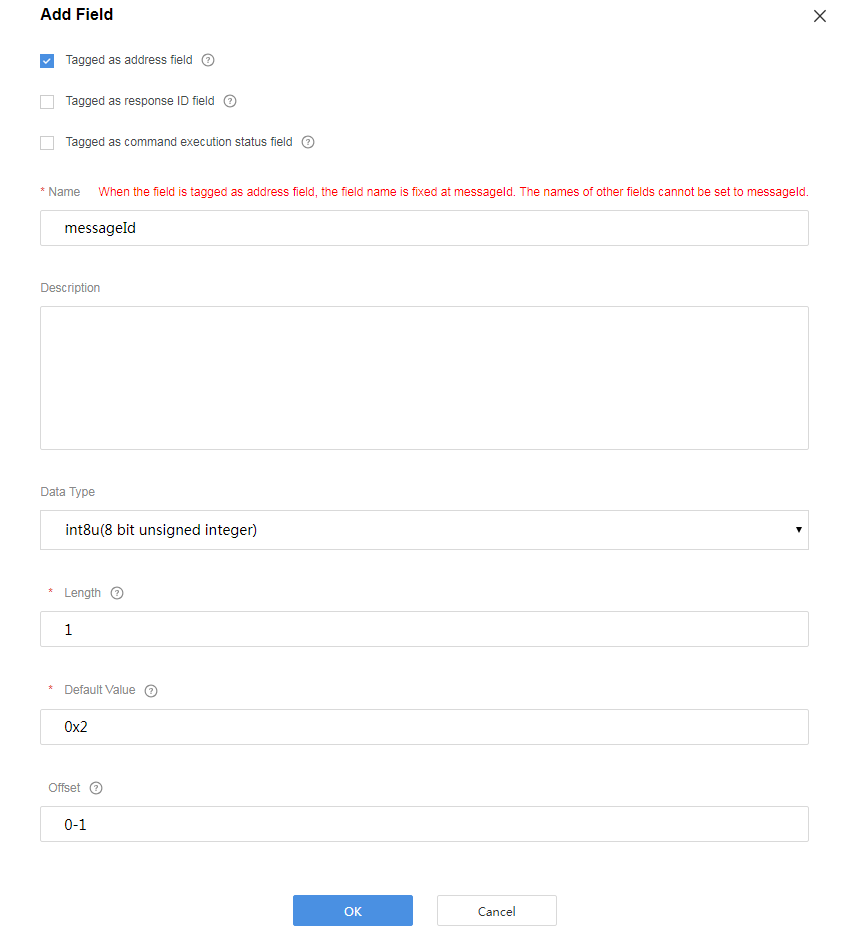
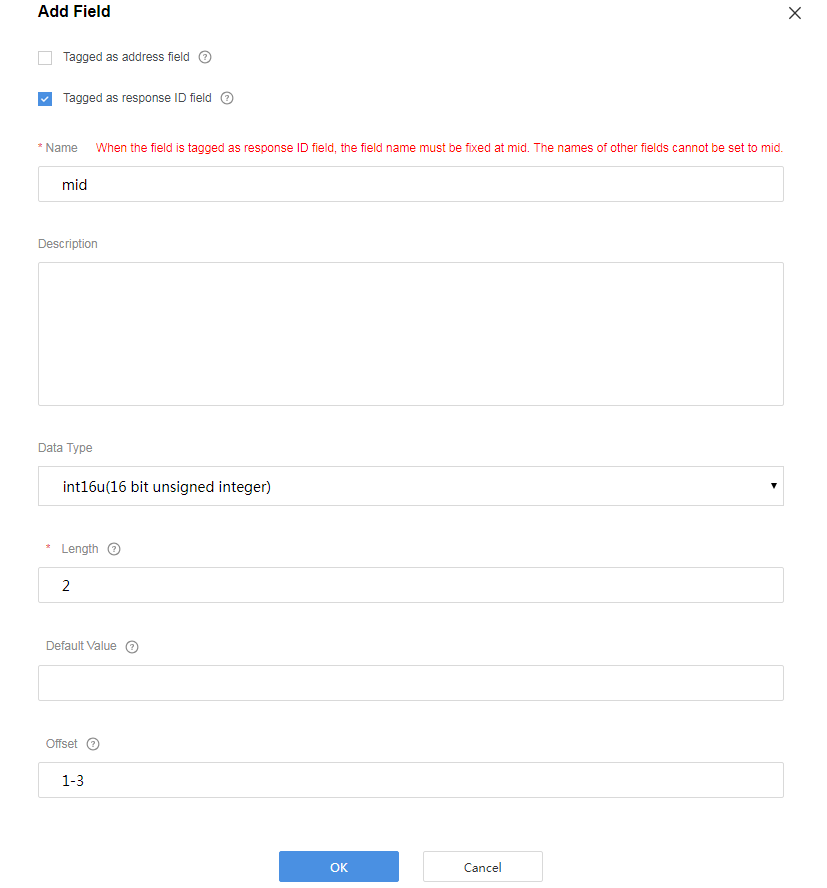
Add the mid field to associate the delivered command with the command execution result.
Add the errcode field to indicate the command execution status. 00 indicates success and 01 indicates failure. If this field is not carried, the command is executed successfully by default.

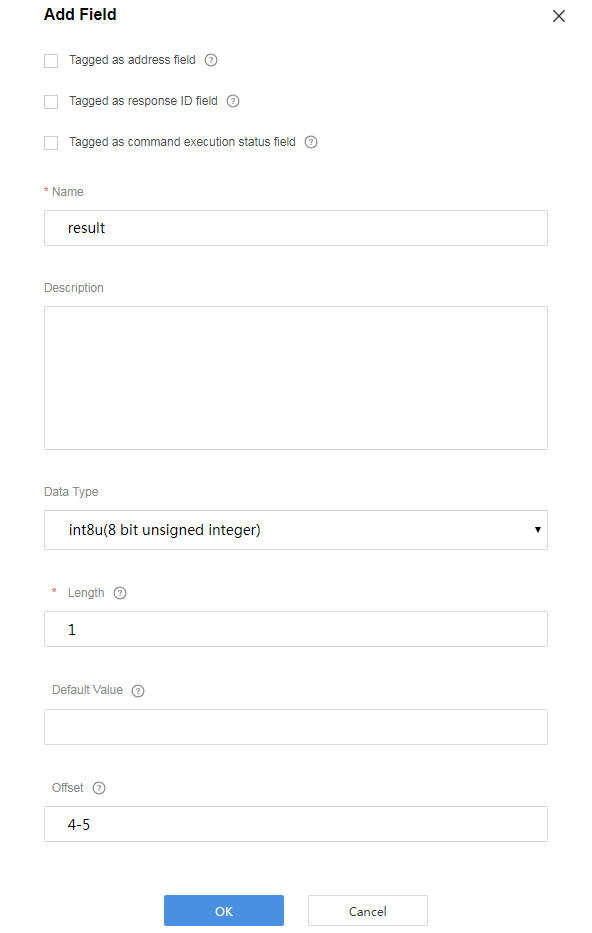
Add the result field to indicate the command execution result.
- Drag the property fields and command fields in Device Model on the right to set up a mapping with the fields in the data reporting message and command delivery message.
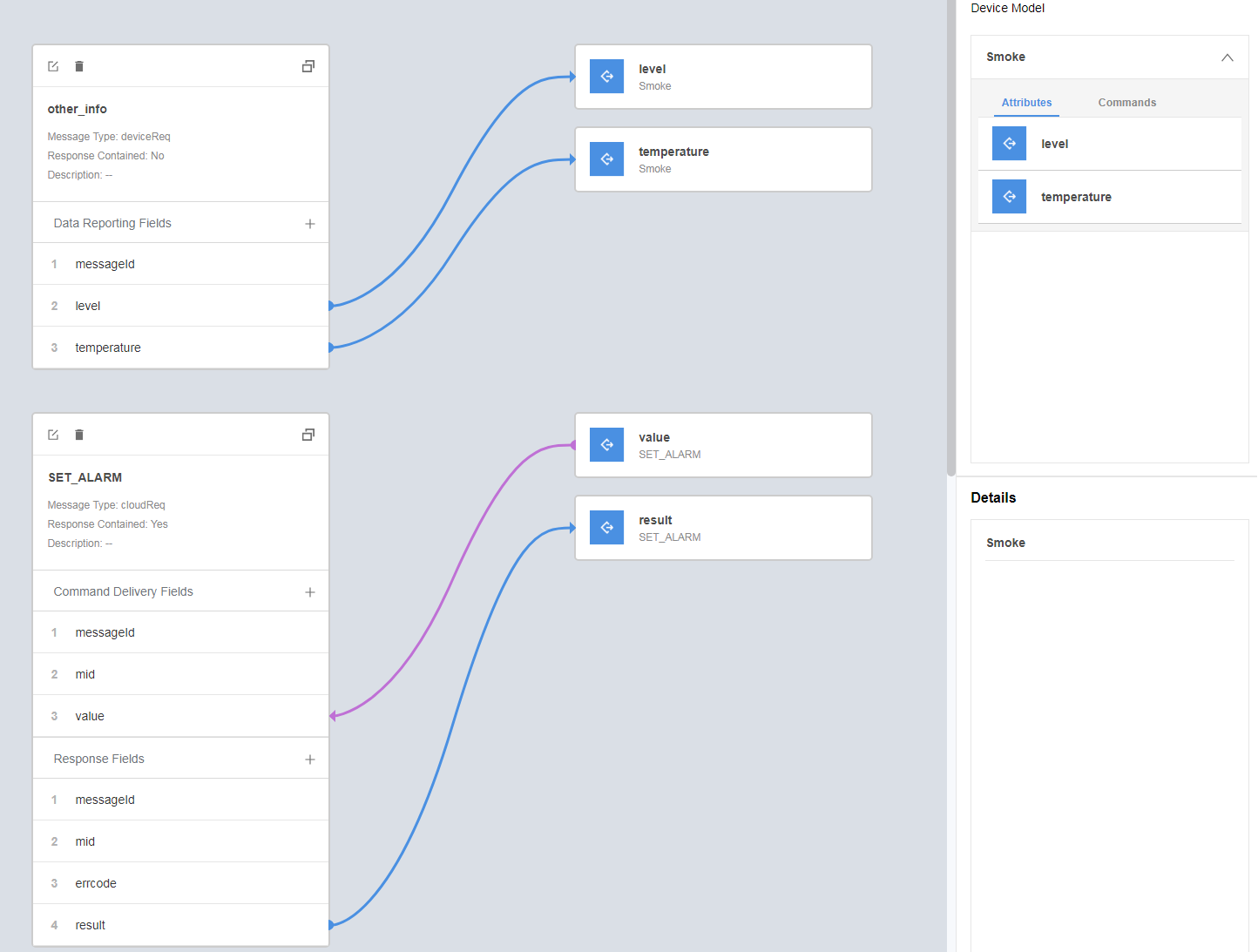
- Click Save and then Deploy to deploy the codec on the IoT platform.

Testing the Codec
- In the development space of the smoke sensor, click Online Testing and add a virtual device to test the codec.
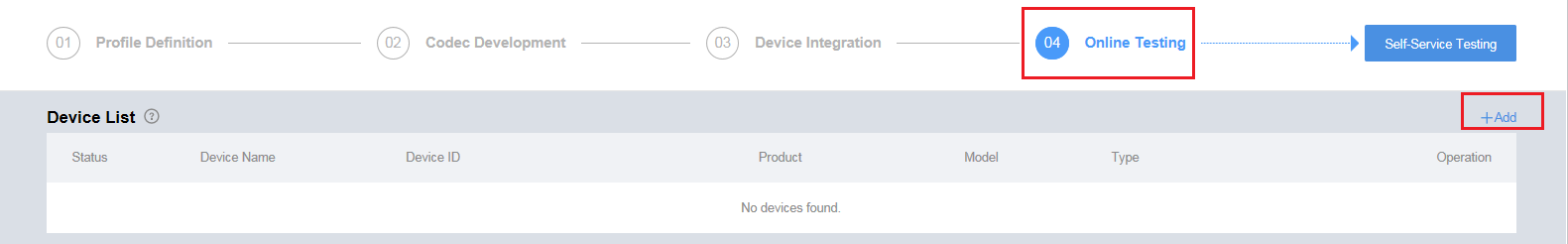
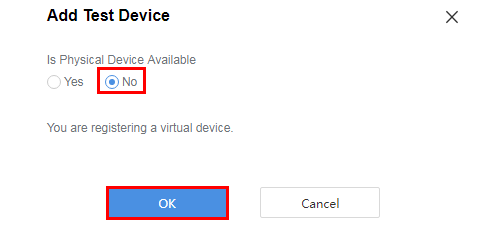
Select No for Is Physical Device Available and click OK.
- Use the application simulator to deliver a command ({ "serviceId": "Smoke", "method": "SET_ALARM", "paras": "{\"value\":0}" }).
View the command receiving result in Device Simulator, which is 01000100. 01 indicates the messageId field, 0001 indicates the mid field, and 00 indicates the value field.
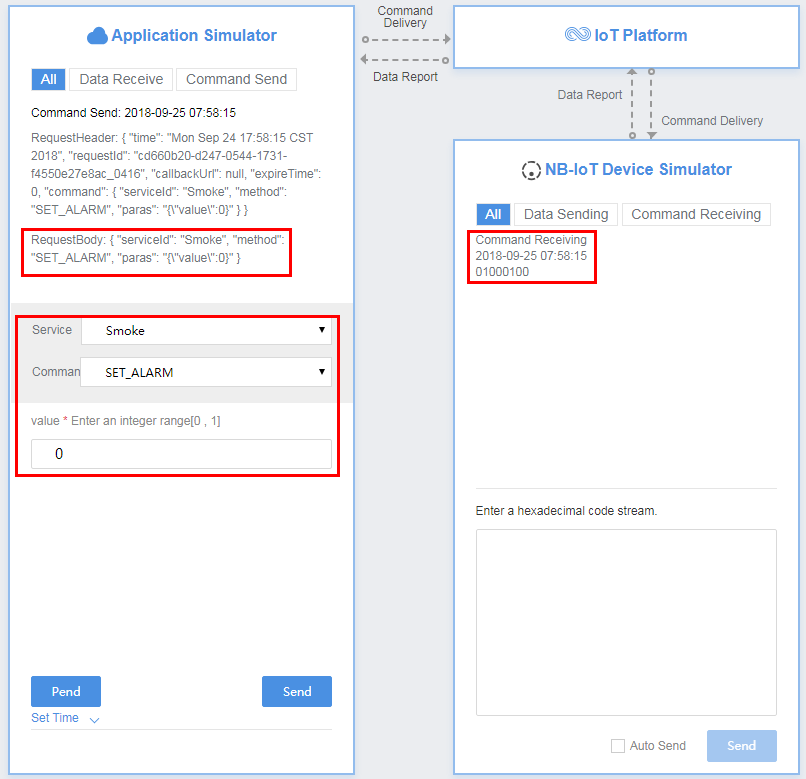
- Use the device simulator to report data.
For example, a hexadecimal code stream (0200010000) is reported. In this code stream, 02 indicates the messageId field and specifies that this message reports the command execution result. 0001 indicates the mid field and its length is two bytes. 00 indicates the command execution status and its length is one byte. The second 00 indicates the command execution result and its length is one byte.
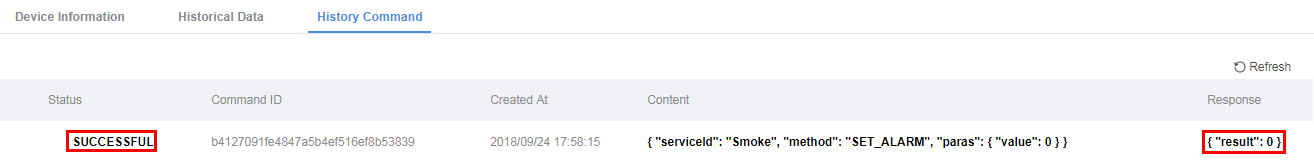
Choose Device Management and select the device that reports the command execution result. On the page displayed, click the Historical Commands tab to view the command execution status. In this case, the status is SUCCESSFUL.
Summary
- If the codec needs to parse the command execution result, the mid field must be defined in the command and the command response.
- The length of the mid field in a command is two bytes. For each device, mid increases from 1 to 65535, and the corresponding code stream ranges from 0001 to FFFF.
- After a command is executed, the mid field in the reported command execution result must be the same as that in the delivered command. In this way, the IoT platform can update the command status.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





