Usage Introduction
Function Description
APIC is the API integration component of ROMA Connect. It encapsulates APIs, data sources, and custom functions into RESTful APIs, and then exposes them to external systems. ROMA Connect has the following advantages for service integration:
- Convenient API lifecycle management
ROMA Connect provides full-lifecycle management for APIs, including creating, debugging, publishing, taking offline, authorizing, editing, and deleting APIs.
- Custom API backend services
ROMA Connect provides two types of backends:
- Data backends: Data sources are exposed as APIs. For details about the supported data source types, see Data Sources Supported by APIC.
- Function backends: Function capabilities are exposed as APIs.
- Visualized API monitoring portal
ROMA Connect provides a visualized dashboard for API calling and analysis to help you monitor the performance metrics related to API calling and identify potential risks that may affect services.
- Multi-layer security protection
ROMA Connect provides multiple authentication modes, refined request throttling, and strict access control to ensure secure API calling.
Process Flow
The following figure shows the process of using ROMA Connect for service integration.
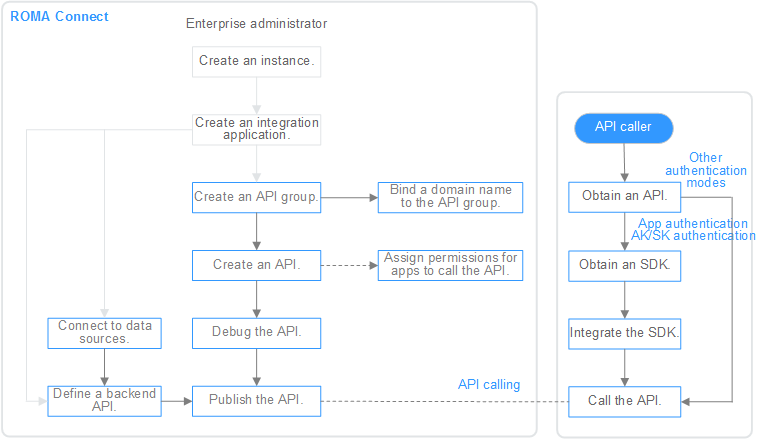
- You have created an instance and integration application.
- Expose an API.
- Exposing APIs
- Create an API group.
Each API belongs to an API group. Before creating an API, create an API group.
- Bind a domain name to the API group.
Before exposing an API, you need to bind an independent domain name to the API group so that users can access the API.
Before binding an independent domain name to an API, you can use the default subdomain name allocated by the system to test API calling. ROMA Connect limits the number of times that the default subdomain name can be accessed. A maximum of 1000 times can be accessed every day.
- Create an API.
Encapsulate existing backend services into RESTful APIs and expose them to external systems.
- Debug the API.
Verify that the API service functions are normal using the debugging function provided by ROMA Connect.
- Publish the API.
Publish an API in an environment. The API can be called only after being published in the environment.
- (Optional) Grant permissions for APIs.
This operation is required only for APIs that use the APP authentication mode. After an API is authorized to a specified integration application, users can use the key and secret of the integration application to perform security authentication on API requests.
- Create an API group.
- Creating and exposing a data API
- Connect to data sources.
Connect to a data source to ensure that data can be read from the data source.
- Create a data API.
Define data sources as APIs and expose them to external systems through ROMA Connect.
- (Optional) Grant permissions for APIs.
This operation is required only for APIs that use the APP authentication mode. After an API is authorized to a specified integration application, users can use the key and secret of the integration application to perform security authentication on API requests.
- Connect to data sources.
- Creating and exposing a function API
- Create a function API.
Define custom functions as APIs and expose them to external systems.
- (Optional) Grant permissions for APIs.
This operation is required only for APIs that use the APP authentication mode. After an API is authorized to a specified integration application, users can use the key and secret of the integration application to perform security authentication on API requests.
- Create a function API.
- Exposing APIs
- Call the API.
Obtain the API and its access address to call the API. API calling requires different authentication operations based on the authentication mode used by the API.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





