Exchanges
Direct, fanout, topic, and headers exchanges are available.
Direct Exchange
How It Works
- A queue is bound to a direct exchange with a routing key.
- The direct exchange routes a received message to the bound queue whose routing key is matched.
Routing
Based on a routing key matching
Scenario
Unicast routing
Example

As shown in this chart, Message A will be sent to Queue 1 and Queue 2. Message B will be sent to Queue 3.
Fanout Exchange
How It Works
A fanout exchange bound with multiple queues routes received messages to each queue. Fanout exchanges forward messages faster than other exchanges.
Routing
The fanout exchange delivers messages to all bound queues.
Scenario
Broadcast routing
Example

As shown in this chart, Message A will be sent to Queue 1 and Queue 2.
Topic Exchange
How It Works
- A queue is bound to a topic exchange with a routing key that includes a wildcard.
- The topic exchange routes a received message to the queue if the message's routing key wildcard is matched.
Supported wildcards are stars (*) and hashes (#). Separate wildcards and words by periods (.), for example, test.#.
- * matches one word.
- # matches zero or more words.
Routing
Based on a routing key wildcard matching
Scenario
Multicast routing
Example

As shown in this chart, Message A will be sent to Queue 1 and Queue 2, Message B to Queue 1, Queue 2, and Queue 3, and Message C to Queue 3.
Headers Exchange
How It Works
- A queue is bound to a headers exchange with a binding expressed in a key-value pair.
- The headers exchange routes a message to the queue if the binding matches the message's key-value header.
The matching algorithm uses a specific binding key-value pair, which is x-match. Values:
- all: Messages are routed only when all header pairs match.
- any: Messages are routed when any header pair matches.
Routing
Based on matching between key-value pairs in the message headers and the binding (a key-value pair)
Example
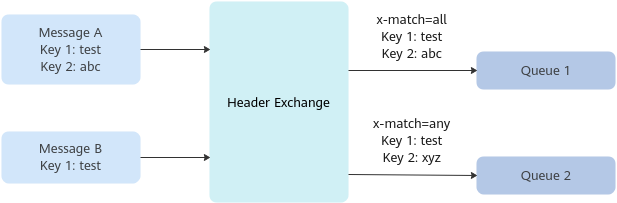
As shown in this chart, Message A will be sent to Queue 1 and Queue 2, and Message B to Queue 2.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





