What Can I Do When Transaction Connections Fail or Time Out?
Symptom
Transaction connections fail or time out.
Fault Locating
Check item 2: Check whether the instance status is abnormal.
Check item 3: Check whether the Fabric SDK version used by the client matches the BCS instance version.
Check item 4: Check whether the ledger of the peer is updated.
Check item 5: Check whether the DB file exists.
Check item 6: If a BCS instance uses CouchDB of an earlier version for ledger storage, check whether BCS becomes unavailable after CouchDB restarts.
Check item 7: Check whether data can be stored to blockchain even though the request initiated from a blockchain client has timed out.
Solution
- Check item 2: Check whether the instance is abnormal.
Log in to the BCS console and rectify the fault based on the instance status by following instructions provided in What Can I Do If a BCS Instance Is in the Abnormal State?
- Check item 3: Check whether the Fabric SDK version used by the client matches the BCS instance version.
Log in to the BCS console, go to the Instance Management page, and click the abnormal instance to view its version.
Record the value of Version. Check whether the Fabric SDK version used by the client is the same as the BCS version. If the versions are inconsistent, transactions may fail or time out.
Solution
Download the Fabric SDK of the version that corresponds to the Hyperledger Fabric version of BCS.
Download link: https://github.com/hyperledger/fabric
- Check item 4: Check whether the ledger of the peer is updated.
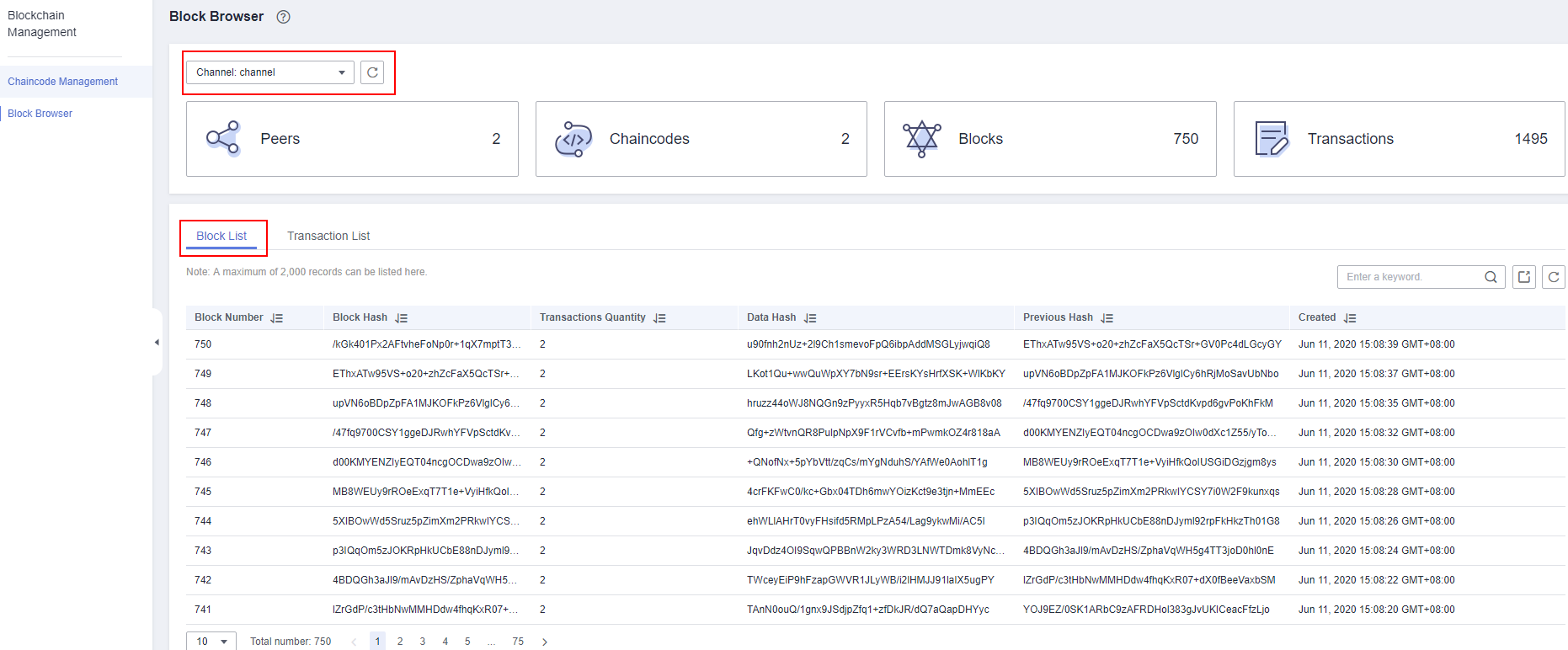
- Log in to the BCS console. In the navigation pane, click Instance Management. On the card containing the abnormal instance, click Manage Blockchain. On the Block Browser page, select the abnormal channel, and view the block quantity on the Block List tab page.
Figure 1 Block List page
- Log in to the ECS where the blockchain is deployed, run the docker ps|grep k8s_peer command to check the peer containers, and record the ID of the container where transactions time out.
Figure 2 Checking the peer containers

- Run the docker exec -it Container ID /bin/bash command to access the container.
Figure 3 Accessing the container

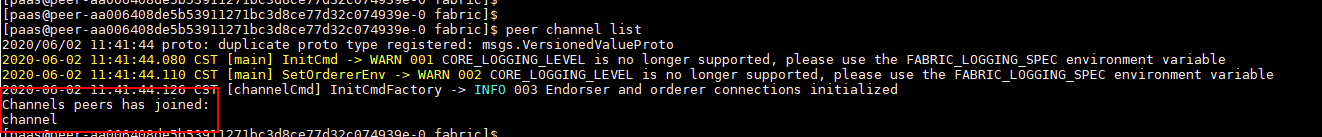
- Run the peer channel list command to query the channel to which the peer is added.
Figure 4 Querying the channel to which the peer is added
- Run the peer channel getinfo -c {Channel name} command to check whether the ledger of the peer is updated.
Figure 5 Checking whether the ledger of the peer is updated

If the block quantity in the ledger of the peer is different from that displayed on the Block Browser page, query the block quantity again after 10 minutes. If the block quantity keeps unchanged, the ledger of the peer is not updated due to insufficient resources or high concurrency. As a result, transactions become abnormal.
- Log in to the BCS console. In the navigation pane, click Instance Management. On the card containing the abnormal instance, click Manage Blockchain. On the Block Browser page, select the abnormal channel, and view the block quantity on the Block List tab page.
- Check item 5: Check whether the DB file exists.
- Log in to the ECS where the blockchain is deployed, run the docker ps|grep k8s_peer command to check the peer containers, and record the ID of the container where transactions are abnormal.
Figure 6 Checking the peer containers

- Run the docker exec -it Container ID /bin/bash command to access the container.
Figure 7 Accessing the container

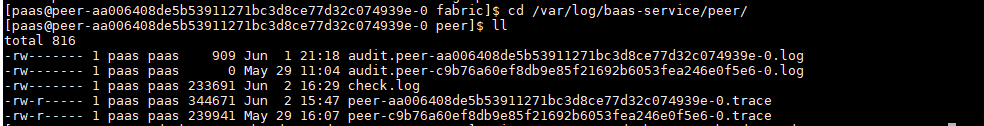
- Run the cd /var/log/baas-service/peer/ command to go to the directory where the logs of the peer are stored, and run the ll command to view all files.
Figure 8 Viewing all files
- Obtain the hash value and sequence number of the peer.
On the Block Browser page of the Blockchain Management console, view the domain name and sequence number of the peer in the Domain of Peer column in the Peer Status list.
Figure 9 Peer Status list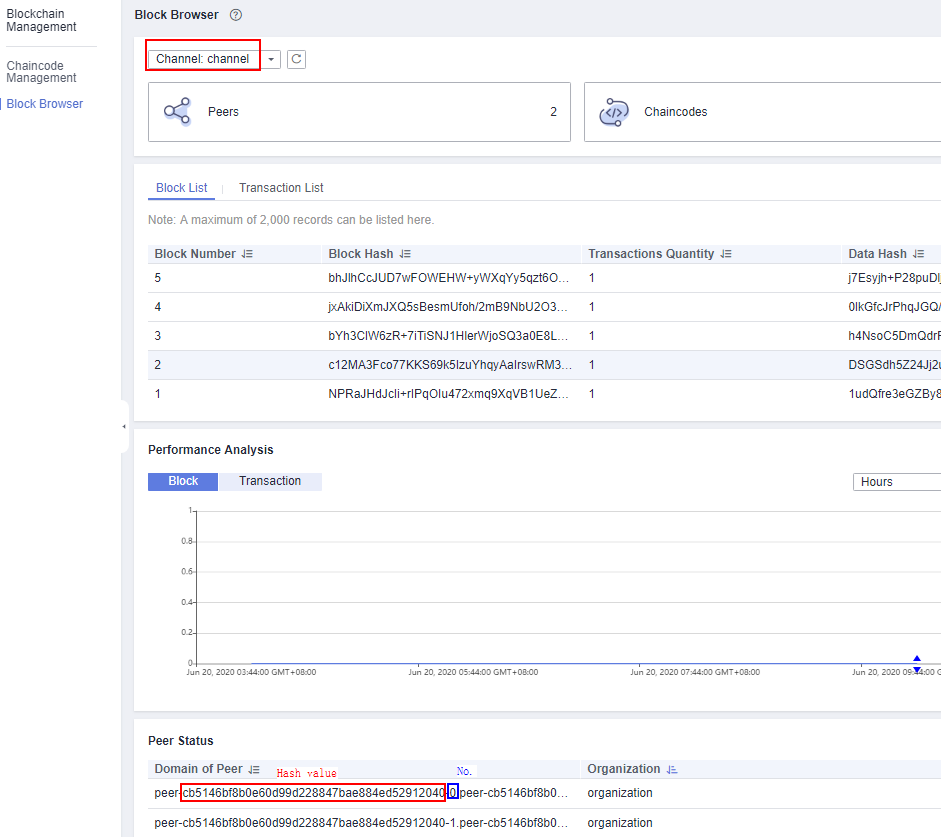
- The peer log file is named in the following format: peer-{Hash value}-{Serial number}.trace. Run cat {File name}|grep -C 5 "Fail to recover DB: file does not exist" to search for exception information.
If you see Fail to recover DB: file does not exist, the DB file of the peer does not exist. As a result, transactions are abnormal.
- Log in to the ECS where the blockchain is deployed, run the docker ps|grep k8s_peer command to check the peer containers, and record the ID of the container where transactions are abnormal.
- Check item 6: If a BCS instance uses CouchDB of an earlier version for ledger storage, check whether BCS becomes unavailable after CouchDB restarts.
If CloudDB is used for ledger storage for an instance of an earlier version, the status data is not stored in the SFS file system. If BCS is restarted, CouchDB will reload the block data to generate the status data, and BCS will be unavailable for a certain period of time.
It takes about 2 hours to synchronize data of 150,000 blocks. During data synchronization, port 7051 of the peer cannot be accessed.
Solution:
- Upgrade the BCS instance to the latest version to avoid this problem when you perform upgrade or restart.
When a BCS instance is upgraded to the latest version for the first time, the CouchDB container mounts the web disk and synchronizes status data. As a result, the BCS instance is unavailable for a certain period of time. This duration increases linearly as the block quantity increases. It takes about 2 hours to synchronize data for every 150,000 blocks. The block quantity can be viewed on the Block Browser page of the Blockchain Management console.
- Log in to the BCS console. Choose More > Upgrade on the instance card.
- In the dialog box that is displayed, view the current instance version or upgrade the BCS instance to the latest version.
- Instances are unavailable during version upgrade. In a consortium, if your blockchain upgrades, all consortium blockchains must also upgrade. Reach an agreement with consortium members before you perform upgrade to eliminate effects on their blockchains.
- Do not initiate version upgrade when the chaincode is being installed or instantiated.
- BCS v4.x.x corresponds to Hyperledger Fabric v2.2.
- You can only upgrade BCS from an earlier version to a later version. Rollback is supported only if the upgrade fails.
- Upgrade the BCS instance to the latest version to avoid this problem when you perform upgrade or restart.
- Check item 7: Check whether data can be stored to blockchain even though the request initiated from a blockchain client has timed out.
If the error message request timed out or been cancelled is displayed on the client and UTC is more than 15mos apart from current server time is displayed in the organization node logs, ensure that the time and time zone of the client are the same as those of the organization node.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





