How Do I Change the DNS Server Addresses of an ECS?
Scenarios
This section describes how to change the DNS server addresses of an ECS and make the new DNS server addresses take effect immediately on the ECS.
The required operations are as follows:
Background
ECSs use private DNS servers for domain name resolution in VPCs. The private DNS servers do not affect the domain name resolution for the ECSs to access the Internet. Additionally, you can use the private DNS servers to directly access the private IP addresses of cloud services, such as OBS and SMN. Using this method to access Huawei Cloud services is faster and involves less latency than accessing them over the Internet.
Before private domain names are available, VPC subnets use the public DNS server (114.114.114.114). To allow ECSs in these VPCs to access private domain names, you can change the public DNS server to the private DNS servers configured for the VPC subnets. For instructions about how to obtain a private DNS server address, see What Are the Private DNS Servers Provided by the Huawei Cloud DNS Service?
Viewing the DNS Server Addresses for an ECS
- Go to the ECS list page.
- In the ECS list, click the name of the target ECS.
- On the Summary tab of the ECS details page, click the VPC name.
The Virtual Private Cloud page is displayed.
- Locate the VPC and click the number in the Subnets column.
The Subnets page is displayed.
- Click the name of the subnet.
In the Gateway and DNS Information area, view the DNS server addresses used by the ECS.
Figure 1 Subnet list Figure 2 Viewing the DNS server address
Figure 2 Viewing the DNS server address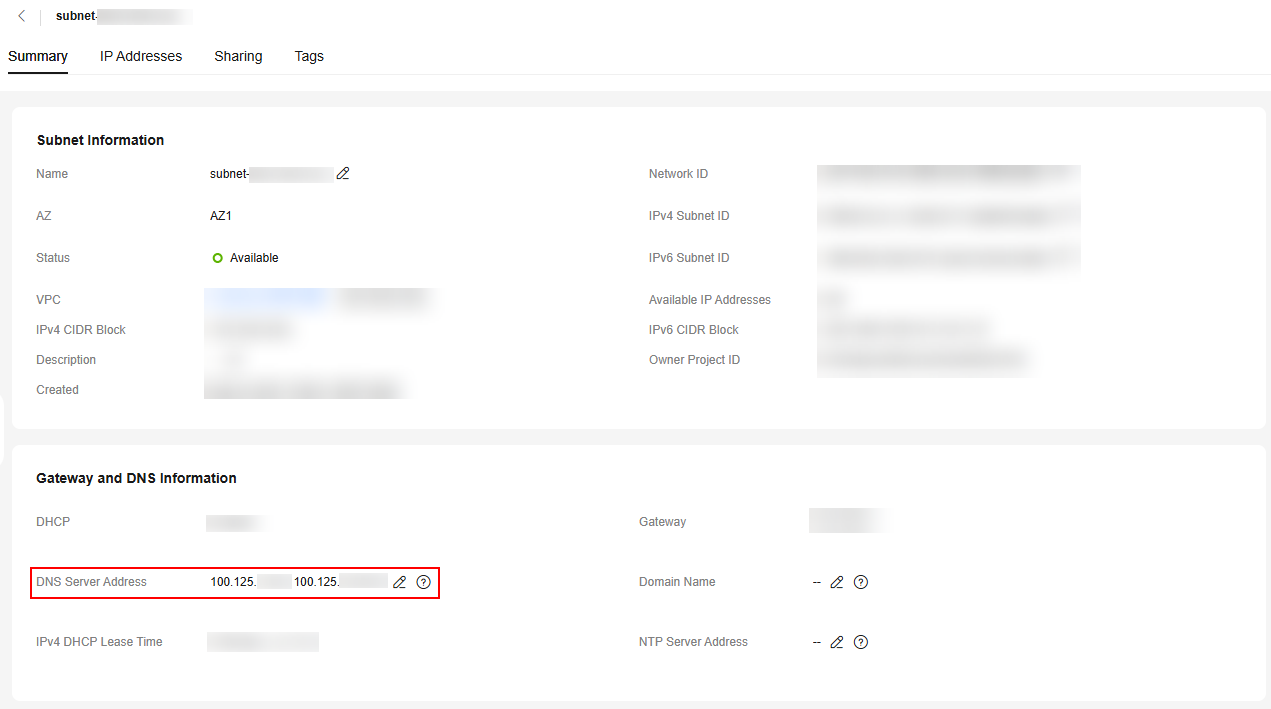
Changing the DNS Server Addresses for a VPC Subnet
If the DNS servers for an ECS are not provided by Huawei Cloud, change them to Huawei Cloud private DNS servers that are in the same region as the ECS.
- Check the private DNS server addresses corresponding to the region where the ECS resides by referring to What Are Huawei Cloud Private DNS Server Addresses?
- In the Gateway and DNS Information area of the subnet details page, click
 next to DNS Server Address.
next to DNS Server Address. - Change the DNS server addresses to private DNS server addresses.
Changing DNS Server Addresses for the ECS
- Method 1: Restart the operating system to update the DHCP configuration for the DNS server addresses to take effect.

Restarting the OS will interrupt services on the ECS. Perform this operation during off-peak hours.
- Method 2: Use dhclient to obtain the new DNS server addresses.

Using VNC to log in to the ECS. After running the dhclient -r command in 4, the IP address of the ECS will be released temporarily. If any other remote login mode is used, the login will be disconnected. To prevent services from being affected, perform the operations during off-peak hours.
- Log in to the ECS.
For details, see How Do I Log In to My ECS?
You are advised to log in to the ECS using VNC.
- Run the following command to view the DNS server address of the ECS:
If information similar to the following is displayed, 114.114.114.114 is the DNS server address of the ECS.

- Run the following command to check whether the dhclient process exists:
ps -ef | grep dhclient | grep -v grep
If information similar to the following is displayed, no process exists (CentOS 8.1 is used as an example).
In this case, run the dhclient command to start the process and check whether the dhclient process exists.

If information similar to the following is displayed, process exists (CentOS 7.2 is used as an example).

- Run the following command to release the current DNS server address:
If the remote login does not use VNC, the login will be disconnected after running the dhclient -r command. In this case, log in to the ECS using VNC and perform 5. Then, you can use other remote login modes to log in to the ECS.
- Run the following command to restart the dhclient process and obtain new DNS server addresses:
dhclient
- Run the following command to view the new DNS server addresses of the ECS:
If information similar to the following is displayed, 100.125.1.250 and 100.125.64.250 are the new DNS server addresses of the ECS.

- Log in to the ECS.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






