Elastic Network Interface Overview
An elastic network interface (referred to as a network interface in this documentation) is a virtual network card. You can create and configure network interfaces and attach them to your cloud servers (such as ECSs and BMSs) to obtain flexible and highly available network configurations.
Network Interface Types
- A primary network interface is created together with an instance by default, and cannot be detached from the instance.
- An extended network interface can be created on the Network Interfaces tab, and can be attached to or detached from an instance.
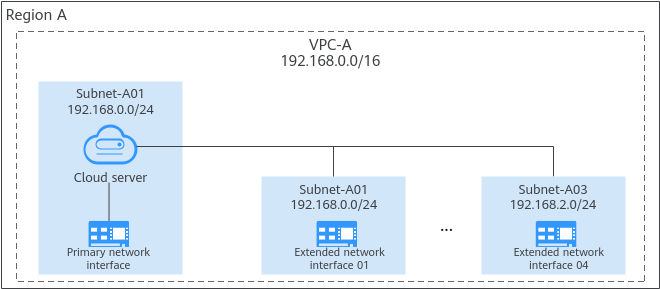
Application Scenarios
- Flexible migration: You can detach an extended network interface from a cloud server and attach it to another one. The private IP address, EIP, and security group rules of the original cloud server can be migrated together, so you do not need to reconfigure them. This allows the service traffic on the faulty cloud server to be quickly switched to the standby one, achieving quick service recovery.
- Service separation: You can configure multiple network interfaces for a cloud server. These network interfaces can be in different subnets of the same VPC and process the internal, external, and management traffic of the cloud server respectively. You can configure access control policies and routes for each subnet, and define security group rules for each network interface to isolate networks and service traffic.
The number of elastic network interfaces that can be attached to a cloud server is limited. If the cloud server specifications support supplementary network interfaces, you can attach supplementary network interfaces to the elastic network interfaces as needed. For details, see Application Scenarios.
Constraints
- The number of extended network interfaces that can be attached to an ECS is determined by the ECS specifications. For details, see the maximum network interfaces of an ECS in A Summary List of x86 ECS Specifications.
- Extended network interfaces cannot be used to directly access public Huawei Cloud services, such as DNS. You can use VPC endpoints to access these services. For details, see Buying a VPC Endpoint.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.