Using MoXing in Notebook
This document describes how to call MoXing Framework APIs in ModelArts.
Logging In to ModelArts and Creating a Notebook Instance
- Log in to the ModelArts console. In the navigation pane, choose Development Workspace > Notebook to access the Notebook page.
- Click Create. On the Create Notebook page that is displayed, create a notebook instance by referring to .
- After a notebook instance is created and enters the Running status, click Open in the Operation column to go to the JupyterLab Notebook page.
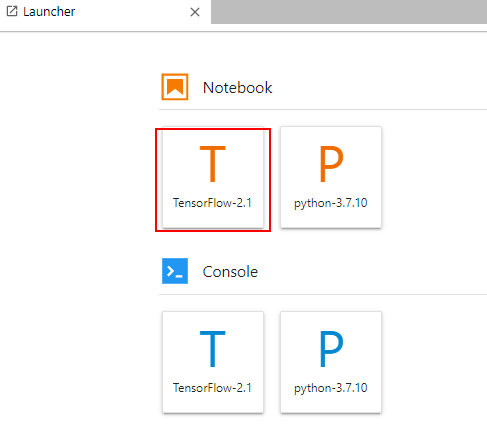
- On the Launcher page of JupyterLab, for example, click TensorFlow to create a file for encoding.
Figure 1 Selecting an AI engine
After the file is created, the JupyterLab page is displayed by default.
Figure 2 Encoding page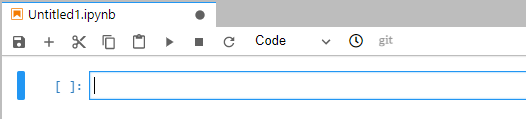
Calling mox.file.
Enter the following code to implement the following simple functions:
- Introduce MoXing Framework.
- Create the test01 folder in the existing modelarts-test08/moxing directory.
- Check whether the test01 folder exists. If the folder exists, the preceding operation is successful.
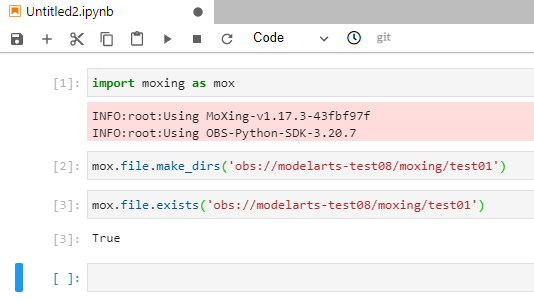
1 2 3 4 |
import moxing as mox mox.file.make_dirs('obs://modelarts-test08/moxing/test01') mox.file.exists('obs://modelarts-test08/moxing/test01') |
Figure 3 shows the result. Note that each time you enter a line of code, click Run. You can also go to OBS Console and check whether the test01 folder has been created in the modelarts-test08/moxing directory. For more common MoXing operations, see Sample Code for Common Operations.
Copying Data to OBS
On the Notebook JupyterLab page, copy the yolov8_train_ascend.zip file to an OBS bucket. The sample code is as follows:
import os
import zipfile
import moxing as mox
mox.file.copy('yolov8_train_ascend.zip','obs://pcb-data-me/pcb.zip')
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.