Restoring a Replica Set Database or Table to a Specific Point in Time
Scenarios
DDS allows you to restore databases and tables using point-in-time recovery (PITR). This ensures your data integrity and minimizes impact on the original instance performance. You can select databases or tables and restore them to a specified point in time. During database or table PITR, the system restores the full and incremental data at the selected time point to a temporary instance, automatically exports the databases and tables to be restored, and then restores the databases and tables to the original instance. The time required depends on the amount of data to be backed up and restored on the instance. Please wait.
Restoring databases and tables will not overwrite data in the instance. You can select databases and tables to be restored.
Precautions
- Currently, only replica set instances of version 4.0 support the point-in-time recovery at the database and table level.
- Before performing the restoration, you need to enable the incremental backup policy.
- After a successful restoration, a new table named original-table-name_bak_timestamp is generated in the instance by default. If the table contains an index, the namespace of the index is changed to original-database-name.original-table-name_bak_timestamp. You can rename the table later as required.
- New databases and tables will be generated in the original DB instance. Ensure that sufficient storage space is available.
- The length of <Database name>.<Table name> cannot exceed 120 characters. The length of <Database name>.<Table name>.<Index name> cannot exceed 128 characters, or the restoration may fail.
- Ensure that the name of the restored table is different from that of the existing table, or the restoration may fail.
- If you perform a table-level restoration and the table does not exist at the required point in time, an empty table is automatically created. If you perform a database-level restoration, the missing table is not created.
- If the incremental oplog traffic is greater than 250 GB/h, the incremental backup speed may not keep up with the oplog generation speed. As a result, some restoration time points may be unavailable.
Restrictions
- Database- and table-level restoration is related to CPU and memory specifications. For details about the maximum size of a single data record that can be restored to a specified time point, see Table 1.
- If a database- and table-level restoration fails, you can upgrade the specifications or batch restore the databases and tables to a specified time point.
|
CPU Type |
Specifications |
vCPUs |
Memory (GB) |
Maximum Size of a Single Data Record That Can Be Restored in a Collection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
x86 |
General-purpose |
2 |
4 |
400 KB |
|
2 |
8 |
800 KB |
||
|
4 |
8 |
1 MB |
||
|
4 |
16 |
1.3 MB |
||
|
8 |
16 |
1.3 MB |
||
|
8 |
32 |
2 MB |
||
|
Enhanced II |
1 |
8 |
400 KB |
|
|
2 |
8 |
800 KB |
||
|
2 |
16 |
800 KB |
||
|
4 |
16 |
1.3 MB |
||
|
4 |
32 |
1.3 MB |
||
|
8 |
32 |
2 MB |
||
|
8 |
64 |
3 MB |
||
|
16 |
64 |
4 MB |
||
|
16 |
128 |
7 MB |
||
|
32 |
128 |
7 MB |
||
|
32 |
256 |
10 MB |
||
|
64 |
256 |
10 MB |
||
|
64 |
512 |
16 MB |
||
|
Kunpeng |
- |
2 |
4 |
400 KB |
|
- |
2 |
8 |
800 KB |
|
|
- |
4 |
8 |
1 MB |
|
|
- |
4 |
16 |
1.3 MB |
|
|
- |
8 |
16 |
1.3 MB |
|
|
- |
8 |
32 |
2 MB |
|
|
- |
16 |
32 |
2 MB |
|
|
- |
16 |
64 |
4 MB |
Procedure
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and a project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and a project. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Document Database Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Document Database Service. - On the Instances page, click the replica set instance.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Backups & Restorations.
- On the Backups & Restorations page, click Restore Database and Table.
- In the displayed dialog box, configure parameters as required. The data in the new database and table is the same as that in the database and table at the selected time point.
Table 2 Database information Parameter
Description
Date
Date when the automated backup of the DB instance is generated.
Time Range
Time range during which the automated backup can be restored.
Time Point
The specific point in time when the automated full backup is generated.
Base Time Range
Time range during which the database and table can be restored based on the automated full backup.
Database and Table
Databases and tables that have been automatically backed up within the base time range are displayed on the left. Select the databases and tables on the left to sync information to the area on the right.
Time Point
The point in time within the base time range.
Custom Database and Table
You can add custom databases and tables as required.
- The system databases cannot be restored. Therefore, the database name cannot be admin, local, or config.
- The database name cannot contain spaces and the following special characters: ".$\/*?~#:|
- A table name cannot use "system" as the prefix.
- The length of <Database name>.<Table name> cannot exceed 120 characters. The length of <Database name>.<Table name>.<Index name> cannot exceed 128 characters, or the restoration may fail.
- Ensure that the name of the restored table is different from that of the existing table. Otherwise, the restoration may fail.
- After a successful restoration, a new table named original-table-name_bak_timestamp is generated in the instance by default. If the table contains an index, the namespace of the index is changed to original-database-name.original-table-name_bak_timestamp. You can rename the table later as required.
To distinguish the point in time of the custom databases and tables from those synchronized on the right, set the point in time to a different value. The system restores data to the custom databases and tables based on the time configured here.
Type
You can restore data to a database or table.
If you perform a table-level restoration and the table does not exist at the required point in time, an empty table is automatically created. If you perform a database-level restore, data will be restored to the database separately, and the table will not be created.
Figure 1 Selecting database and table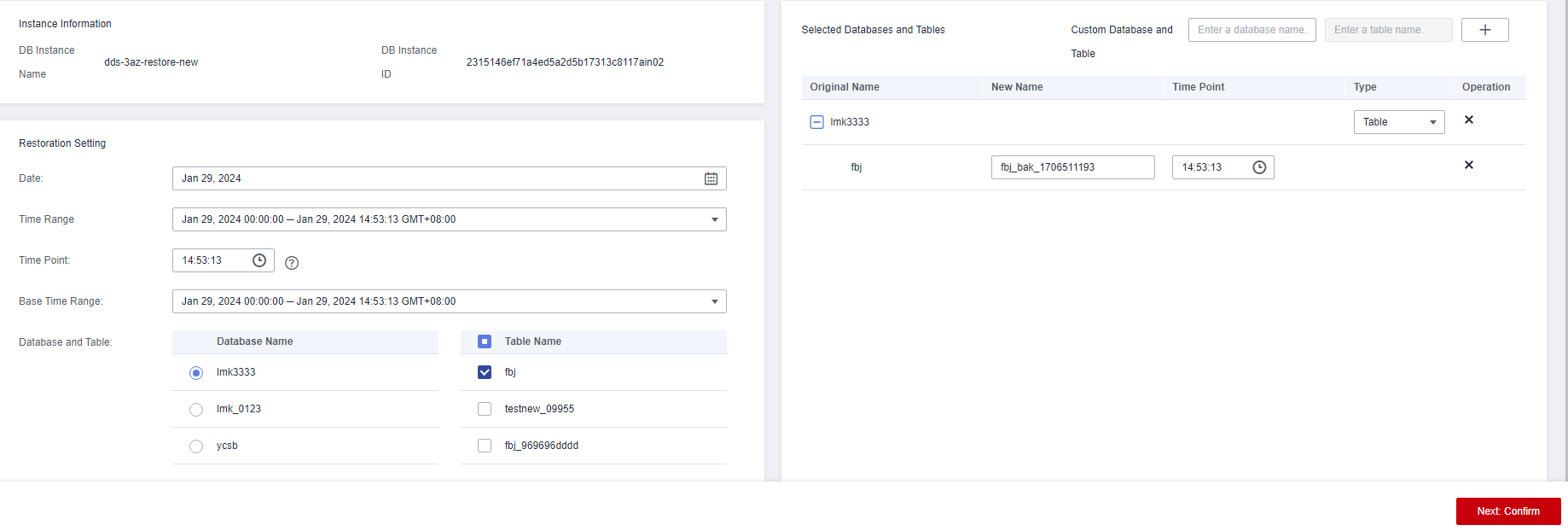
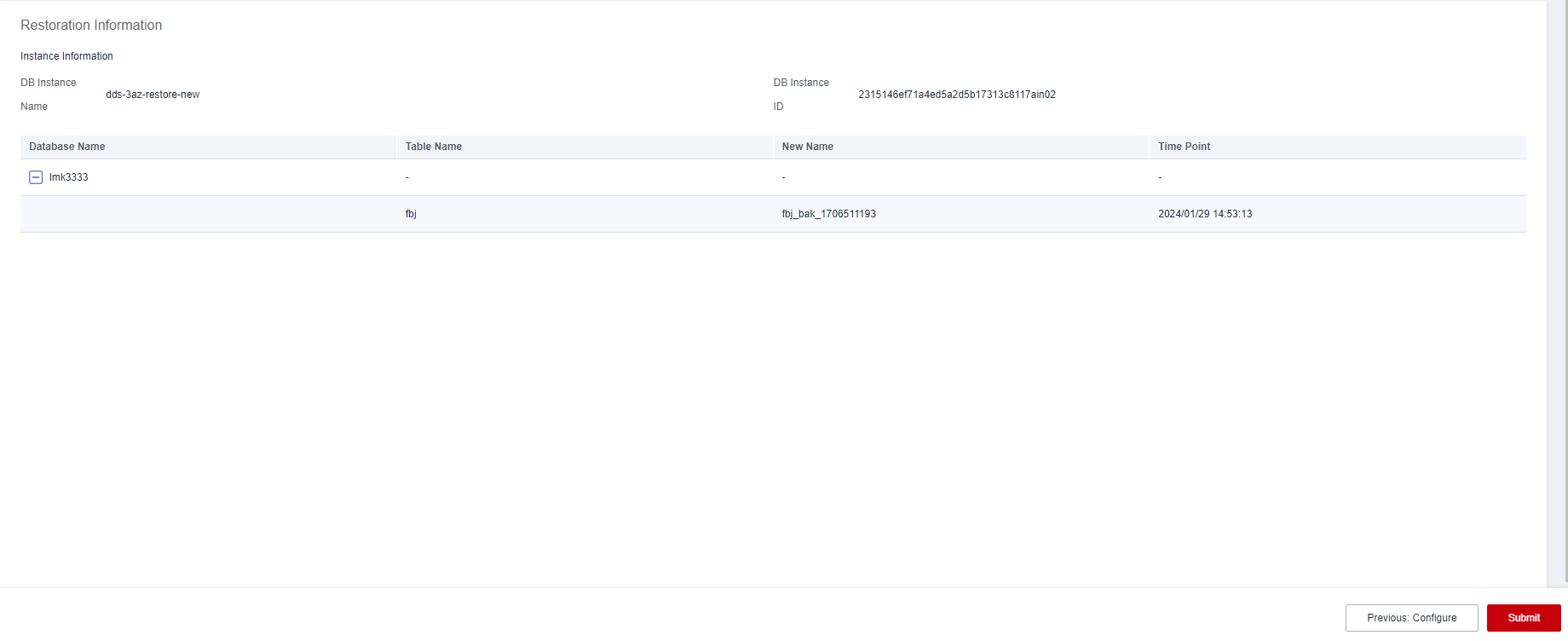
- Click Next: Confirm.
- Click Submit to start the restoration.
Figure 2 Confirming the information
- On the Instances page, the DB instance status is Restoring. During the restoration process, services are not interrupted.
- After the restoration is successful, manage data in the database and table as required.
If you need to use the original database and table names, you can use a rename operation to back up the original database and table and switch your service to the restored database and table. Then, delete the original database and table after ensuring that your services are normal.
Example:
db.adminCommand({renameCollection: "db1.test1", to: "db2.test2"})
The above command is used to move the test1 table from the db1 database to the db2 database and rename the table to test2.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






