Managing Database Audit Instances
After purchasing a database audit instance, you can view, enable, restart, and disable the instance.
Prerequisites
- Before restarting and disabling an instance, ensure that its Status is Running.
- Before enabling an instance, ensure that its Status is Disabled.
Viewing the Instance
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed.
and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed. - In the navigation tree on the left, choose Instances.
- View the database audit instances information. For details about related parameters, see Table 1.
Figure 1 Viewing database audit instances
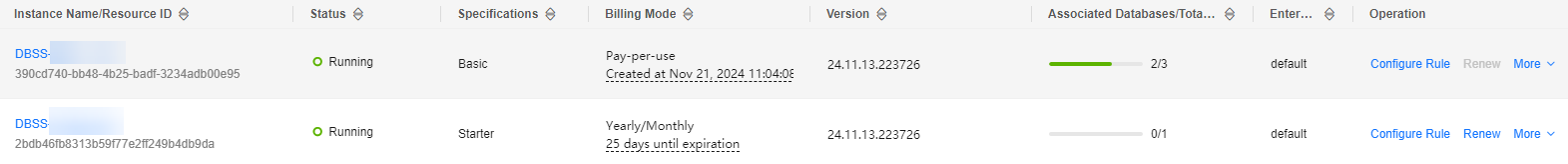
- You can click the name of an instance to view its overview.
- You can search for an instance by instance name, status, instance specifications, resource ID, billing mode, version, or enterprise project in the filter box above the list.
Table 1 Parameters Parameter
Description
Instance Name/Resource ID
Instance name and resource ID. The resource ID is automatically generated by the system.
Specifications
Edition of an instance
Billing Mode
Billing mode (yearly/monthly) and expiration time of the instance
Version
Version of database audit instance
Status
Running status of an instance. The options are as follows:
- Running
- Creating
- Faulty
- Disabled
- Frozen
- Frozen for legal management
- Frozen due to abuse
- Frozen due to lack of identity verification
- Frozen for partnership
- Creation failed
Associated Databases/Total Databases
Number of databases an instance has associated with and Number of databases an instance supports
Enterprise Project
Enterprise project name of the instance
Operation
Operations can be performed on the instance. The options are as follows:
- Configure Rules
- Renewal
- Enable
- Disable
- Restart
- View Details
- View Metric
- Auto-renew
- Unsubscribing
- Release
- Delete
You can perform the following operations on instances as required:
- Restart
Locate the row that contains the desired instance, choose More > Restart in the Operation column, and click OK in the displayed dialog box.
- Enable
Locate the row that contains the desired instance, choose More > Enable in the Operation column, and click OK in the displayed dialog box.
- Disable
Locate the row that contains the desired instance, choose More > Disable in the Operation column, and click OK in the displayed dialog box. When an instance is disabled, the audit function is disabled for the databases on the instance.
- Delete
Locate the row that contains the instance that failed to be created, choose More > Delete in the Operation column, and click Delete in the displayed dialog box. Deleted instances will not be displayed in the instance list.
- View Details
Locate the row that contains the instance that failed to be created, choose More > View Details in the Operation column. In the dialog box that is displayed, view the instance creation failure details.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






