Managing SQL Injection Rules
SQL injection rules of database audit are enabled by default. You can disable, enable, edit, and set priorities for SQL injection rules.

One piece of audited data can match only one SQL injection rule.
Prerequisites
- The database audit instance is in the Running state.
- Before enabling an SQL injection rule, ensure that the rule is in the Disabled state.
- Before disabling an SQL injection rule, ensure that the rule is in the Enabled state.
Disabling SQL Injection Rules
SQL injection rules are enabled by default. You can disable the injection rules as required. When an SQL injection rule is disabled, the audit rule does not take effect.
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed.
and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed. - In the navigation tree, choose Rules.
- In the Instance drop-down list, select the instance for which you want to disable SQL injection rule.
- Click the SQL Injection tab.
- Locate the SQL injection rule you want to disable, and click Disable in the Operation column.
Figure 1 Disabling an SQL injection rule

When the status of an SQL injection rule is Disabled, SQL injection rule is disabled successfully.
Enabling SQL Injection Rules
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed.
and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed. - In the navigation tree, choose Rules.
- In the Instance drop-down list, select the instance for which you want to enable SQL injection rule.
- Click the SQL Injection tab.
- In the Operation column of the row containing the SQL injection rule, click Enable to enable the rule.
Figure 2 Enabling an SQL injection rule
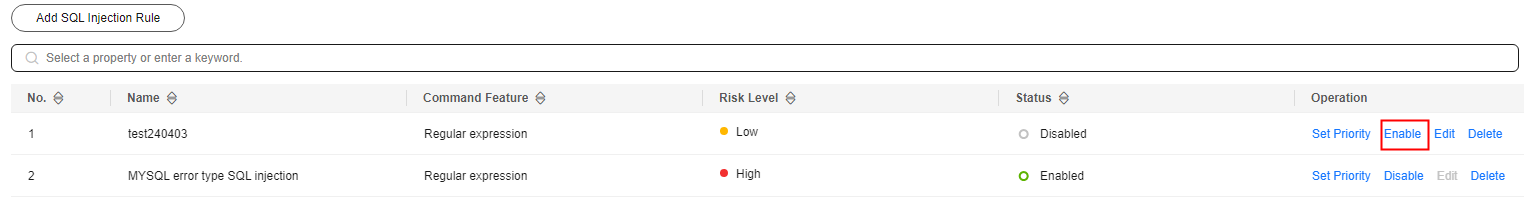
- The SQL injection rule is enabled and its status changes to Enabled.
Setting the Priority of SQL Injection Rules
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed.
and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed. - In the navigation tree, choose Rules.
- In the Select Instance drop-down list, select the instance for which you want to set the priority for the SQL injection rule.
- Click the SQL Injection tab.
- In the Operation column of a rule, click Set Priority. In the displayed dialog box, select a priority. The smallest number indicates the highest priority. Click OK.
Figure 3 Configuring the priority

Editing an SQL Injection Rule
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed.
and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed. - In the navigation tree, choose Rules.
- In the Instance drop-down list, select the instance for which you want to edit SQL injection rule.
- Click the SQL Injection tab.
Only user-defined SQL injection rules can be edited. Default rules can only be enabled and disabled.
- Click Edit in the Operation column to edit the parameters of the target rule. For details about the parameters, see Table 1.
Figure 4 Editing an SQL injection rule
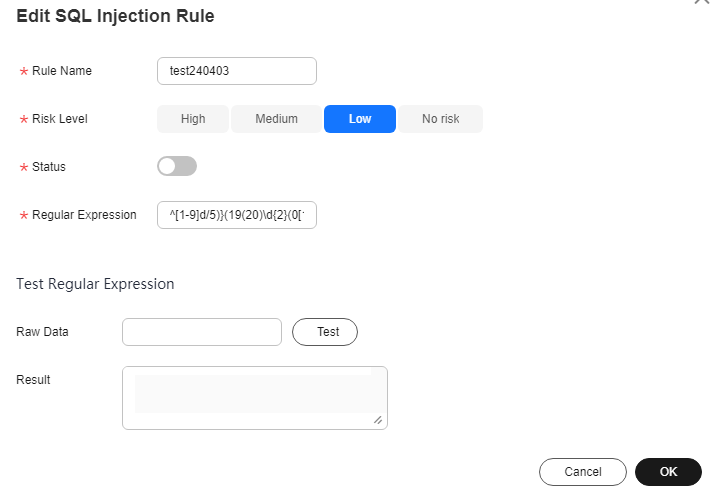
Table 1 SQL injection rule parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
Name
Name of an SQL rule.
Postal Code SQL injection Rule
Risk Level
Level of risks matching a SQL rule. Its value can be:
- High
- Moderate
- Low
- No risk
Moderate
Status
Enables or disables an SQL injection rule.
 : enabled
: enabled : disabled
: disabled

Test Regular Expression
Regular expression that checks for content in certain pattern.
^\d{6}$
Data
Content that matches the regular expression.
Enter content and click Test to verify that the regular expression works properly.
628307
Result
Test result. It can be:
- Hit
- Miss
NOTE:
- If the test result is Hit, the regular expression is correct.
- If the test result is Miss, the regular expression is incorrect.
Hit
- Confirm the information and click OK.
Deleting an SQL Injection Rule
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed.
and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed. - In the navigation tree, choose Rules.
- In the Instance drop-down list, select the instance for which you want to delete SQL injection rule.
- Click the SQL Injection tab.
Only user-defined SQL injection rules can be deleted. Default rules can only be enabled or disabled.
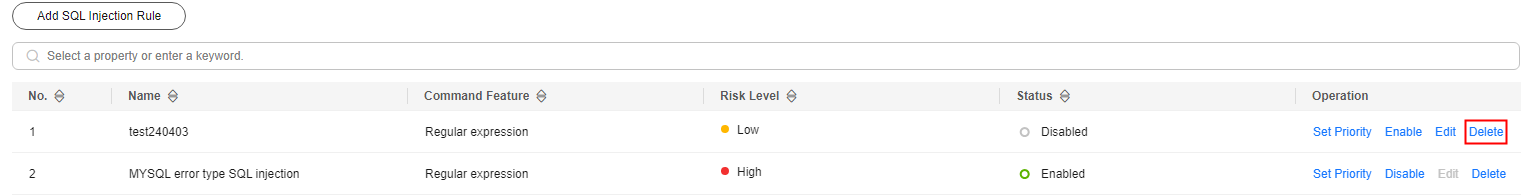
- In the Operation column, click Delete.
Figure 5 Deleting SQL injection
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






