Optimizing the Parameters of a Job for Migrating Data from PostgreSQL to MRS Hudi
Optimizing Source Parameters
Optimization of data extraction from PostgreSQL
No optimization configuration items are available.
Optimizing Destination Parameters
Optimization of data writing to Hudi
If data is written to the Hudi table slowly, check whether the table is properly designed. You are advised to use an MOR table that uses Hudi bucket indexes and configure the number of buckets to achieve an optimal migration performance.
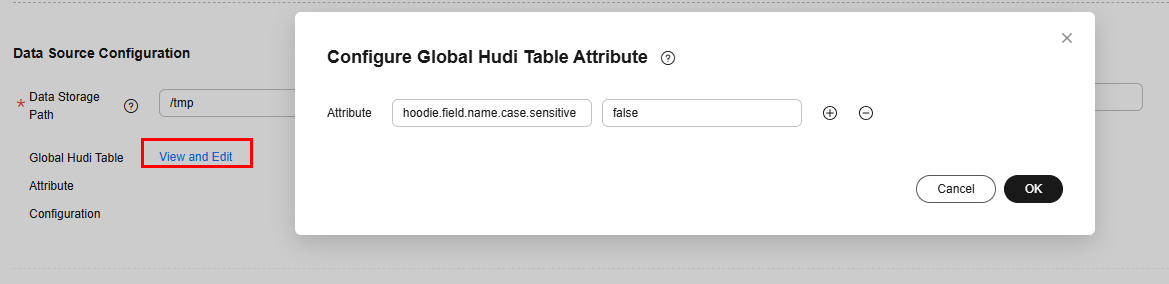
- Using bucket indexes: You can configure the index.type and hoodie.bucket.index.num.buckets attributes in Global Configuration of Hudi Table Attributes or Edit Table Attribute of the mapped table.
- Determine whether to use partitioned or non-partitioned tables.
There are two types of tables, fact tables and dimension tables.
- Fact tables generally have a large amount of data, most of which is new data and a small proportion of which is the data updated in a recent period (years, months, or days). A downstream system that reads a fact table for ETL calculation splits the table based on the data creation time (for example, last day, month, or year) into partitioned tables, ensuring optimal read and write performance.
- Dimension tables generally contain a small amount of data, most of which is updated data and a small proportion of which is new data. The data volume of a dimension table is stable, and all data is read for ETL calculation such as join. Therefore, non-partitioned tables are more suitable as they provide better performance.
- Determine the number of buckets in a table.
If you use a Hudi bucket table, you need to set the number of buckets, which affects the table performance.
- Number of buckets for a non-partitioned table = MAX(Data volume of the table (GB)/2 GB x 2, rounded up, 4)
- Number of buckets for a partitioned table = MAX(Data volume of a partition (GB)/2 GB x 2, rounded up, 1)
- The total data volume of a table, rather than the size of a compressed file, is used.
- An even number is preferred for the number of buckets. Set the minimum number of buckets for a non-partitioned table to 4 and that for a partitioned table to 1.
In addition, you can click Global Configuration of Hudi Table Attributes in the Hudi destination configuration or click Edit Table Attribute in the mapped table to add optimization parameters.
|
Parameter |
Type |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
hoodie.sink.flush.tasks |
int |
1 |
Number of concurrent Hudi flush tasks. The default value is 1, indicating sequential writing. If Hudi commits a large number of FleGroups (for example, a large amount of historical data of the source table is updated), you can increase the value of this parameter. FileGroup data flushed by a single thread = Number of FileGroups committed at a time/Number of concurrent jobs If the number of FileGroups flushed by a single thread is less than or equal to 5, the recommended value for this parameter is 2. If the number of FileGroups flushed by a single thread is less than or equal to 10, the recommended value for this parameter is 5. If the number of FileGroups flushed by a single thread is less than or equal to 25, the recommended value for this parameter is 10. If the number of FileGroups flushed by a single thread is less than or equal to 50, the recommended value for this parameter is 20. If the number of FileGroups flushed by a single thread is greater than 50, the recommended value for this parameter is 30. The larger the number of concurrent flush tasks, the higher the memory during flushing. Adjust the value based on the memory monitoring of the real-time processing migration job. |
|
hoodie.context.flatmap.parallelism |
int |
1 |
When Hudi performs commit operations, it scans partitions. By default, one scan operation is performed at a time. If a large number of partitions are involved in a commit operation, you can increase the value of this parameter to accelerate the commit operation. If the number of partitions committed at a time is less than or equal to 10, the recommended value for this parameter is 5. If the number of partitions committed at a time is less than or equal to 25, the recommended value for this parameter is 10. If the number of partitions committed at a time is less than or equal to 50, the recommended value for this parameter is 20. If the number of partitions committed at a time is greater than 50, the recommended value for this parameter is 30. |
|
compaction.async.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Whether to enable compaction. The default value is true, indicating that compaction is enabled for Hudi. The compaction operation affects the write performance of a real-time migration job. To ensure the stability of the migration job, you can set this parameter to false and split Hudi Compaction into Spark jobs for MRS to execute. For details, see |
|
compaction.delta_commits |
int |
5 |
Frequency at which compaction requests are generated for real-time processing migration jobs. The default value is 5, indicating that a compaction request is generated every five commits. Lowering the compaction request generation frequency reduces the compaction frequency and improves job performance. If the incremental Hudi data is small, you can increase the value of this parameter. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






