Java
Scenarios
To use Java to call an API through app authentication, obtain the Java SDK, create a project or import an existing project, and then call the API by referring to the API calling example.
This section uses Eclipse 4.5.2 as an example.
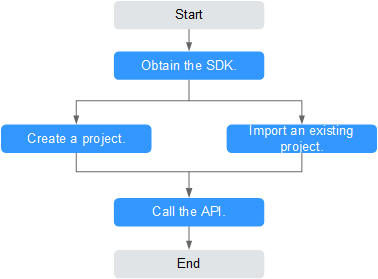
Prerequisites
- You have obtained the domain name, ID, request URL, and request method of the API to be called, and the AppKey and AppSecret of the App for calling the API. For more information, see Preparation.
- You have installed Eclipse 3.6.0 or a later version. If not, download Eclipse from the official Eclipse website and install it.
- You have installed Java Development Kit (JDK) 1.8.111 or a later version. If not, download JDK from the official Oracle website and install it.
Obtaining the SDK
- Log in to the DataArts Studio console.
- Click DataArts DataService.
- In the navigation pane, choose DataArts DataService Exclusive > SDKs.
- On the SDKs page, download the SDK package.
- Verify integrity of the SDK package. In Windows, open the CLI and run the following command to generate the SHA-256 value of the downloaded SDK package. In the command, D:\java-sdk.zip is an example local path and name of the SDK package. Replace it with the actual value.
certutil -hashfile D:\java-sdk.zip SHA256
The following is an example command output:
SHA-256 hash value of D:\java-sdk.zip 96fced412700cf9b863cb2d867e6f4edf76480bc679416efab88a9e1912503b9 CertUtil: -hashfile command executed.
Compare the SHA-256 value of the downloaded SDK package with that provided in the following table. If they are the same, no tampering or packet loss occurred during the package download.
Table 1 SDK packages and the corresponding SHA-256 values Language
SHA-256 Value of the SDK Package
Java
96fced412700cf9b863cb2d867e6f4edf76480bc679416efab88a9e1912503b9
Go
f448645da65b4f765d9569fc97ca45dc3e8f1ce4f79d70c5c43934318521d767
Python
54b4984d91db641d2b1b0e77064c162850cb2511a587f95e2f8b8340e7afa128
C#
b66caf856ffccb61fe758872aac08876aa33fb0cf5f4790e3bec163593b2cbae
JavaScript
43da0b54d6b04d1f5ed7f278c2918c2a63a1ddb8048e2d1c5db60baafb17663c
PHP
394c068420a3817f32d5d88b6c1632978f573f2a685e4a1d10c2f698e0f6786e
C++
abae5473d47594f88dcd5eaa0902dc12cd6f1e3bd63c0b82d9d1fab8b4351f54
C
a376573fe8aa3a636a6d123926ddc3dca11748b289b8c2c16a5056830a095acb
Android
c19175d736f05b1945dab4675df19311834ede0d9b1978b11b50c86687baf85c
Obtain the ApiGateway-java-sdk.zip package. The following table shows the files decompressed from the package.
|
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
libs\ |
SDK dependencies |
|
libs\java-sdk-core-x.x.x.jar |
SDK package |
|
src\com\apig\sdk\demo\Main.java |
Sample code for signing requests |
|
src\com\apig\sdk\demo\OkHttpDemo.java |
|
|
src\com\apig\sdk\demo\LargeFileUploadDemo.java |
|
|
src\com\apig\sdk\demo\WebSocketDemo.java |
|
|
.classpath |
Java project configuration files |
|
.project |
Importing a Project
- Open Eclipse and choose File > Import.
The Import dialog box is displayed.
- Choose General > Existing Projects into Workspace and click Next.
The Import Projects dialog box is displayed.
Figure 2 Importing a project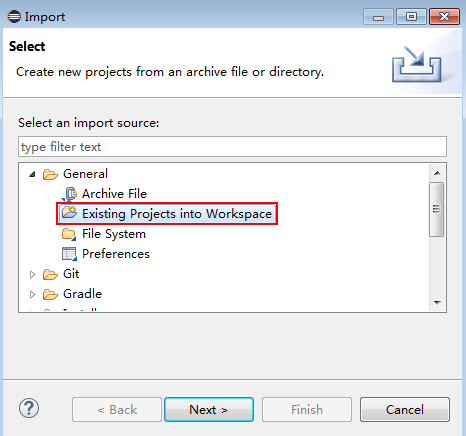
- Click Browse and select the directory where the SDK is decompressed.
Figure 3 Selecting the demo project
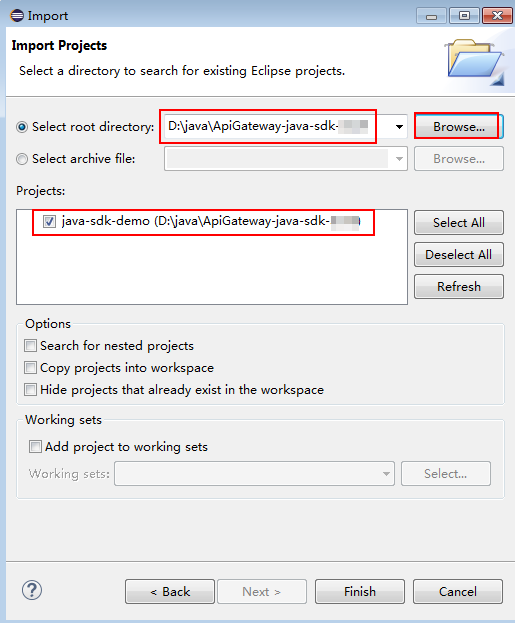
- Click Finish.
The following figure shows the directory structure of the project.
Figure 4 Directory structure of the imported project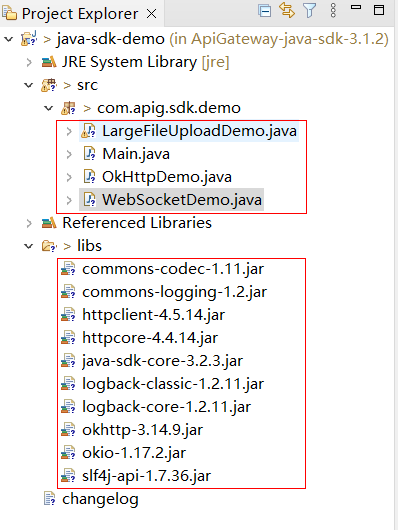
Modify the parameters in sample code Main.java as required. For details about the sample code, see API Calling Example.
Creating a Project
- Open Eclipse and choose File > New > Java Project.
The New Java Project dialog box is displayed.
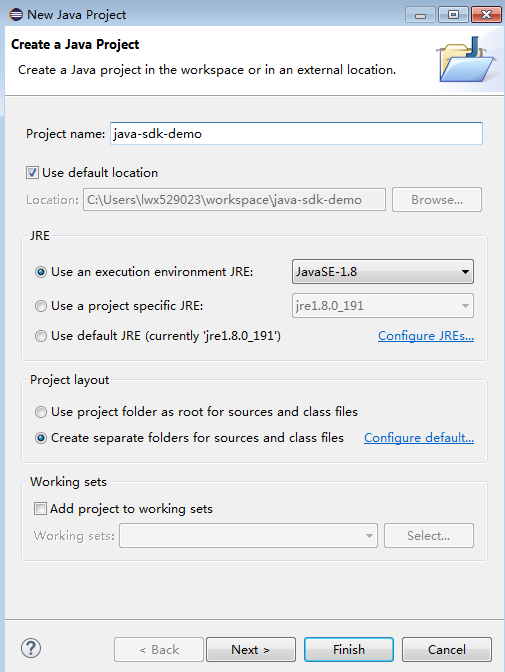
- Enter a project name, for example, java-sdk-demo, retain the default settings for other parameters, and click Finish.
Figure 5 Creating a project
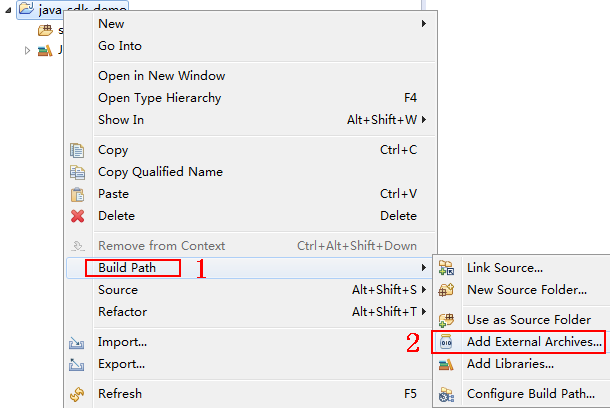
- Import the .jar files in the API Gateway Java SDK.
- Choose java-sdk-demo, right-click, and choose Build Path > Add External Archives from the shortcut menu.
Figure 6 Importing the .jar files
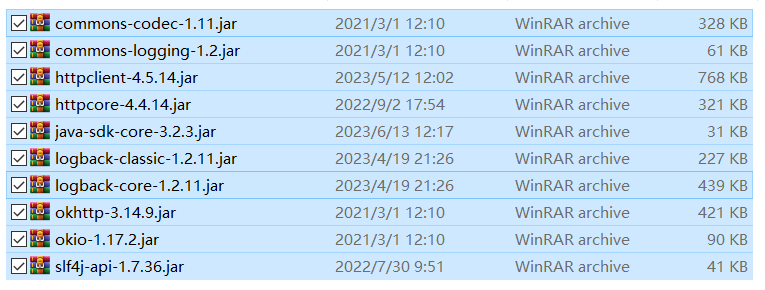
- Select all .jar files in the \libs directory.
Figure 7 Selecting all .jar files
- Choose java-sdk-demo, right-click, and choose Build Path > Add External Archives from the shortcut menu.
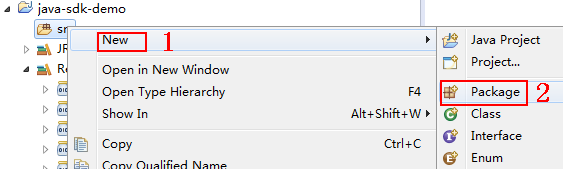
- Create a package and Main file.
- Choose src, right-click, and choose New > Package from the shortcut menu.
Figure 8 Creating a package
- Enter com.apig.sdk.demo for Name.
Figure 9 Setting a package name
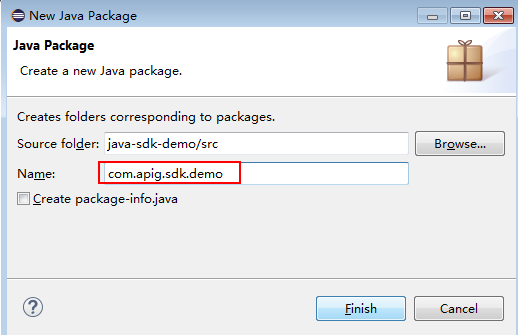
- Click Finish.
The package is created.
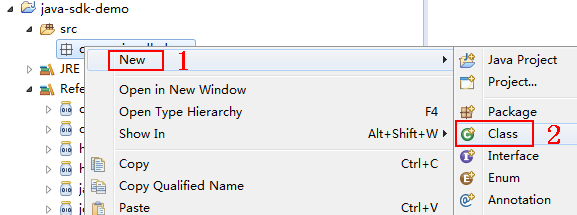
- Choose com.apig.sdk.demo, right-click, and choose New > Class from the shortcut menu.
Figure 10 Creating a class
- Enter Main for Name and select public static void main(String[] args).
Figure 11 Configuring the class
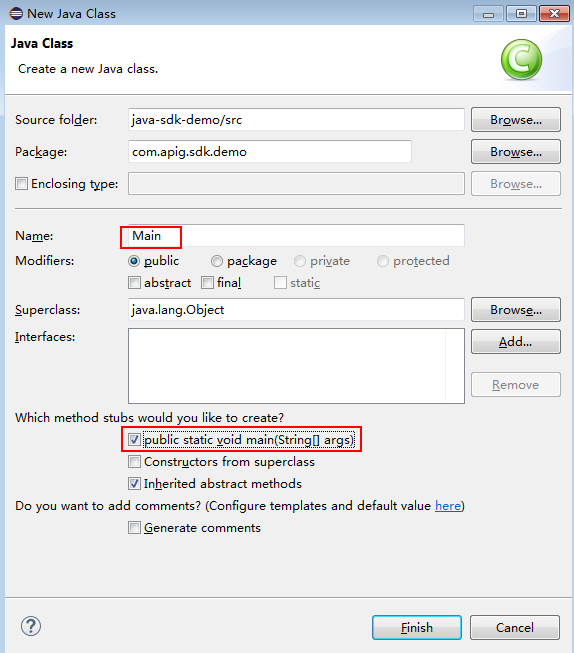
- Click Finish.
The Main file is created.
- Choose src, right-click, and choose New > Package from the shortcut menu.
- View the directory structure of the project.
Figure 12 Directory structure of the new project
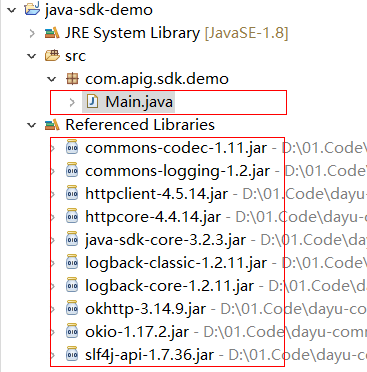
Before using Main.java, enter the required code according to API Calling Example.
API Calling Example
- This section demonstrates how to access a published API.
- You need to create and release an API on the DataArts DataService management console. For details about how to create and publish an API, see Creating an API and Publishing an API.
- The backend of this API is a fake HTTP service, which returns response code 200 and message body Congratulations, sdk demo is running.
- Add the following references to Main.java:
import com.cloud.apigateway.sdk.utils.Client; import com.cloud.apigateway.sdk.utils.Request; import org.apache.http.Header; import org.apache.http.HttpEntity; import org.apache.http.HttpResponse; import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpRequestBase; import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient; import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients; import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
- Construct a request by configuring the following parameters:
- AppKey: Obtain it by referring to Preparation. Coded or plaintext AK and SK in code pose significant security risks. You are advised to encrypt and store them in configuration files or environment variables and decrypt them when needed. This example takes environment variables as an example.
- AppSecret: Obtain it by referring to Preparation. Coded or plaintext AK and SK in code pose significant security risks. You are advised to encrypt and store them in configuration files or environment variables and decrypt them when needed. This example takes environment variables as an example.
- Method: Specify a request method. The sample code uses POST.
- url: Request URL of the API, excluding the QueryString and fragment parts. For the domain name, use your own independent domain name bound to the group to which the API belongs. Use the sample code in http://{apig-endpoint}/java-sdk.
- queryString: Specify query parameters to be carried in the URL. Characters (0-9a-zA-Z./;[]\-=~#%^&_+:") are allowed. The sample code uses name=value.
- Header: Request header. Set a request header as required. It cannot contain underscores (_). The sample code uses Content-Type:text/plain.
- body: Specify the request body. The sample code uses demo.
The sample code is as follows:
Request request = new Request(); try { // Coded or plaintext AK and SK in code pose significant security risks. You are advised to encrypt and store them in configuration files or environment variables and decrypt them when needed. // In this example, the AK and SK stored in the environment variables are used for identity authentication. Before running this example, configure environment variables SDK_AK and SDK_SK in the local environment. String ak = System.getenv("SDK_AK"); String sk = System.getenv("SDK_SK"); request.setKey(ak); request.setSecret(sk); request.setMethod("POST"); request.setUrl("http://{apig-endpoint}/java-sdk"); //Obtain the URL when creating an API group. request.addQueryStringParam("name", "value"); request.addHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain"); //request.addHeader("x-stage", "publish_env_name"); //Specify an environment name before publishing the API in a non-RELEASE environment. request.setBody("demo"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return; } - Sign the request, add header x-Authorization, access the API, and print the result.
The sample code is as follows:
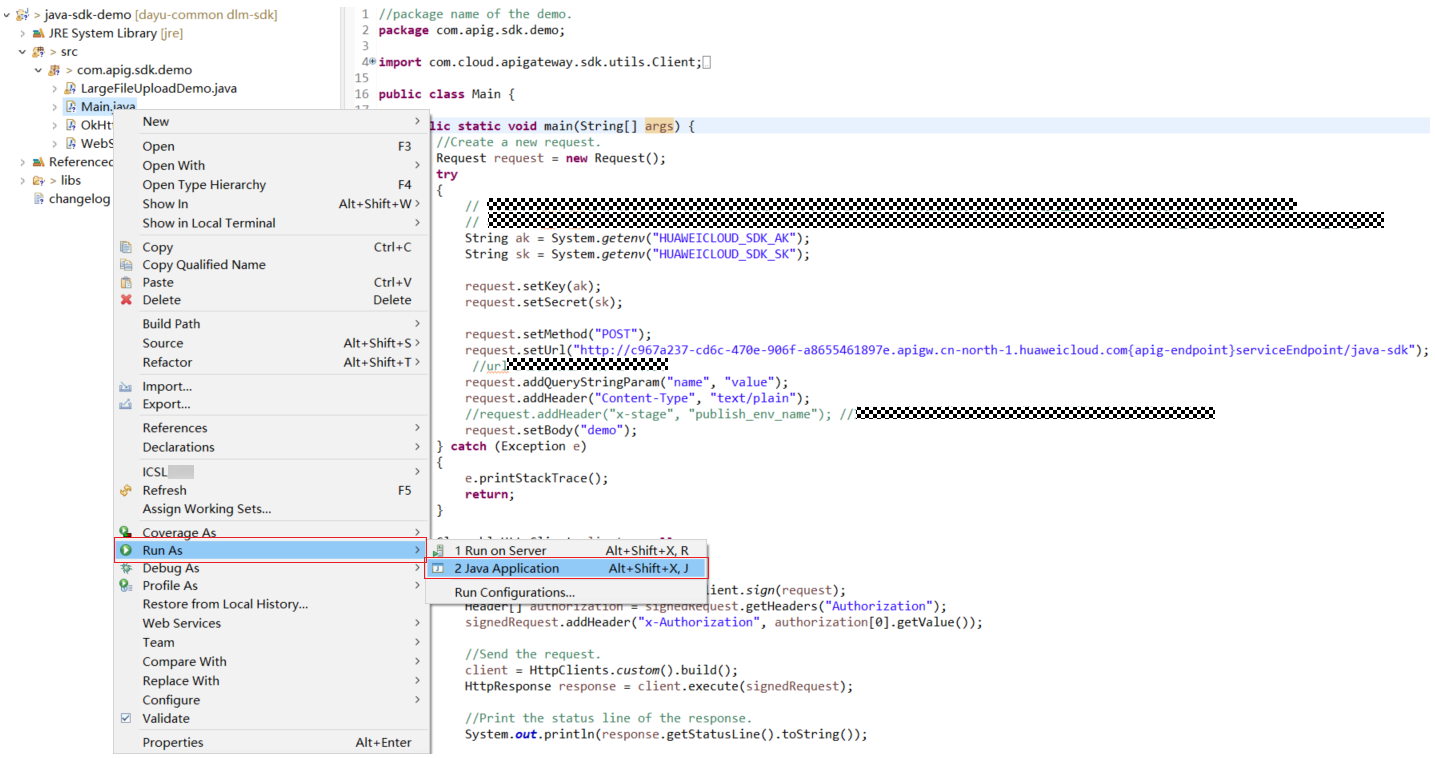
CloseableHttpClient client = null; try { HttpRequestBase signedRequest = Client.sign(request); Header[] authorization = signedRequest.getHeaders("Authorization"); signedRequest.addHeader("x-Authorization",authorization[0].getValue()); client = HttpClients.custom().build(); HttpResponse response = client.execute(signedRequest); System.out.println(response.getStatusLine().toString()); Header[] resHeaders = response.getAllHeaders(); for (Header h : resHeaders) { System.out.println(h.getName() + ":" + h.getValue()); } HttpEntity resEntity = response.getEntity(); if (resEntity != null) { System.out.println(System.getProperty("line.separator") + EntityUtils.toString(resEntity, "UTF-8")); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (client != null) { client.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } - Choose Main.java, right-click, and choose Run As > Java Application to run the project test code.
Figure 13 Running the project test code
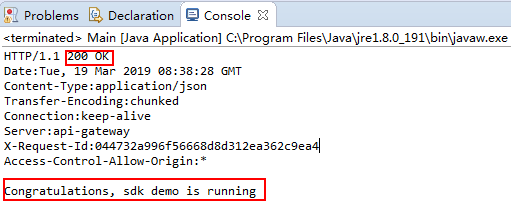
- On the Console tab page, view the running result.
Figure 14 Response displayed if the calling is successful
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






