Migrating Data from Amazon ElastiCache for Redis to GeminiDB Redis API
Migration Principles
After backing up and exporting an RDB file in an Amazon ElastiCache for Redis database, you can use Redis-Shake to restore data to a GeminiDB Redis instance.
Usage Notes
- AWS does not support the psync/sync command and data cannot be incrementally migrated.
- Before the migration, ensure that the network between the ECS where Redis-shake is deployed and the destination GeminiDB Redis is normal.
- Ensure that the security group configuration on the source and target ends is enabled.
Procedure
- Deploy the required migration tool.
- Obtain Redis-Shake.
Download the Redis-Shake release package and decompress it.
- Modify the Redis-Shake.conf configuration file and configuring the following items:
log.level = info #Default log level. A printed INFO log contains migration progress information, based on which you can judge whether the migration is complete.
source.rdb.input = /xx/xx.rdb # Absolute path of the source RDB file
target.address = <host>:6379 # Destination instance IP address
target.password_raw = ***** # Password for logging in to a destination instance
target.version = 5.0 # Version of the destination Redis instance
target.type = standalone # Destination instance type
target.db = 0 #Data is migrated to the specified database of the destination GeminiDB Redis. The default value is db0.
big_key_threshold = 1 #Setting the big key threshold
- Specify whether data of the destination is overwritten.
If there are duplicate keys on the source and destination, specify whether data of the destination is overwritten. The options are as follows:
- rewrite indicates that the source overwrites the destination.
- none indicates that the migration process exists once duplicate keys are detected.
- ignore indicates that keys in the source are retained and keys in the destination are ignored. This value does not take effect in rump mode.
none is recommended. There will be no duplicate data because the source is an RDB file. If the migration exits unexpectedly, you can choose Service Tickets > Create Service Ticket in the upper right corner of the console and contact the customer service.
- Obtain Redis-Shake.
- Migrate data.
Run the following command to start migration:
./redis-shake.linux -conf=redis-shake.conf -type=restore
Use the restore mode because the source is an RDB file.
Stop the migration process after the migration is complete.
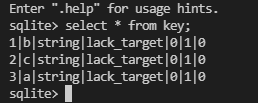
- Verify data.
Data is obtained from the RDB file. Therefore, you need to check the GeminiDB Redis data at the destination end from the service perspective.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.