Connecting to an Instance with SASL
This section describes how to connect to a Kafka instance in a private or public network using a CLI and SASL certificates.
Private network access and public network access differ only in the connection IP addresses and ports. For intra-VPC access, use port 9093. For public access, use port 9095.
The following describes only the procedure for public network access. For private network access, replace the IP addresses with the actual ones.
- If intra-VPC plaintext access is enabled for an instance, data is transmitted in plaintext when you connect to the instance through a private network. For details about how to connect, see Connecting to an Instance Without SASL.
- Each Kafka broker allows a maximum of 1000 connections from each IP address by default. Excess connections will be rejected. You can change the limit by modifying the Kafka parameters.
Prerequisites
- You have correctly configured security group rules. For details, see Table 1.
- The instance connection address has been obtained.
- For intra-VPC access, use port 9093. Obtain the instance connection address in the Connection section of the Basic Information tab page.
Figure 1 Kafka instance connection addresses for intra-VPC access with SASL

- For public access, use port 9095. Obtain the instance connection address in the Connection section of the Basic Information tab page.
Figure 2 Kafka instance connection addresses for public access with SASL

- For intra-VPC access, use port 9093. Obtain the instance connection address in the Connection section of the Basic Information tab page.
- The SASL mechanism in use is known.
In the Connection area on the Kafka instance details page, view SASL Mechanism. If both SCRAM-SHA-512 and PLAIN are enabled, configure either of them for connections. If SASL Mechanism is not displayed, PLAIN is used by default.
Figure 3 SASL mechanism in use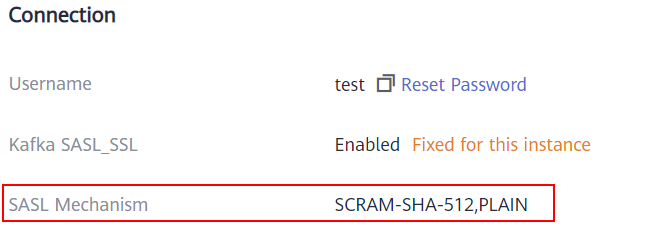
- If automatic topic creation is not enabled for the Kafka instance, obtain the topic name.
You can obtain the name of the topic created in (Optional) Step 3: Create a Topic on the Topics tab page of the instance.
Figure 4 Viewing the topic name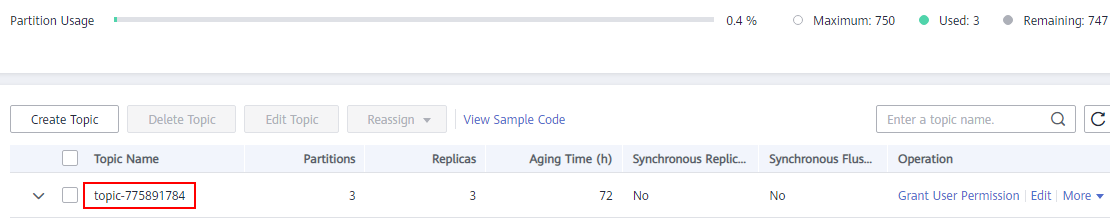
- You have purchased an ECS, installed the JDK, configured the environment variables, and downloaded a Kafka client. For details, see Step 1: Prepare the Environment.
Configuring the Configuration File for Message Creation and Retrieval
- Log in to a Linux ECS.
- Map hosts to IP addresses in the /etc/hosts file on the ECS, so that the client can quickly parse the instance brokers.
Set IP addresses to the instance connection addresses obtained in Prerequisites. Set hosts to the names of instance hosts. Specify a unique name for each host.
For example:
10.154.48.120 server01
10.154.48.121 server02
10.154.48.122 server03
- Download client.truststore.jks. On the Kafka console, click the instance. On the instance details page, click Download next to SSL Certificate in the Connection area.
Decompress the package to obtain the client certificate file client.truststore.jks.
- Modify the Kafka CLI configuration file based on the SASL mechanism.
- If PLAIN is used, find the consumer.properties and producer.properties files in the /config directory of the Kafka CLI and add the following content to the files:
sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required \ username="**********" \ password="**********"; sasl.mechanism=PLAIN security.protocol=SASL_SSL ssl.truststore.location={ssl_truststore_path} ssl.truststore.password=dms@kafka ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm=Parameter description:
- username and password: username and password you set when enabling SASL_SSL during Kafka instance creation or when creating a SASL_SSL user.
- ssl.truststore.location: path for storing the certificate obtained in 3.
- ssl.truststore.password: server certificate password, which must be set to dms@kafka and cannot be changed.
- ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm: whether to verify the certificate domain name. This parameter must be left blank, which indicates disabling domain name verification.
- If SCRAM-SHA-512 is used, find the consumer.properties and producer.properties files in the /config directory of the Kafka CLI and add the following content to the files:
sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required \ username="**********" \ password="**********"; sasl.mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-512 security.protocol=SASL_SSL ssl.truststore.location={ssl_truststore_path} ssl.truststore.password=dms@kafka ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm=Parameter description:
- username and password: username and password you set when enabling SASL_SSL during Kafka instance creation or when creating a SASL_SSL user.
- ssl.truststore.location: path for storing the certificate obtained in 3.
- ssl.truststore.password: server certificate password, which must be set to dms@kafka and cannot be changed.
- ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm: whether to verify the certificate domain name. This parameter must be left blank, which indicates disabling domain name verification.
- If PLAIN is used, find the consumer.properties and producer.properties files in the /config directory of the Kafka CLI and add the following content to the files:
Creating Messages
Go to the /bin directory of the Kafka client file and run the following command to create messages:
./kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list ${connection-address} --topic ${topic-name} --producer.config ../config/producer.properties
Parameter description:
- {connection-address}: the address obtained in Prerequisites
- {topic-name}: the name of the topic created for the Kafka instance
For example, 10.3.196.45:9095,10.78.42.127:9095,10.4.49.103:9095 are the connection addresses of the Kafka instance.
After running the preceding command, you can send a message to the Kafka instance by entering the information as prompted and pressing Enter. Contents in each line are sent as a message.
[root@ecs-kafka bin]#./kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list 10.3.196.45:9095,10.78.42.127:9095,10.4.49.103:9095 --topic topic-demo --producer.config ../config/producer.properties >Hello >DMS >Kafka! >^C[root@ecs-kafka bin]#
To stop creating messages, press Ctrl+C to exit.
Retrieving Messages
Run the following command to retrieve messages:
./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server ${connection-address} --topic ${topic-name} --group ${consumer-group-name} --from-beginning --consumer.config ../config/consumer.properties
Parameter description:
- {connection-address}: the address obtained in Prerequisites
- {topic-name}: the name of the topic created for the Kafka instance
- {consumer-group-name}: the consumer group name set based on your service requirements. If a consumer group name has been specified in the configuration file, ensure that you use the same name in the command line. Otherwise, consumption may fail. If a consumer group name starts with a special character, such as a number sign (#), the monitoring data cannot be displayed.
The following is an example:
[root@ecs-kafka bin]# ./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server 10.xxx.xxx.202:9095,10.xxx.xxx.197:9095,10.xxx.xxx.68:9095 --topic topic-demo --group order-test --from-beginning --consumer.config ../config/consumer.properties Hello Kafka! DMS ^CProcessed a total of 3 messages [root@ecs-kafka bin]#
To stop retrieving messages, press Ctrl+C to exit.
Follow-Up Procedure
You can configure alarm rules for monitoring metrics to receive notifications in a timely manner when instances, brokers, or topics are abnormal.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






