Step 2: Create a Kafka Instance
Prerequisites
Ensure that a VPC is available. For details about how to create a VPC, see the Virtual Private Cloud User Guide.
If you already have an available VPC, you do not need to create a new one.
Procedure
- Log in to the Kafka console, and click Buy Instance in the upper right corner.
- Select a billing mode.
- Select a region closest to your application to reduce latency and accelerate access.
- Select a project from the drop-down list.
- Retain the default AZ settings.
- Specify the instance name and the enterprise project.
- Configure the following instance parameters:
Specifications: Select Default or Custom.
If you select Default, specify the version, broker flavor, number of brokers, and storage space to be supported by the Kafka instance based on the site requirements.
- Version: Kafka v1.1.0, v2.3.0, and v2.7 are supported. v2.7 is recommended. The version cannot be changed once the instance is created.
- CPU Architecture: The x86 architecture is supported.
- Broker Flavor: Select broker specifications that best fit your business needs. For Brokers, specify the broker quantity.
Maximum number of partitions per broker x Number of brokers = Maximum number of partitions of an instance. If the total number of partitions of all topics exceeds the maximum number of partitions allowed for an instance, topic creation will fail.
- Storage Space: Disk type and total disk space for storing the instance data. The disk type cannot be changed once the instance is created.
The storage space is the total space to be consumed by all replicas. Specify the storage space based on the expected service message size and the number of replicas. For example, if the required disk size to store the data for the retention period is 100 GB, the disk capacity must be at least: 100 GB x Number of replicas + 100 GB (reserved).
Disks are formatted when an instance is created. As a result, the actual available disk space is 93% to 95% of the total disk space.- Flavor kafka.2u4g.cluster: The value range of Storage Space is 300–300,000 GB.
- Flavor kafka.4u8g.cluster: The value range of Storage Space is 300–600,000 GB.
- Flavor kafka.8u16g.cluster: The value range of Storage Space is 300–900,000 GB.
- Flavor kafka.12u24g.cluster: The value range of Storage Space is 300–900,000 GB
- Flavor kafka.16u32g.cluster: The value range of Storage Space is 300–900,000 GB
- Capacity Threshold Policy: policy used when the disk usage reaches the threshold. The capacity threshold is 95%.
- Automatically delete: Messages can be created and retrieved, but 10% of the earliest messages will be deleted to ensure sufficient disk space. This policy is suitable for scenarios where no service interruption can be tolerated. Data may be lost.
- Stop production: New messages cannot be created, but existing messages can still be retrieved. This policy is suitable for scenarios where no data loss can be tolerated.
Figure 1 Default specifications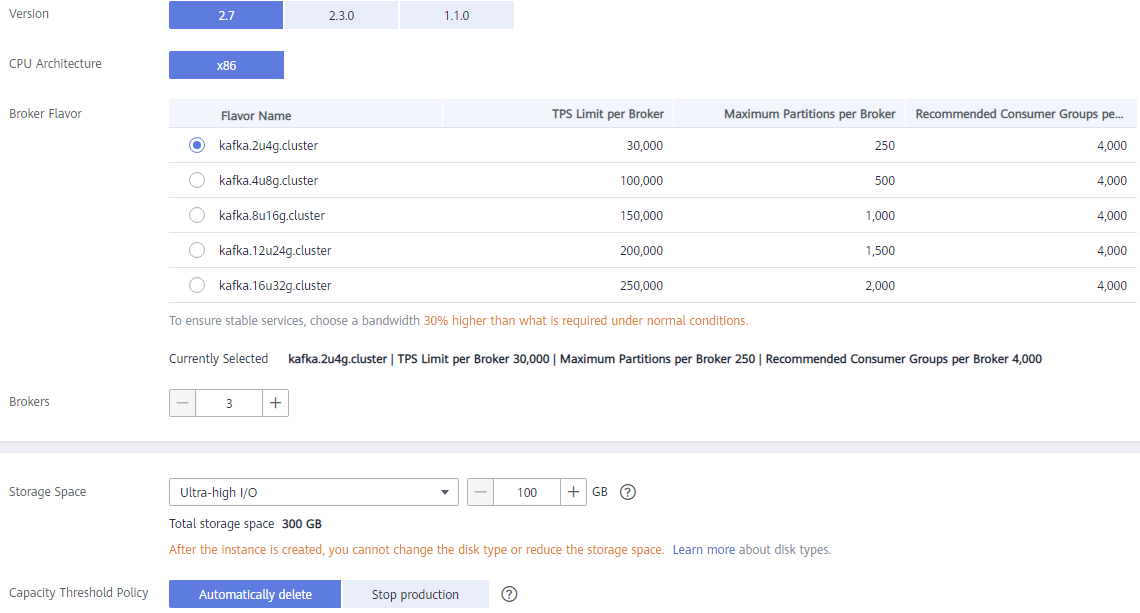
If you select Custom, the system calculates the number of brokers and broker storage space for different flavors based on your specified peak creation traffic, retrieval traffic, number of replicas per topic, total number of partitions, and size of messages created during the retention period. You can select one of the recommended flavors as required.
Figure 2 Specification calculation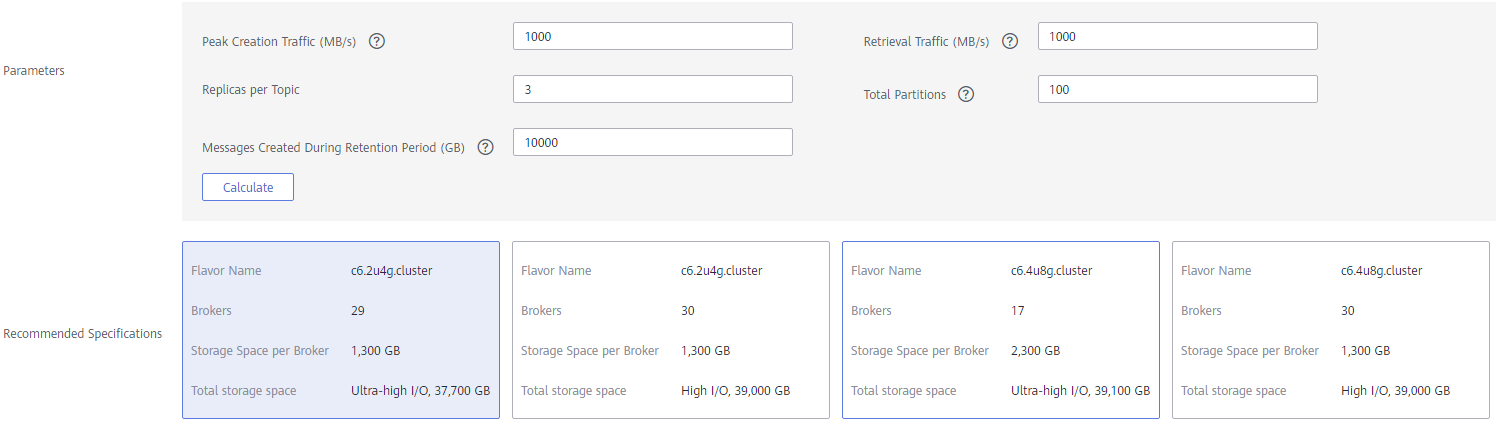
- Configure the instance network parameters.
- Configure the username and password for logging in to Kafka Manager. The Kafka Manager username cannot be changed once an instance is created.
Kafka Manager is an open-source tool for managing Kafka clusters. After a Kafka instance is created, you can go to the instance details page to obtain the address for logging in to Kafka Manager. In Kafka Manager, you can view the monitoring statistics and broker information of your Kafka clusters.
- Click More Settings to configure more parameters.
- Configure Public Access.
Public access is disabled by default. You can enable it or keep it disabled as required. After public access is enabled, configure an IPv4 EIP for each broker.
After enabling Public Access, you can enable or disable Intra-VPC Plaintext Access. If it is enabled, data will be transmitted in plaintext when you connect to the instance through a private network, regardless of whether SASL_SSL is enabled. This setting cannot be changed after the instance is created. Exercise caution. If you want to use a different setting, you must create a new instance.
Figure 3 Configuring public access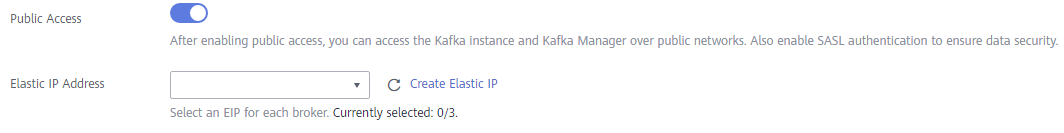
- Configure Kafka SASL_SSL.
This parameter indicates whether to enable SSL authentication when a client connects to the instance. If you enable Kafka SASL_SSL, data will be encrypted before transmission to enhance security.
Kafka SASL_SSL is disabled by default. You can enable or disable it as required. This setting cannot be changed after the instance is created. If you want to use a different setting, you must create a new instance.
If you enable Kafka SASL_SSL, you can determine whether to enable SASL/PLAIN. If SASL/PLAIN is disabled, the SCRAM-SHA-512 mechanism is used to transmit data. If SASL/PLAIN is enabled, both the SCRAM-SHA-512 and PLAIN mechanisms are supported. You can select either of them as required. The SASL/PLAIN setting cannot be changed once the instance is created.
What are SCRAM-SHA-512 and PLAIN mechanisms?
- SCRAM-SHA-512: uses the hash algorithm to generate credentials for usernames and passwords to verify identities. SCRAM-SHA-512 is more secure than PLAIN.
- PLAIN: a simple username and password verification mechanism.
If you enable Kafka SASL_SSL, you must also set the username and password for accessing the instance.
- Configure Automatic Topic Creation.
This setting is disabled by default. You can enable or disable it as required.
If automatic topic creation is enabled, the system automatically creates a topic when a message is created in or retrieved from a topic that does not exist. This topic has the following default settings: 3 partitions, 3 replicas, aging time 72 hours, and synchronous replication and flushing disabled.
After you change the value of the log.retention.hours, default.replication.factor, or num.partitions parameter, automatically created topics later use the new value. For example, if num.partitions is set to 5, an automatically created topic will have the following settings: 5 partitions, 3 replicas, aging time 72 hours, and synchronous replication and flushing disabled.
- Specify tags.
Tags are used to identify cloud resources. When you have many cloud resources of the same type, you can use tags to classify cloud resources by dimension (for example, by usage, owner, or environment).
- If you have created predefined tags, select a predefined pair of tag key and value. You can click View predefined tags to go to the Tag Management Service (TMS) console and view or create tags.
- You can also create new tags by entering Tag key and Tag value.
Up to 20 tags can be added to each Kafka instance. For details about tag requirements, see Managing Instance Tags.
- Enter a description of the instance.
- Configure Public Access.
- Click Buy.
- Confirm the instance information.
- Return to the Kafka Premium page and check whether the instance has been created.
It takes 3 to 15 minutes to create an instance. During this period, the instance status is Creating.
- If the instance is created successfully, its status changes to Running.
- If the instance fails to be created, view Instance Creation Failures. Delete the instance and create another instance. If the instance creation fails again, contact customer service.
Instances that fail to be created do not occupy other resources.
Follow-Up Procedure
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






