Edition Differences
WAF supports yearly/monthly and pay-per-use billing. Different billing modes support different editions. You can select a proper service edition based on your service requirements and website deployment mode.
- Access modes
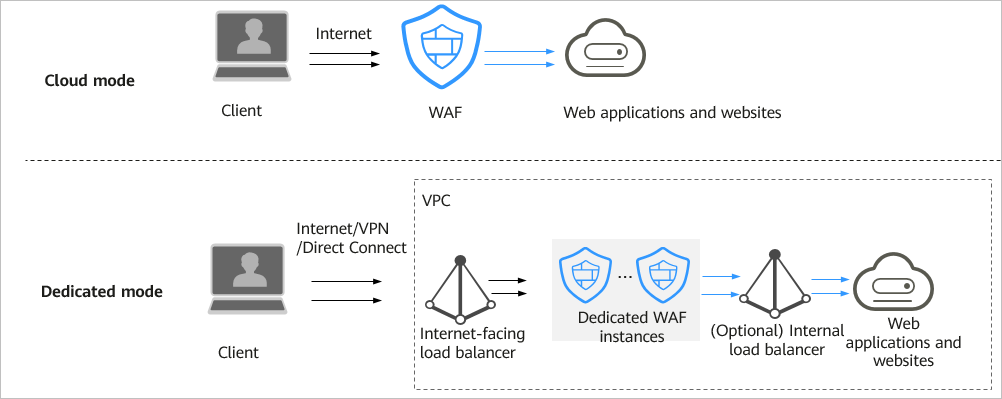
WAF provides cloud mode and dedicated mode. For details about the different access modes and service editions, see Figure 1. You can select a proper access mode and the service edition by referring to Cloud and Dedicated WAF Modes.
- Service edition specifications
To support different workloads scales, WAF provides multiple editions. You can check Specifications Supported by Each Edition and select a service version suitable for your workloads scale.
- Service edition functions
The service functions you can use may differ in different editions and different access modes. Before you start, check the service edition and access mode you plan to use by referring to Functions Supported by Each Service Edition and make sure the one you select can meet your service needs.
Cloud and Dedicated WAF Modes
To support different service scenarios, WAF provides cloud and dedicated access modes. The deployment architecture is shown in Figure 2. For details about the differences, see Table 1.
Specifications Supported by Each Edition
Table 2 lists the service specifications supported by each WAF edition. In cloud mode, to protect more domain names and traffic, you can either purchase domain name, QPS, and rule expansion packages or change the edition of your cloud WAF instance.
WAF provides the same service specifications in the Cloud Mode - Load Balancer Access and Cloud Mode - CNAME Access modes. So the two modes can share the domain name, QPS, and rule expansion package quotas.
|
Service Scale |
Standard Edition (Cloud Mode) |
Professional Edition (Cloud Mode) |
Platinum Edition (Cloud Mode) |
Pay-per-use Billing (Cloud Mode) |
Pay-per-Use Billing (Dedicated Mode) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Peak rate of normal service requests |
|
|
|
WAF-to-Server connections: 6,000 per domain name |
The following lists the specifications of a single instance.
NOTICE:
Maximum QPS values are for your reference only. They may vary depending on your businesses. The real-world QPS is related to the request size and the type and quantity of protection rules you customize. |
|
Service bandwidth threshold (The origin server is deployed on the cloud.) |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
Service bandwidth threshold (The origin server is not deployed on Huawei Cloud.) |
|
|
|
- |
N/A |
|
Number of domains |
|
|
|
200 (Supports 20 top-level domain names.) |
2,000 (Supports 2,000 top-level domain names) |
|
Back-to-source IP address quantity (the number of WAF back-to-source IP addresses that can be allowed by a protected domain name) |
20 |
50 |
80 |
20 |
N/A |
|
Peak rate of CC attack defense |
100,000 QPS |
200,000 QPS |
1,000,000 QPS |
N/A |
|
|
Number of CC attack defense rules |
20 |
50 |
100 |
200 |
100 |
|
Number of precise protection rules |
20 |
50 |
100 |
200 |
100 |
|
Number of reference table rules |
N/A |
50 |
100 |
200 |
100 |
|
Number of IP address blacklist or whitelist rules |
|
|
|
200 |
1,000 |
|
Number of geolocation access control rules |
N/A |
50 |
100 |
200 |
100 |
|
Number of web tamper protection rules |
20 |
50 |
100 |
200 |
100 |
|
Website anti-crawler protection |
N/A |
50 |
100 |
200 |
100 |
|
Number of information leakage prevention rules |
N/A |
50 |
100 |
200 |
100 |
|
Global protection whitelist rules |
1,000 |
1,000 |
1,000 |
2,000 |
1,000 |
|
Number of data masking rules |
20 |
50 |
100 |
200 |
100 |

- The number of domains is the total number of top-level domain names (for example, example.com), single domain names/second-level domains (for example, www.example.com), and wildcard domain names (for example, *.example.com). For example, the standard edition WAF can protect up to 10 domain names. You can add one top-level domain name and nine subdomain names or wildcard domain names related to the top-level domain name.
- If a domain name maps to different ports, each port is considered to represent a different domain name. For example, www.example.com:8080 and www.example.com:8081 are counted towards your quota as two distinct domain names.
- You can upload as many certificates in WAF as the number of domain names that can be protected by your WAF instances in the same account. For example, if you purchase a standard edition WAF instance, which can protect 10 domain names, a dedicated WAF instance, which can protect 2,000 domain names, and a domain name expansion package (20 domain names), your WAF instances can protect 2,030 domain names total (2,000 + 20 +10). In this case, you can upload 2,030 certificates.
Functions Supported by Each Service Edition
WAF provides different features in different WAF editions and access modes. For details, see Table 3.
Notes:
- √: The function is included in the current edition.
- x: The function is not included in the current edition.
- -: This function is not involved because the similar functions are available in ELB.
|
Function |
Standard Edition (Cloud Mode) |
Professional Edition (Cloud Mode) |
Platinum Edition (Cloud Mode) |
Pay-per-Use Billing (Dedicated Mode) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Domain Expansion Package |
One domain package can protect 10 domain names, including a maximum of one top-level domain name. |
√ |
√ |
√ |
× |
|
QPS Expansion Package |
A QPS expansion package protects up to:
|
√ |
√ |
√ |
× |
|
Rule Expansion Package |
A rule expansion package allows you to configure up to 10 IP address blacklist and whitelist rules. |
√ |
√ |
√ |
× |
|
Wildcard domain name |
Wildcard domain names (for example, *.example.com) can be added to WAF. |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
Protection for ports except 80 and 443 |
WAF can protect services on specific non-standard ports in addition to standard ports 80 and 443. |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
Protection for ports except ports 80 and 443 |
Non-standard ports can be protected. |
× |
√ |
√ |
× |
|
Batch configuring defense policies |
You can flexibly configure protection policies for protected domain names in batches. |
× |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
Batch adding domain names to a policy |
Batch adding domain names to a policy |
× |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
Common web application attack defense |
WAF defends against attacks such as SQL injections, XSS, remote overflow vulnerabilities, file inclusions, Bash vulnerabilities, remote command execution, directory traversal, sensitive file access, and command/code injections. |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
Zero-day vulnerability protection |
WAF can update protection rules against zero-day vulnerabilities to the latest on the cloud and deliver virtual patches in a timely manner |
√ |
√ |
√ |
× |
|
Webshell Detection |
WAF can protect web applications from web shells. |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
Deep Inspection |
WAF can identify and block evasion attacks, such as the ones that use homomorphic character obfuscation, command injection with deformed wildcard characters, UTF7, data URI scheme, and other techniques. |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
Header Inspection |
WAF detects all header fields in the requests. |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
CC Attack Protection |
You can customize a CC attack protection rule to restrict access to your website based on an IP address, cookie, or Referer, mitigating CC attacks. |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
Precise Protection |
You can configure complex conditions by combining common HTTP fields to match requests precisely. You can log only, allow, or block matched requests. |
√ (excluding full detection) |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
Reference Table Management |
You can configure single-type protection metrics, such as paths, user agent, IP, params, cookie, referer, and headers, in batches. |
× |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
IP Address Blacklist and Whitelist |
You can allow or block specific IP addresses in one click. IP addresses or IP address segments can be imported in batches. |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
Geolocation Access Control |
You can allow or block web requests based on the countries that the requests originate from. |
× |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
Web Tamper Protection |
You can lock website pages (such as sensitive pages) to prevent malicious content tampering. |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
Anti-crawler Protection |
WAF can identify and block crawler behavior such as search engines, scanners, script tools, and other crawlers. |
× |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
WAF supports JavaScript-based anti-crawler protection. |
× |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
|
Number of information leakage prevention rules |
WAF can prevent leakage of privacy data, such as ID card numbers, phone numbers, and email addresses. |
× |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
Global protection whitelist rules |
You can configure global protection whitelist to ignore false positives. |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
Data Masking |
You can configure data masking rules to prevent sensitive data such as passwords from being displayed in event logs. |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
Resource requirement suggestions |
When using dedicated instances, you are advised to configure resource monitoring and alarms on Cloud Eye. It is recommended that the CPU usage be no more than 70% and the memory usage be no more than 80%.
NOTE:
When there are a large number of service requests or complex user-defined protection policies, the CPU and memory usage increases. In extreme cases, the performance fluctuates greatly. You are advised to evaluate the performance specifications based on the pressure tests made on your service model. |
- |
N/A |
- |
√ |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.