Record Set
Overview
A record set provides information about a domain name, including the IP addresses associated with and how to handle requests for the domain name and its subdomains.
If you have created a zone on the DNS console, you can add record sets to define how you want to route traffic for the domain name or its subdomains.
Table 1 describes the record set types and their application scenarios.
|
Record Set Type |
Where to Use |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
A |
Public and private zones |
Maps domains to IPv4 addresses. |
|
CNAME |
Public and private zones |
Maps one domain name to another domain name or multiple domain names to one domain name. |
|
Mail exchanger (MX) |
Public and private zones |
Maps domain names to email servers. |
|
AAAA |
Public and private zones |
Maps domain names to IPv6 addresses. |
|
Text (TXT) |
Public and private zones |
TXT record sets are usually used to record the following:
|
|
Service (SRV) |
Public and private zones |
Records servers providing specific services. |
|
Nameserver (NS) |
Public and private zones |
Delegates subdomains to other name servers.
|
|
Start of authority (SOA) |
Public and private zones |
Identifies the base information about a domain name. The SOA record set is automatically generated by the DNS service and cannot be added manually. |
|
Certification Authority Authorization (CAA) |
Public zone |
Grants certificate issuing permissions to CAs. CAA record sets can prevent the issuance of unauthorized HTTPS certificates. |
|
Pointer (PTR) |
Public and private zones |
Maps IP addresses to domain names. |
Usage
Record sets are used in following scenarios:
- Routing Internet traffic to a website
A and AAAA record sets are usually used to map domain names used by websites to IPv4 or IPv6 addresses of web servers where the websites are deployed.
Figure 1 Accessing a website over the Internet using domain name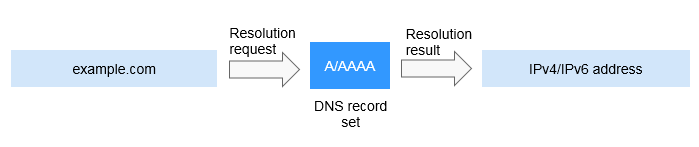
- Private domain name resolution
On a private network, A and AAAA record sets translate private domain names into private IP addresses.
Figure 2 Private domain name resolution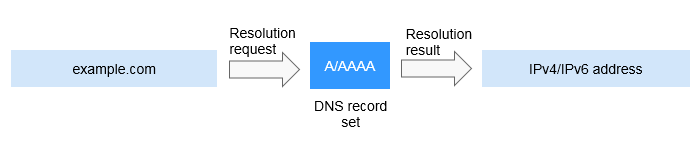
- Email domain name resolution
MX, CNAME, and TXT record sets are usually used for email services.
Figure 3 Email domain name resolution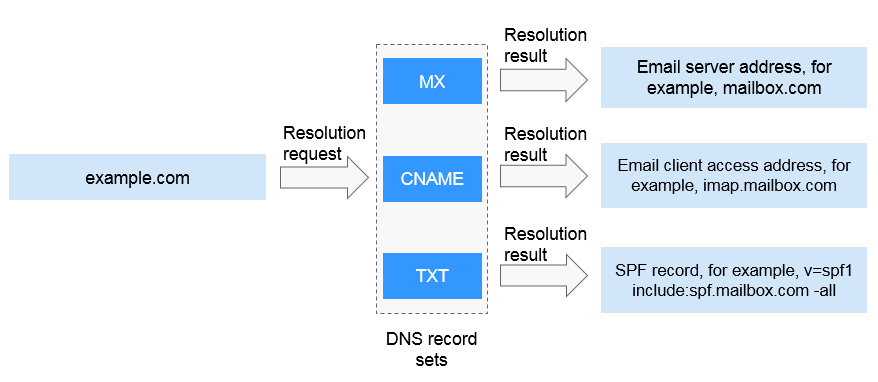
- Reverse resolution on a private network
PTR records translate private IP addresses into private domain names.
Figure 4 Reverse resolution on a private network
Helpful Links
For details about how to add and manage record sets, see Record Set.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






