Data Lineage Overview
What Is Data Lineage?
In the era of big data, various types of data are rapidly generated due to explosive data growth. The massive and complex data information is converged, transformed, and transferred to generate new data and aggregate into an ocean of data.
- Belongingness: Specific data belongs to a specific organization or individual.
- Multi-source: One piece of data can have multiple sources. One piece of data may be generated by processing multiple pieces of data, and there may be multiple such processes.
- Traceability: The data lineage is traceable. It reflects the data lifecycle and the entire process from data generation to data disappearance.
- Hierarchy: The data lineage is hierarchical. Data classification and summary form new data, and different levels of description result in data layers.
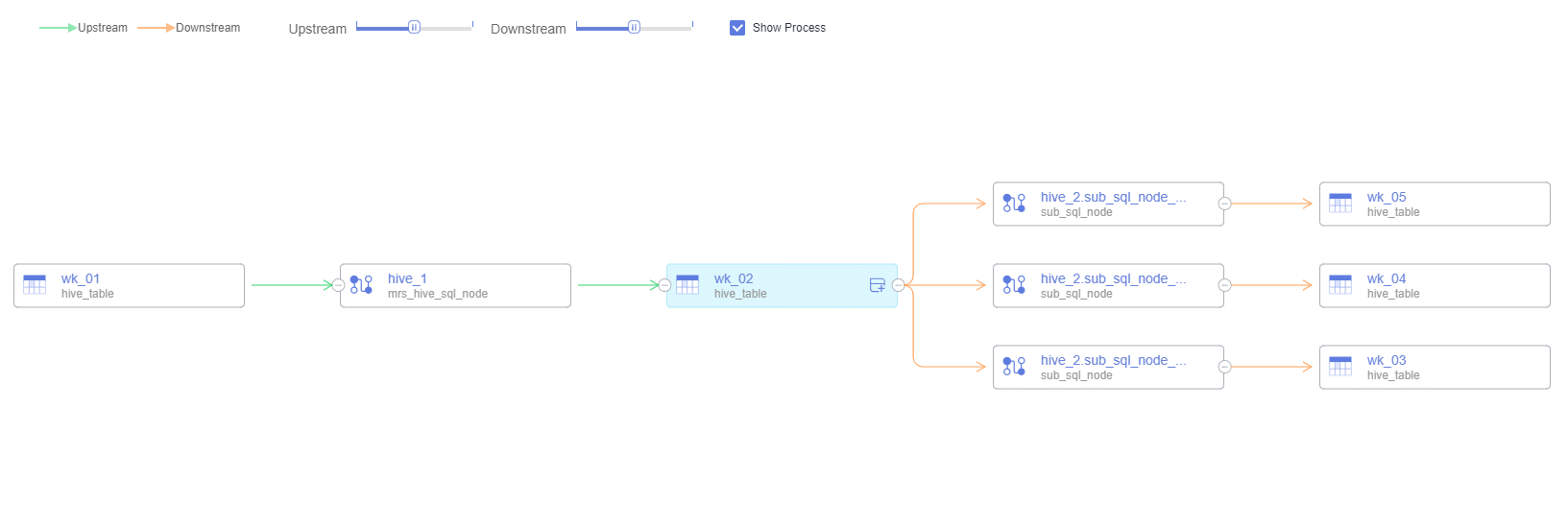
 indicates a data table, and
indicates a data table, and  indicates a job node. They are orchestrated using arrows. As shown in the graph, the data in table wk_01 is processed on the hive_1 job node and then written to table wk_02. The data in table wk_02 is processed on the hive_2 job node and written to tables wk_03, wk_04, and wk_05, respectively.
indicates a job node. They are orchestrated using arrows. As shown in the graph, the data in table wk_01 is processed on the hive_1 job node and then written to table wk_02. The data in table wk_02 is processed on the hive_2 job node and written to tables wk_03, wk_04, and wk_05, respectively.
How DataArts Studio Data Lineage Is Implemented
- Generation of data lineages:
The DataArts Studio data lineage parsing solution supports automatic lineage analysis and manual lineage configuration. Automatic lineage parsing is recommended. In this mode, lineages can be generated without manual configuration. If automatic lineage parsing is not supported, manually configure lineages.
- Automatic lineage parsing: Lineages are automatically generated after the system parses the data processing and data migration nodes in data development jobs. No manual configuration is required. For details about the node types and scenarios that support automatic lineage parsing, see Automatic Lineage Parsing.
- Manual lineage configuration: Customize the input and output tables of lineages in data development job nodes. If you configure lineages manually for a node, the automatic lineage parsing does not take effect for this node. For details about the node types that support manual lineage configuration, see Manually Configuring a Lineage.
- Display of data lineages:
You need to create a metadata collection task in DataArts Catalog first. When a data development job meets the automatic lineage parsing requirements or lineages have been manually configured, and when the job is successfully scheduled, you can view the data lineages in DataArts Catalog.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.