Generating an API Using Configuration
This section describes how to generate an API using configuration.
Generating data APIs using configuration is simple. You do not need to write any code. Wizard mode is designed for users who do not have high requirements on API functions or have no experience in code development.
Prerequisites
You have configured data sources on the Data Connection Management page of Management Center.
Notes and Constraints
APIs cannot be generated for the Chinese tables and columns in Hive data sources.
Creating an API Directory
An API catalog is an API index that is orchestrated and recorded in a certain sequence. It is a tool for reflecting categories, guiding API usage, and searching for APIs, helping API developers effectively classify and manage API services.
- Log in to the DataArts Studio console by following the instructions in Accessing the DataArts Studio Instance Console.
- On the DataArts Studio console, locate a workspace and click DataArts DataService.
- In the left navigation pane, choose an edition, for example, Exclusive Edition. The Overview page is displayed.
- Choose and click
 .
.
In the dialog box displayed, enter an API catalog name, and click OK.
- Right-click the API catalog and select Edit or Delete to edit or delete the API catalog.
Configuring Basic API Information
- On the DataArts Studio console, locate a workspace and click DataArts DataService.
- In the left navigation pane, choose an edition, for example, Exclusive Edition. The Overview page is displayed.
- Choose from the left navigation bar, and click Create. On the displayed page, enter the basic information.
Table 1 API basic configuration Parameter
Description
API
An API name consists of 3 to 64 characters and starts with a letter. Only letters, numbers, and underscores (_) are allowed.
API Catalog
A collection of APIs for a specific function or scenario. It is similar to a folder and specifies the location of APIs. You can search for APIs in a specified API catalog.
The API catalog is the minimum organization unit of APIs in DataArts DataService. You can select an API catalog you have created by referring to Creating an API Directory.
Request Path
API access path, for example, /getUserInfo
It is the part between the domain name and query parameters in the URL of a request path, for example, /blogs/xxxx shown in the following figure.Figure 1 API access path in the URL
Braces ({}) can be used to identify parameters in a request path as wildcard characters. For example, /blogs/{blog_id} indicates that any parameter can follow /blogs. /blogs/188138 and /blogs/0 can both match /blogs/{blog_id}, and are processed by this API.
In addition, duplicate request paths are not allowed for the same domain name. When a path parameter is used as a wildcard, the name is not unique. For example, /blogs/{blog_id} and /blogs/{xxxx} are considered as the same path.
Parameter Protocol
Protocol used to transmit requests. The exclusive edition supports HTTPS.
HTTPS is recommended. HTTP is insecure and may have security risks.
- HTTP is a basic network transmission protocol. It is stateless, connectionless, simple, fast, and flexible, and uses plaintext for transmission. It is easy to use but has poor security.
- HTTPS is an HTTP-based protocol with SSL or TLS encryption verification. It can effectively verify identities and protect data integrity. To access HTTPS APIs, you need to configure related SSL certificates or skip SSL verification.
Request Method
HTTP request method, indicating the type of the requested operation, such as GET and POST. The method complies with the resultful style.- GET requests the server to return specified resources. This method is recommended.
- POST requests the server to add resources or perform special operations. The POST request does not have a body. Instead, it involves transparent transmission.
Description
A brief description of the API to create.
Tag
API tag. The tag is used to mark the API attributes. After the API is created, you can quickly search for the API by tag. A maximum of 20 tags can be set for an API.
Reviewer
A reviewer who has permissions to review APIs. Click Add to enter the page and click Add on the Reviewers tab page to add a reviewer.
Security Authentication
When creating an API, you can select one of the following security authentication modes. The three modes differ in how the API is called. You are advised to select App authentication, which is more secure that the other two modes.- App authentication: After the API is authorized to an application, the key pair (AppKey and AppSecret) of the application is used for security authentication. The API can be called using an SDK or API calling tool. This authentication mode is highly secure and recommended.
- IAM authentication: After the API is authorized to the current account or another account, the user token obtained from IAM is used for security authentication. The API can be called using an API invoking tool. The security level of this mode is medium.
- Non-authentication: This mode allows all users to access APIs, which may pose security risks. It is recommended only for testing APIs. In this mode, no authentication information is required. The security level is low. You can use an API invoking tool or browser to directly call the API.
Display Scope
After the API is published, all users in the selected scope can view the API in the service catalog.- Current workspace APIs
- Current project APIs
- Current tenant's APIs
Access Log
If you select this option, the API query result will be recorded and retained for seven days. You can choose Operations Management > Access Logs and select the request date to view the logs.
Min. Retention Period
Minimum retention period of the API publishing status, in hours. Value 0 indicates that the retention period is not limited.
You can suspend, unpublish, or cancel authorization for an API only after the minimum retention period ends. The system notifies the authorized users. If all authorized users have processed the notifications or unbound the API from their apps, the API will be suspended or unpublished, or the API authorization will be canceled. Otherwise, the system will forcibly suspend, unpublish, or cancel authorization for the API when the minimum retention periods ends.
For example, if the minimum retention period is set to 24 hours, the API can be suspended 24 hours after it is published. If the authorized user handles the notifications in the review center or unbind the API from the app, the API will be directly suspended. Otherwise, the API will be forcibly suspended when the minimum retention period ends.
Input Parameters
Parameters required for calling the API. The parameters are used as the request parameters on the Set Data Extract Logic page.
An input parameter consists of the parameter location, parameter type, whether the parameter is mandatory, whether a null value is allowed, and the default value.- The parameter location can be Query, Header, Path, or Body. In addition, static parameters are supported.
- Query is the query parameter following the URL. It starts with a question mark (?) and connects multiple parameters with &.
- Header is located in the request header and is used to transfer current information, for example, host and token.
- Path is a request parameter in the request path. If you configure a path parameter, you must also add this parameter to the request path.
- Body is a parameter in the request body and is generally in JSON format.
- Static is a static parameter that does not change with the value transferred by the API caller. It is supported only when Security Authentication is App authentication. The value of a static parameter is determined during API authorization. (If the parameter value is not set during authorization, the default value of the API input parameter is used when the API is called using an SDK, and an error is reported indicating that the static parameter value is missing when the API is called using an API tool.)
- The parameter type can be Number or String. Number corresponds to numeric data types such as int, double, and long. String corresponds to text data types such as char, vachar, and text.
- Whether the parameter is mandatory, whether a null value is allowed, and default value
- If the parameter is mandatory, it must be transferred for accessing the API.
- If this parameter is not mandatory and if it is not transferred during API access, the default value will be used. If the parameter is not transferred and no default value is available, null will be used if it is allowed and this parameter will be ignored if null is not allowed.
NOTE:When defining an input parameter, ensure that the following size requirements are met:
- Query and Path: 32 KB.
- HEADER: The maximum size is 128 KB.
- BODY: The maximum size is 128 KB.
You need to set input parameters based on the designed request parameters for the API. For example, the request path of the API used to query user information in a table by user ID is /getUserInfo. You can configure input parameters as follows:- If the request parameter for calling the API is id, and the information about the user with id needs to be returned, configure an input parameter as follows:
- Click Add and enter id for Name.
- Set Parameter Location to Query.
- Set Type to Number.
- Select Yes for Mandatory.
- Retain the default value.
- If the request parameters for calling the API are id1 and id2, and the user information between id1 and id2 needs to be returned, configure input parameters as follows:
- Click Add and enter id1 for Name.
- Set Parameter Location to Query.
- Set Type to Number.
- Select Yes for Mandatory.
- Retain the default value.
- Click Add again and configure parameter id2.
- After the basic API information is complete, click Next to go to the Data Extract Logic page.
Configuring the Data Extraction Logic
- Select a data source, data connection, database, and data table to obtain the tables to be configured.
For details on the data sources supported by DataArts DataService, see Data Sources Supported by DataArts Studio. Configure data sources in Management Center in advance. You can search for a data table by name.
- Configure parameter fields.
Click Add next to Parameter Settings. All fields in the table are displayed on the page for adding parameters. Select the request parameters, response parameters, and ranking parameters that you want to add to the corresponding lists.
In addition, you can enable Return Total Records. Then the total number of script execution results will be returned.
Figure 2 Add Parameter dialog box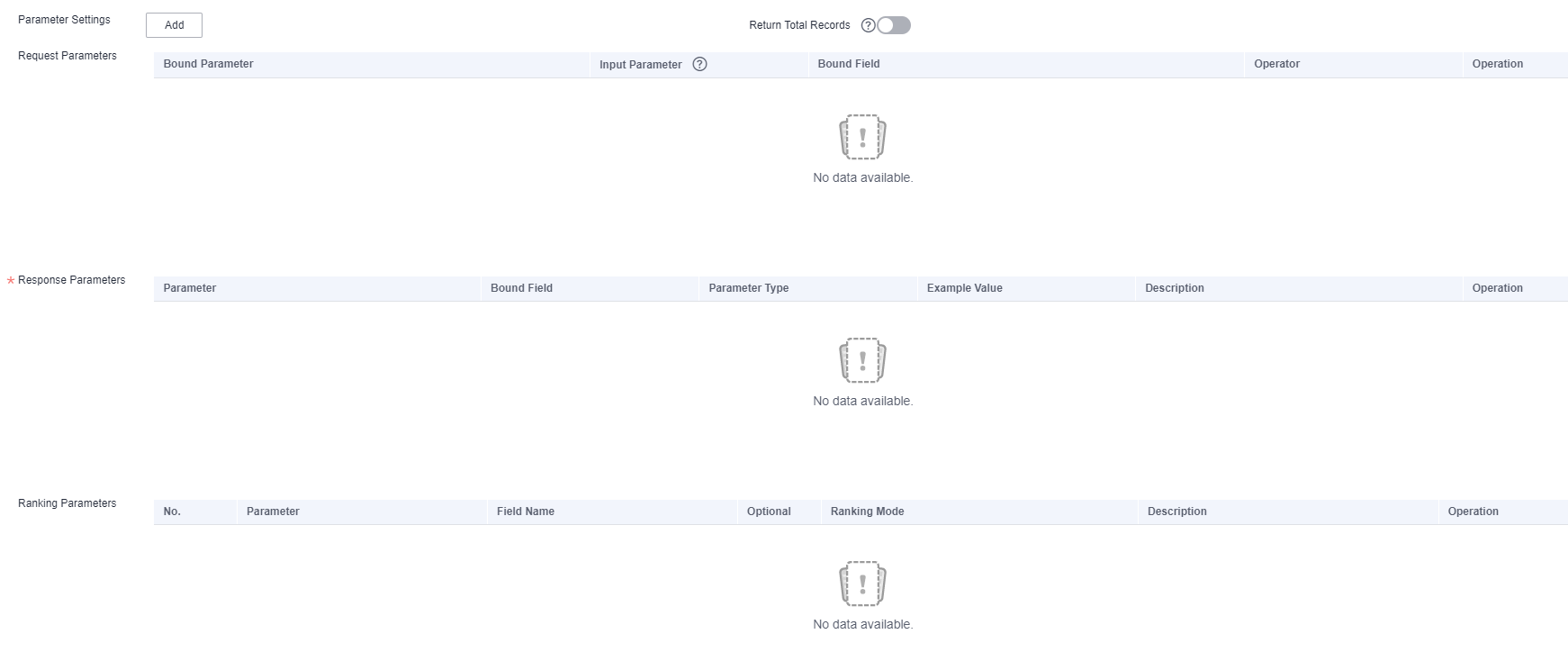
- Edit request parameters.
A request parameter consists of a bound parameter, bound field, and operator. In the request parameter list, select a bound parameter and an operator.
- Bound parameters are available to external systems. They are the input parameters defined on the Configure Basic Details page and are directly used to access the API.
- Bound fields are invisible to external systems. They are fields of the selected tables and are accessed during an API call.
- Operators determine how bound fields and parameters in access requests are processed. A bound field is on the left of an operator and a bound parameter is on the right. The following table lists the available operators.
Table 2 Available operators Operator
Description
=
Checks whether the values of two operands are equal.
The condition is true if the bound field is equal to the bound parameter.
NOTE:The values of FLOAT4 and FLOAT8 parameters of the DWS database cannot be compared.
<>
Checks whether the values of two operands are equal.
The condition is true if the bound field is not equal to the bound parameter.
NOTE:The values of FLOAT4 and FLOAT8 parameters of the DWS database cannot be compared.
>
Checks whether the value of the left operand is greater than that of the right operand.
The condition is true if the bound field is greater than the bound parameter.
>=
Checks whether the value of the left operand is greater than or equal to that of the right operand.
The condition is true if the bound field is greater than or equal to the bound parameter.
<
Checks whether the value of the left operand is less than that of the right operand.
The condition is true if the bound field is less than the bound parameter.
<=
Checks whether the value of the left operand is less than or equal to that of the right operand.
The condition is true if the bound field is less than or equal to the bound parameter.
%like%
Ignores the prefix and suffix in character matching.
The condition is true if the bound field (excluding the prefix and suffix) can match the bound parameter.
%like
Ignores the prefix in character matching.
The condition is true if the bound field (excluding the prefix) can match the bound parameter.
like%
Ignores the suffix in character matching.
The condition is true if the bound field (excluding the suffix) can match the bound parameter.
in
Compares a value with a specified list of values.
The condition is true if the bound field can match the values in multiple bound parameters.
not in
Compares a value with values not in a specified list. It is the opposite of the in operator.
The condition is true if the bound field cannot match the values in multiple bound parameters.
You can copy and set operators in request parameters to match input bound parameters with bound fields.
As shown in Figure 3, you can enter parameters id1 and id2 when accessing an API to match the values of x columns between id1 and id2.
- Edit response parameters.
A response parameter consists of the parameter name, bound field, and parameter type.
- Parameters are available to external systems and can be customized. They are returned to API callers.
- Bound fields are invisible to external systems. They are fields of the selected tables and are returned during an API call.
- The parameter type is the data display format when the API is called, and can be a numeric or character.
Figure 4 Response parameters

- Edit ranking parameters.
A ranking parameter consists of the parameter name, field name, whether the parameter is optional, and ranking mode. Multiple ranking parameters are allowed.
- Parameter names can be customized and associated with field names.
- Field names are invisible to external systems. They are fields of the selected tables and are accessed during an API call.
- Whether the parameter is optional for calling the API. If you select it, this parameter is optional. You can use the value of pre_order_by to configure whether this parameter is used for ranking. If you do not select it, this parameter is mandatory. Even if this parameter is not set for pre_order_by, this parameter is still used for ranking.
- The ranking mode can be ascending, descending, or custom. The default ranking mode of a custom ranking parameter is ascending. You can change the ranking mode by setting pre_order_by. If the ranking mode of a parameter is ascending or descending, the ranking mode cannot be changed using pre_order_by. If the value of pre_order_by is different from the ranking mode set, an error is reported during configuration debugging or API calling.
- If there are multiple ranking parameters, when the first ranking parameter is the same, the subsequent parameters are used for ranking. The order of ranking parameters cannot be adjusted using pre_order_by. To adjust the order, click Addnext to Parameter Settings to open the Add Parameter dialog box and adjust the order of ranking parameters.
Figure 5 Ranking parameters
- Click Next to go to the API test page.
Testing the API
- Set values for input parameters.
If you want to set multiple values for a parameter, observe the following format:
- String: 'a','b','c'
- Value: 1,2
- Field: a,b,c
Figure 6 Setting values for input parameters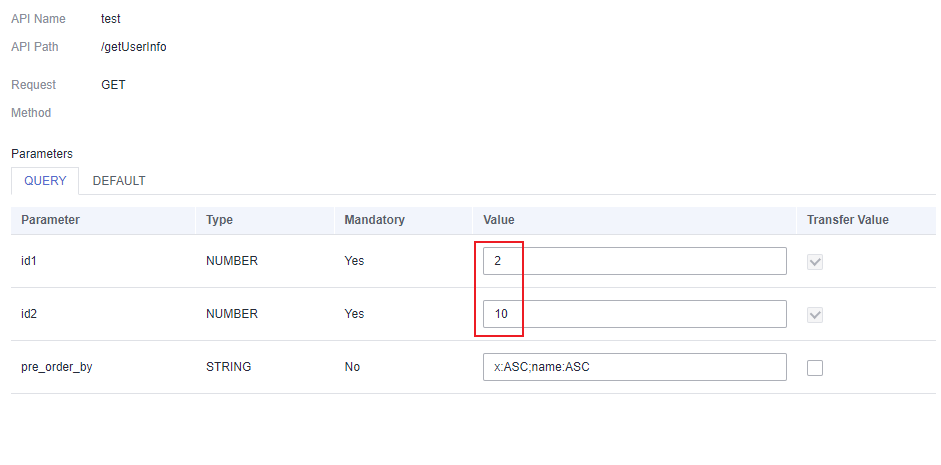
- (Optional) Change the value of pre_order_by, which indicates the ranking parameter description.
The system provides the default value of pre_order_by based on all the ranking parameters configured in 5. The default ranking mode is ascending. The value of pre_order_by is in either of the following formats: Ranking parameter name:ASC (ascending order) or Ranking parameter name:DESC (descending order). Separate multiple ranking parameter descriptions by semicolons (;). If you select Transfer Value, test results are sorted by the value of pre_order_by.
You can change the value of pre_order_by as follows:- Delete an optional ranking parameter. The parameter is no longer used for ranking.
- Change the ranking mode of a ranking parameter whose ranking mode is custom to ascending or descending. The ranking parameter is sorted based on the new ranking mode.
 The value of pre_order_by cannot be changed in any of the following ways. Otherwise, the change does not take effect or an error is reported during API calling.
The value of pre_order_by cannot be changed in any of the following ways. Otherwise, the change does not take effect or an error is reported during API calling.- If a mandatory ranking parameter is deleted, the parameter is still used for ranking and the deletion does not take effect.
- If the sequence of ranking parameters is adjusted, the sequence of the parameters is still the same as that configured during the configuration of these parameters. The adjustment does not take effect.
- If you change the ranking mode of a ranking parameter whose ranking mode is ascending or descending, the API cannot be called. Such a change is not allowed.
Figure 7 Changing the value of pre_order_by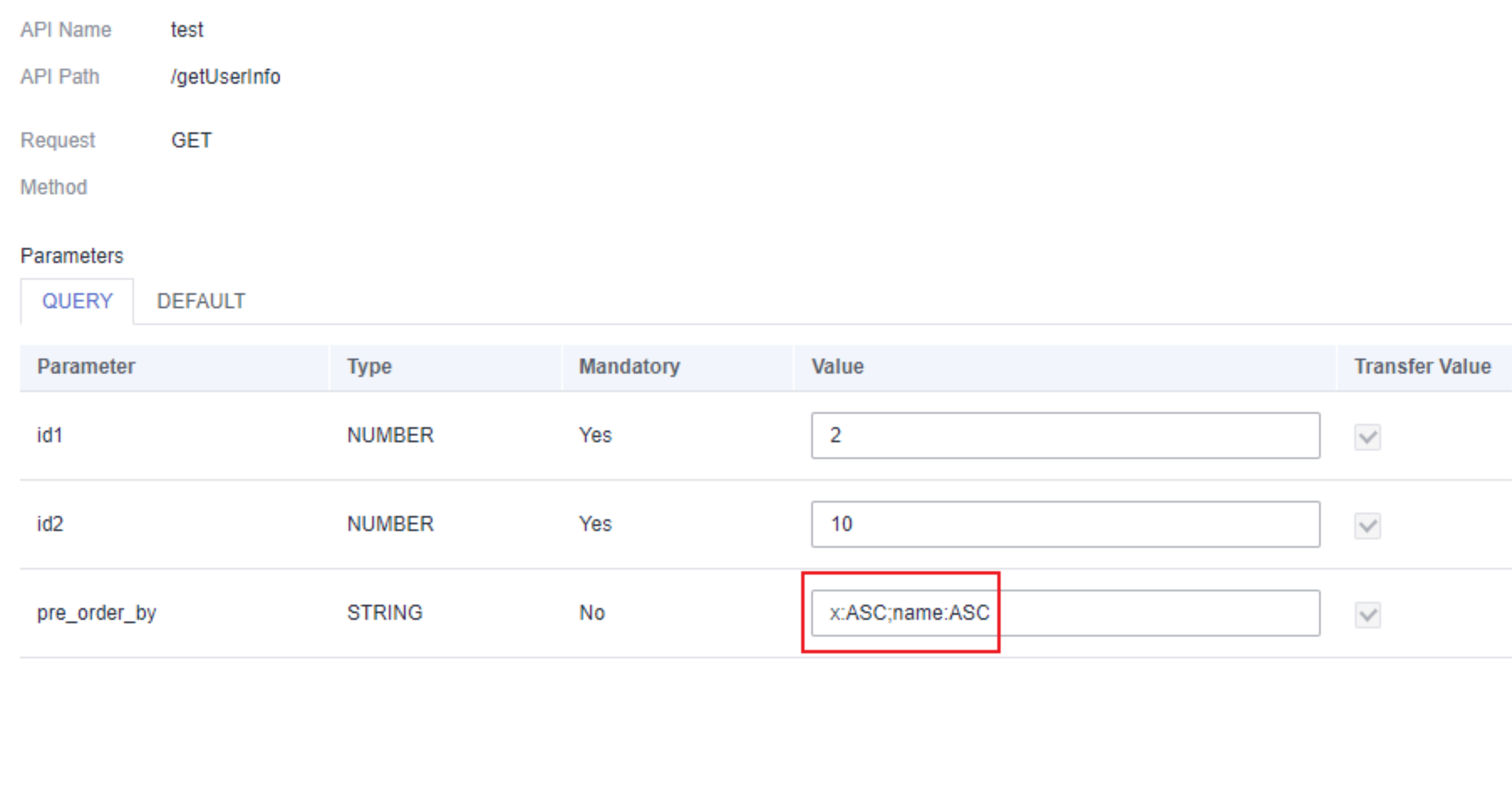
- (Optional) Change the values of pagination parameters.
The system displays the returned data on multiple pages. Parameter pageSize indicates the size of a page, and pageNum indicates the page number. During API debugging, the default page size is 100, and data on the first page is returned.
During API debugging, the maximum value of page_size is 100. If the value of page_size is greater than 100, 100 records are returned by default.
Figure 8 Changing the values of pagination parameters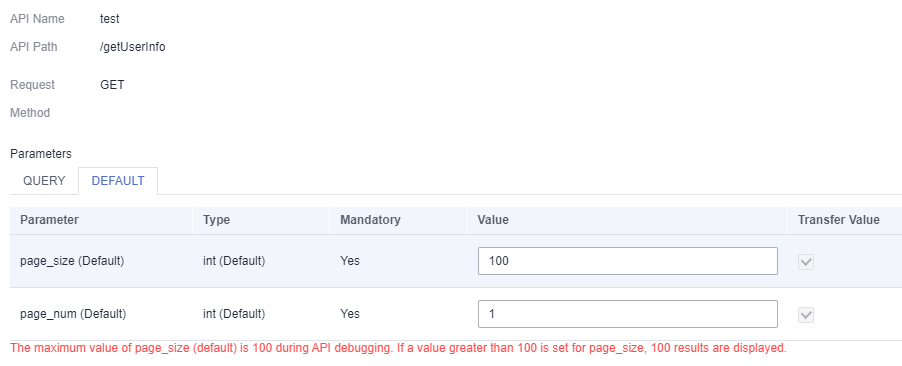
- After setting and saving all parameters, click Next.
Specify Value and click Debug. You can view the Request and Response details on the right part of the displayed page.
- If the total duration of API query and response exceeds the default value 60 seconds, a timeout error is reported.
- If the test fails, modify parameters based on the error message and try again.
After the test is complete, click OK.
Modifying the API
To modify an API, choose API Development > API Catalogs or API Development > APIs, locate the API, and click Edit to modify the API.
An API cannot be edited if it is in the pending review or execution state after published, unpublished, suspended, or resumed.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.







