Hive Supporting Transactions
Scenario
Hive supports transactions at the table and partition levels. When the transaction mode is enabled, transaction tables can be incrementally updated, deleted, and read, implementing atomicity, isolation, consistency, and durability of operations on transaction tables.
This section applies to MRS 3.x or later.
Introduction to Transaction Features
A transaction is a group of unitized operations. These operations are either executed together or not executed together. A transaction is an inseparable unit of work. The four basic elements of a transaction are usually called ACID features, which are as follows:
- Atomicity: A transaction is an inseparable unit of work. All operations in a transaction occur or do not occur together.
- Consistency: The database integrity constraints are not damaged before and after a transaction starts.
- Isolation: When multiple transactions are concurrently accessed, the transactions are isolated from each other. A transaction does not affect the running of other transactions. The impacts between transactions are as follows: dirty read, non-repeatable read, phantom read, and lost update.
- Durability: After a transaction is complete, changes made by the transaction lock to the database are permanently stored in the database.
Characteristics of transaction execution:
- A statement can be written to multiple partitions or tables. If the operation fails, the user cannot see partial write or insert. Even if data is frequently changed, operations can still be quickly performed.
- Hive can automatically compress ACID transaction files without affecting concurrent queries. When querying many small partition files, automatic compression can improve query performance and metadata occupation.
- Read semantics include snapshot isolation. When the read operation starts, the Hive data warehouse is logically locked. The read operation is not affected by any changes that occur during the operation.
Lock Mechanism
Transactions implement the ACID feature through the following two aspects:
- Write-ahead logging ensures atomicity and durability.
- Locking ensures isolation.
|
Operation |
Type of Held Locks |
|---|---|
|
Insert overwrite |
If hive.txn.xlock.iow is set to true, the exclusive lock is held. If hive.txn.xlock.iow is set to false, the semi-shared lock is held. |
|
Insert |
Shared lock. When performing this operation, you can perform read and write operations on the current table or partition. |
|
Update/delete |
Semi-shared lock. When this operation is performed, an operation of holding a shared lock can be performed, but an operation of holding an exclusive lock or a semi-shared lock cannot be performed. |
|
Drop |
Exclusive lock. You cannot perform any other operations on the current table or partition when performing this operation. |
If a conflict caused by the lock mechanism exists in the write operation, the operation that preferentially holds the lock succeeds, and other operations fail.
Procedure
Starting a Transaction
- Log in to FusionInsight Manager. For details, see Accessing FusionInsight Manager (MRS 3.x or Later). Choose Cluster > Name of the desired cluster > Services > Hive > Configurations > All Configurations > MetaStore(Role) > Transaction.
- Set metastore.compactor.initiator.on to true.
- Set metastore.compactor.worker.threads to a positive integer.
metastore.compactor.worker.threads: Specifies the number of working threads for running the compression program on MetaStore. Set this parameter based on the actual requirements. If the value is too small, the transaction compression task is executed slowly. If the value is too large, the MetaStore execution performance deteriorates.
You are advised to set metastore.compactor.worker.threads to 15. You can run the show compactions command to view the compactor tasks that are being executed and have been executed. If compactor tasks cannot be combined in a timely manner due to frequent services, you can choose a larger value for this parameter, but the value should not exceed 50.
- Log in to the Hive client and run the following command to enable the following parameters. For details, see Using a Hive Client.
set hive.support.concurrency=true;
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nonstrict;
set hive.txn.manager=org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.lockmgr.DbTxnManager;
Create a transaction table.
- Run the following command to create a transaction table:
CREATE TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] [db_name.]table_name (col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...) [ROW FORMAT row_format] STORED AS orc ...... TBLPROPERTIES ('transactional'='true'[,'groupId'='group1' ... ] );
For example:
CREATE TABLE acidTbl (a int, b int) STORED AS ORC TBLPROPERTIES ('transactional'='true');
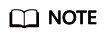
- Currently, the transactions support only the ORC format.
- External tables are not supported.
- Sorted tables are not supported.
- To create a transaction table, you must add the table attribute transactional'='true'.
- The transaction table can be read and written only in transaction mode.
Use the transaction table.
- Run commands to use the transaction table. The following uses the acidTbl table as an example:
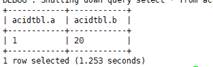
- Insert data into an existing transaction table:
- Update an existing transaction table:
UPDATE acidTbl SET b = 10 where a = 1;
The content of acidTbl is changed to:
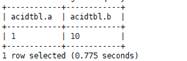
- Merge the old and new transaction tables:
The acidTbl_update table contains the following data:
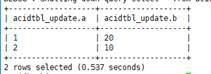
MERGE INTO acidTbl AS a
USING acidTbl_update AS b ON a.a = b.a
WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE SET b = b. b
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT VALUES (b.a, b.b);
The content of acidTbl is changed to:
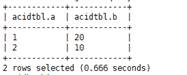
If "Error evaluating cardinality_violation" is displayed when you run the merge command, check whether duplicate connection keys exist or run the set hive.merge.cardinality.check=false command to avoid this exception.
Checking the Transaction Execution Status
- Run the following command to check the transaction execution status:
- Check the lock:
- Check the compression task:
- Check the task execution status:
- Interrupt a transaction:
abort transactions TransactionId;
TransactionId is the value in the Transaction ID column in the command output of Check the task execution status.
Configuring the Compression Function
HDFS does not support in-place file changing. For the new content, HDFS does not provide read consistency either. To provide these features on HDFS, we follow the standard approach used in other data warehouse tools: table or partition data is stored in a set of base files, and new, updated, as well as deleted records are stored in incremental files. Each transaction creates a new set of incremental files to change the table or partition. When read, the base files and the incremental files are merged and the changes of the update or deletion are applied.
Writing a transaction table generates some small files in HDFS. Hive provides major and minor compression policies for combining these small files.
Procedure of Automatic Compression
- Log in to FusionInsight Manager. For details, see Accessing FusionInsight Manager (MRS 3.x or Later). Choose Cluster > Name of the desired cluster > Services > Hive > Configurations > All Configurations > MetaStore(Role) > Transaction.
- Set the following parameters as required:
Table 1 Parameter description Parameter
Description
hive.compactor.check.interval
Interval of executing compression threads. Unit: second. Default value: 300
hive.compactor.cleaner.run.interval
Interval of executing cleaning threads. Unit: millisecond. Default value: 5,000.
hive.compactor.delta.num.threshold
Threshold of the number of incremental files that trigger minor compression. Default value: 10
hive.compactor.delta.pct.threshold
Ratio threshold of the total size of incremental files (delta) that trigger Major compression to the size of base files. The value 0.1 indicates that Major compression is triggered when the ratio of the total size of delta files to the size of base files is 10%. Default value: 0.1
hive.compactor.max.num.delta
Maximum number of incremental files that the compressor will attempt to process in a single job. Default value: 500
metastore.compactor.initiator.on
Indicates whether to run the startup program thread and cleanup program thread on the MetaStore instance. The value must be true. Default value: false.
metastore.compactor.worker.threads
Number of compression program work threads running on MetaStore. If this parameter is set to 0, no compression is performed. To use a transaction, you must set this parameter to a positive number on one or more instances of the MetaStore service. Unit: second Default value: 0
- Log in to the Hive client and perform compression. For details, see Using a Hive Client.
CREATE TABLE table_name ( id int, name string ) CLUSTERED BY (id) INTO 2 BUCKETS STORED AS ORC TBLPROPERTIES ("transactional"="true", "compactor.mapreduce.map.memory.mb"="2048", -- Specify the properties of a compression map job. "compactorthreshold.hive.compactor.delta.num.threshold"="4", -- If there are more than four incremental directories, slight compression is triggered. "compactorthreshold.hive.compactor.delta.pct.threshold"="0.5" -- If the ratio of the incremental file size to the basic file size is greater than 50%, deep compression is triggered. );or
ALTER TABLE table_name COMPACT 'minor' WITH OVERWRITE TBLPROPERTIES ("compactor.mapreduce.map.memory.mb"="3072"); -- Specify the properties of a compression map job. ALTER TABLE table_name COMPACT 'major' WITH OVERWRITE TBLPROPERTIES ("tblprops.orc.compress.size"="8192"); -- Modify any other Hive table attributes.
After compression, small files are not deleted immediately. After the cleaner thread performs cleaning, the files are deleted in batches.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.