Overview
Scenario
Direct Connect establishes a dedicated, secure, and stable network connection between your on-premises data center and VPCs. It can work together with an enterprise router to build a large-scale hybrid cloud network.
VPN establishes a secure, encrypted communication tunnel between your on-premises data center and your VPC. Compared with Direct Connect, VPN is cost-effective and can be quickly deployed.
To ensure high reliability of the hybrid cloud network and reduce costs, you can use Enterprise Router, Direct Connect, and VPN to connect the on-premises data center to the cloud, and use VPN to back up Direct Connect. If a Direct Connect connection becomes faulty, VPN automatically takes over, which minimizes service interruptions.
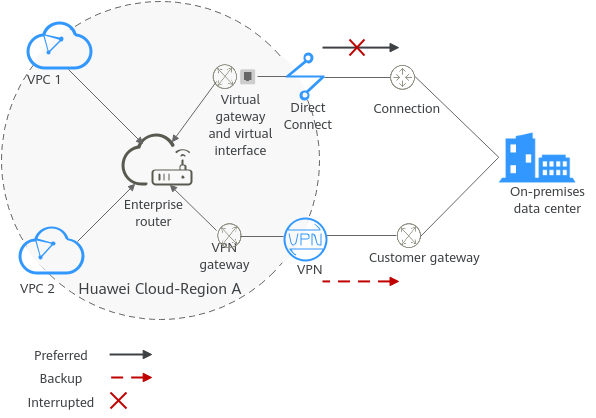
Architecture
- Two VPCs (VPC 1 and VPC 2), and the Direct Connect virtual gateway are attached to the enterprise router. VPC1 and VPC 2 can communicate with each other and communicate with the on-premises data center over the Direct Connect connection.
- A VPN gateway is also attached to the enterprise router. If the Direct Connect connection becomes faulty, VPC 1 and VPC 2 can communicate with the on-premises data center over the VPN connection.
Advantages
An enterprise router enables automatic switchover between active and standby Direct Connect and VPN connections. This prevents service loss and reduces maintenance costs.
Notes and Constraints
The CIDR blocks of the VPCs and of the on-premises data center cannot overlap.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






