Planning Networks and Resources
- Network Planning: Plan the VPC route table and enterprise router route table.
- Resource Planning: Plan the quantity, names, and main parameters of cloud resources: virtual gateways and virtual interfaces, VPC, ECSs, and enterprise router.
Network Planning
During the migration, you need to add routes to the VPC and enterprise router route tables. For details, see Table 1.
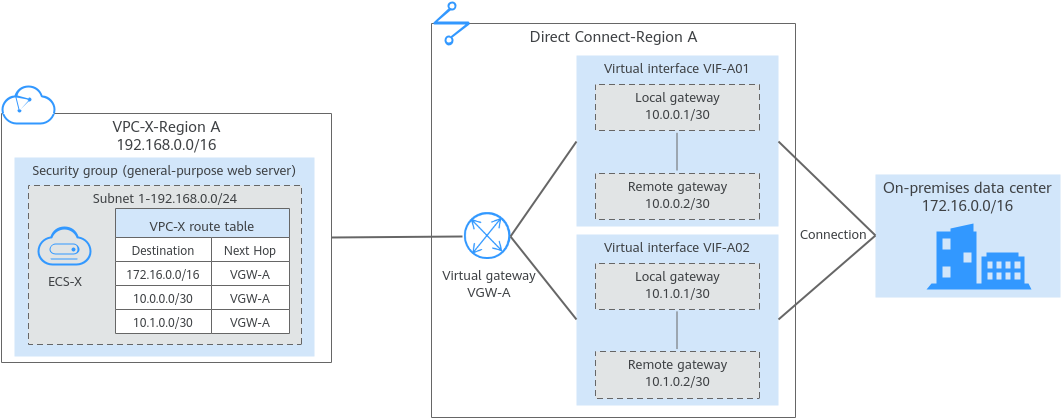
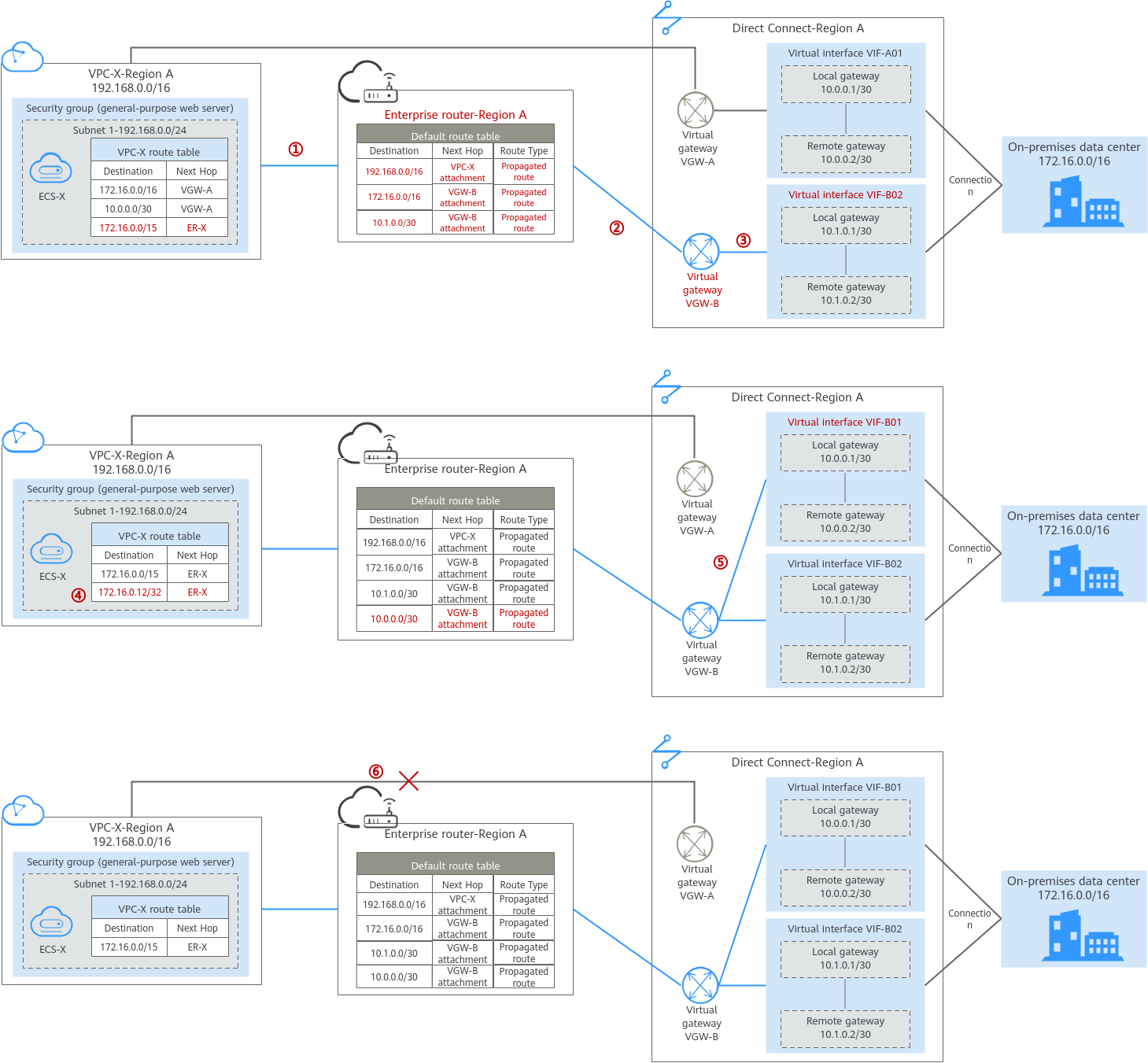
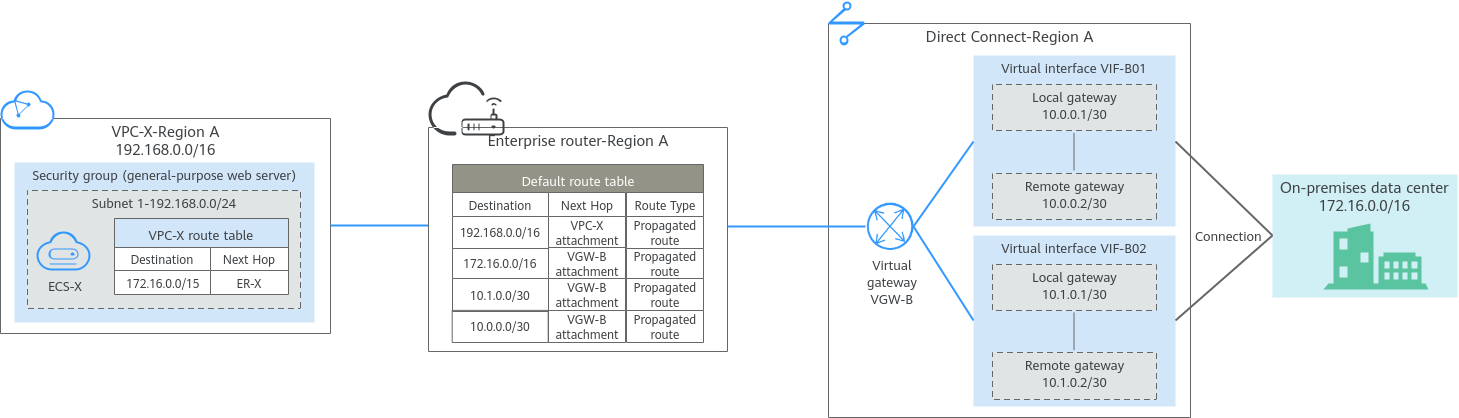
The following figures show the networking in different phases.

The routes in the figures are only examples for your reference. You need to plan routes based on actual service requirements.
|
Route Table |
Description |
|---|---|
|
VPC route table |
Table 2 lists the routes in this route table.
|
|
Enterprise router route table |
Table 3 lists the routes in this route table. During the migration, add routes pointing to the VPC CIDR block and virtual gateway to forward the traffic between the VPC and Direct Connect connection through the enterprise router.
If Default Route Table Association and Default Route Table Propagation are enabled for the enterprise router, routes with destinations set to the attachments are automatically added when you attach the VPC and virtual gateways to the enterprise router.
|
|
VPC |
Route Table |
Destination |
Next Hop Type |
Next Hop |
Route Type |
Description |
Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
VPC-X |
rtb-vpc-X |
172.16.0.0/16 |
Virtual gateway |
vgw-A |
System |
Destined for the on-premises CIDR block |
|
|
10.0.0.0/30 |
Virtual gateway |
vgw-A |
System |
Destined for the local and remote gateways of VIF-A01. |
|
||
|
10.1.0.0/30 |
Virtual gateway |
vgw-A |
System |
Destined for the local and remote gateways of VIF-A02. |
|
||
|
172.16.0.0/15 |
Enterprise router |
ER-X |
Custom |
Destined for the larger CIDR block |
|
||
|
172.16.0.12/32 |
Enterprise router |
ER-X |
Custom |
Destined for any on-premises server to verify communications |
During migration |
|
Enterprise Router |
Route Table |
Destination |
Next Hop |
Attached Resource |
Route Type |
Description |
Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ER-X |
defaultRouteTable |
192.168.0.0/16 |
er-attach-VPC-X |
VPC-X |
Propagated route |
Destination: VPC-X |
|
|
172.16.0.0/16 |
er-attach-VGW-B |
VGW-B |
Propagated |
Destination: on-premises CIDR block |
|
||
|
10.0.0.0/30 |
er-attach-VGW-B |
VGW-B |
Propagated |
Destination: local and remote gateways of VIF-B01 |
|
||
|
10.1.0.0/30 |
er-attach-VGW-B |
VGW-B |
Propagated route |
Destination: local and remote gateways of VIF-B02. |
|
Resource Planning
During the migration, you need to create the required number of enterprise routers, virtual gateways, and virtual interfaces. After the migration is complete, the original resources can be released. Table 4 describes the required resources.

The following resource planning details are only examples for your reference. You need to plan resources based on actual service requirements.
|
Resource |
Quantity |
Description |
Phase |
|---|---|---|---|
|
VPC |
1 |
A VPC for running your services.
|
|
|
Direct Connect connection |
1 |
One connection |
|
|
2 |
The virtual gateway connected to the VPC.
|
|
|
|
The virtual gateway used to replace VGW-A.
|
|
||
|
4 |
The virtual interfaces before the migration.
|
|
|
|
The virtual interfaces after the migration. They are used to replace VIF-A01 and VIF-A02.
|
|
||
|
Enterprise Router |
1 |
The enterprise router that is in the same region as the service VPC.
NOTICE:
Do not enable Auto Add Routes when you create the VPC attachment. If this option is enabled, Enterprise Router automatically adds routes (with this enterprise router as the next hop and 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, and 192.168.0.0/16 as the destinations) to all route tables of the VPC. During the migration, manually add routes with destinations set to the larger CIDR block in the VPC route table. |
|
|
ECS |
1 |
An ECS used to verify connectivity.
|
|
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.