Basic Concepts
Instances
The smallest management unit of GaussDB is the instance. A DB instance is an isolated database environment on the cloud. You can create and manage GaussDB instances on the management console. For details about the storage types, versions, and instance statuses, see DB Instance Description.
DB Engine Versions
GaussDB supports the following versions: V2.0-3.226, V2.0-8.102, V2.0-8.103, and V2.0-8.210.
Instance Types
- Distributed instances allow you to add nodes as needed to handle large volumes of concurrent requests.
- Centralized instances are suitable for scenarios with small and stable volumes of data, where data reliability and service availability are extremely important.
Instance Specifications
The instance specifications determine the computation (vCPUs) and memory capacity (in GB) of an instance. For details, see Instance Specifications.
Coordinator Nodes
A coordinator node (CN) receives access requests from applications, distributes tasks to DNs for parallel processing, and returns execution results to clients.
Data Nodes
A data node (DN) stores data, executes data query tasks, and returns execution results to CNs.
Shards
A shard contains multiple DNs. The number of DNs in a shard depends on the value of Replicas, for example, if Replicas is set to 3, there are three DNs (one primary and two standby DNs) in a shard.
Automated Backups
When you buy a GaussDB instance, an automated backup policy is enabled by default with the retention period set to seven days. You can modify it as required. GaussDB automatically creates full backups for the instance based on your configuration.
Manual Backups
Manual backups are user-initiated full backups of instances. They are retained until you delete them manually.
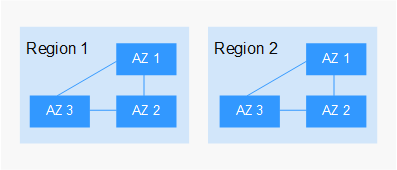
Regions and AZs
A region and availability zone (AZ) identify the location of a data center. You can create resources in a specific region and AZ.
- A region is a physical data center. Each region is isolated from the other regions, improving fault tolerance and stability. The region that is selected during resource creation cannot be changed after the resource is created.
- An AZ is a physical location using independent power supplies and networks. Faults in an AZ do not affect other AZs. A region contains one or more AZs that are physically isolated but interconnected through internal networks. This ensures the independence of AZs and provides low-cost, low-latency network connections.
Figure 1 shows the relationship between regions and AZs.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.