Small-Size Sensitive Data Encryption and Decryption
KMS is mainly used to encrypt sensitive data that is smaller than 4 KB, such as keys, certificates, and configurations, into ciphertext using root keys (CMKs). The data is decrypted only in the memory and transmitted using HTTPS. Plaintext data is not transmitted out of the memory, stored in disks, or recorded in logs, ensuring sensitive data security.
To use KMS to perform high-performance encryption and decryption for massive data, see Large-Size Envelope Encryption and Decryption.
Sensitive Data Example
|
Sensitive Information |
Usage |
Loss Risk |
|---|---|---|
|
Key certificate |
Encrypt service data, communication channels, and digital signatures. |
Confidential information will be stolen, encrypted channels will be intercepted, and signatures will be forged. |
|
Backend configuration file |
Store system architecture and other service information, such as database IP addresses and passwords. |
Service data breach will occur and will be used to attack other systems. |
Encryption and Decryption Principles
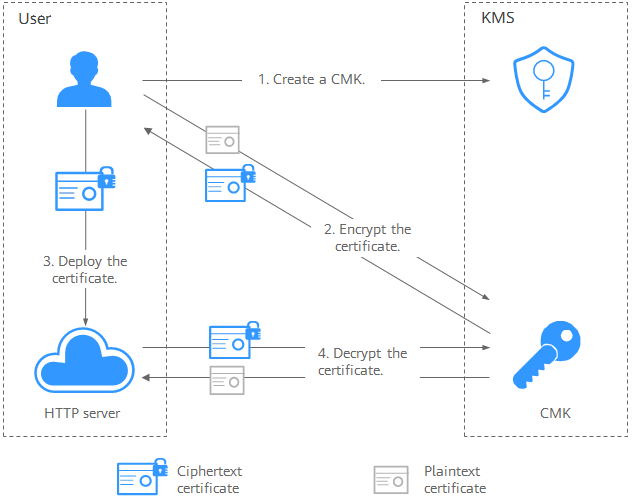
Figure 1 shows an example about how to call KMS APIs to encrypt and decrypt an HTTPS certificate.
Preparations
- You have obtained the Huawei Cloud SDK and installed it.
- You have obtained a Huawei Cloud tenant account and its AK/SK. You can create or view the AK/SK on the page of the Huawei Cloud console.
Procedure
- Create a CMK with the AES_256 algorithm. For details, see Creating a Key.
- Encrypt and decrypt sensitive information.
- Console mode
You can use the online tool to perform one-time or non-batch encryption and decryption, for example, generating a key ciphertext for the first time. You do not need to develop additional tools for non-batch encryption and decryption. Instead, you can focus on core service capabilities. For details, see Encrypting and Decrypting Small-size Data Online Using a Custom Key.
- GO mode
Encrypt data that is smaller than 4 KB. It can be used to encrypt database passwords, RSA keys, and other small-size sensitive information. This following uses Go as an example. You can also use other supported programming languages.
Call the KMS API for encrypting a data key and use the specified CMK to encrypt the plaintext certificate.
Go code example
package main import ( "log" "os" "github.com/huaweicloud/huaweicloud-sdk-go-v3/core/auth/basic" "github.com/huaweicloud/huaweicloud-sdk-go-v3/core/config" "github.com/huaweicloud/huaweicloud-sdk-go-v3/core/region" kms "github.com/huaweicloud/huaweicloud-sdk-go-v3/services/kms/v2" kmsModel "github.com/huaweicloud/huaweicloud-sdk-go-v3/services/kms/v2/model" ) const plainText = "Hello World!" // There will be security risks if the AK/SK used for authentication is directly written into code. Encrypt the AK/SK in the configuration file or environment variables for storage. // In this example, the AK and SK are stored in environment variables. Before running this example, set environment variables HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_AK and HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_SK. var ak = os.Getenv("HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_AK") var sk = os.Getenv("HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_SK") var iamEndpoint = "https://<IAM_ENDPOINT>" var endpoint = "<ENDPOINT>" var regionID = "<REGION_ID>" func main() { // CMK ID keyId := "xxxxxxxx-xxx-xxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxx1" // 1. Prepare the authentication information. auth := basic.NewCredentialsBuilder(). WithAk(ak). WithSk(sk). WithIamEndpointOverride(iamEndpoint). Build() httpConfig := config.DefaultHttpConfig() httpConfig.WithIgnoreSSLVerification(true) // 2. Initialize the SDK and import the authentication information and KMS endpoint information. client := kms.NewKmsClient( kms.KmsClientBuilder(). WithRegion(region.NewRegion(regionID, endpoint)). WithHttpConfig(httpConfig). WithCredential(auth). Build()) // 3. Encrypt data. encryptDataRequest := kmsModel.EncryptDataRequest{ Body: &kmsModel.EncryptDataRequestBody{KeyId: keyId, PlainText: plainText}, } encryptDataResponse, err := client.EncryptData(&encryptDataRequest) if err != nil { log.Fatal("Encrypt data occur error.") } // 4. Decrypt data. decryptDataRequest := kmsModel.DecryptDataRequest{ Body: &kmsModel.DecryptDataRequestBody{KeyId: &keyId, CipherText: *encryptDataResponse.CipherText}, } decryptDataResponse, err := client.DecryptData(&decryptDataRequest) if err != nil { log.Fatal("Decrypt data occur error.") } // 5. Compare the decryption results. log.Printf("result is %t", *decryptDataResponse.PlainText == plainText) }
- Console mode
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.