How Do I Change Default DNS Servers of an ECS to Huawei Cloud Private DNS Servers?
Huawei Cloud provides private DNS servers for domain name resolution. ECSs use public domain names to access the Internet, but use private domain names to access cloud services like OBS and SMN, with no need to connect to the Internet.
For the ECSs that are created before private DNS is available, public DNS servers (like 114.114.114.114) are configured for VPC subnets of the ECSs by default. To allow ECSs on these subnets to use private domain names, change the default public DNS server addresses to those of Huawei Cloud private DNS servers. For details about private DNS servers, see What Are Huawei Cloud Private DNS Server Addresses?
Viewing the DNS Server Addresses for an ECS
- Go to the ECS list page.
- In the ECS list, click the name of the target ECS.
- On the Summary tab of the ECS details page, click the VPC name.
The Virtual Private Cloud page is displayed.
- Locate the VPC and click the number in the Subnets column.
The Subnets page is displayed.
- Click the name of the subnet.
In the Gateway and DNS Information area, view the DNS server addresses used by the ECS.
Figure 1 Subnet list Figure 2 Viewing the DNS server address
Figure 2 Viewing the DNS server address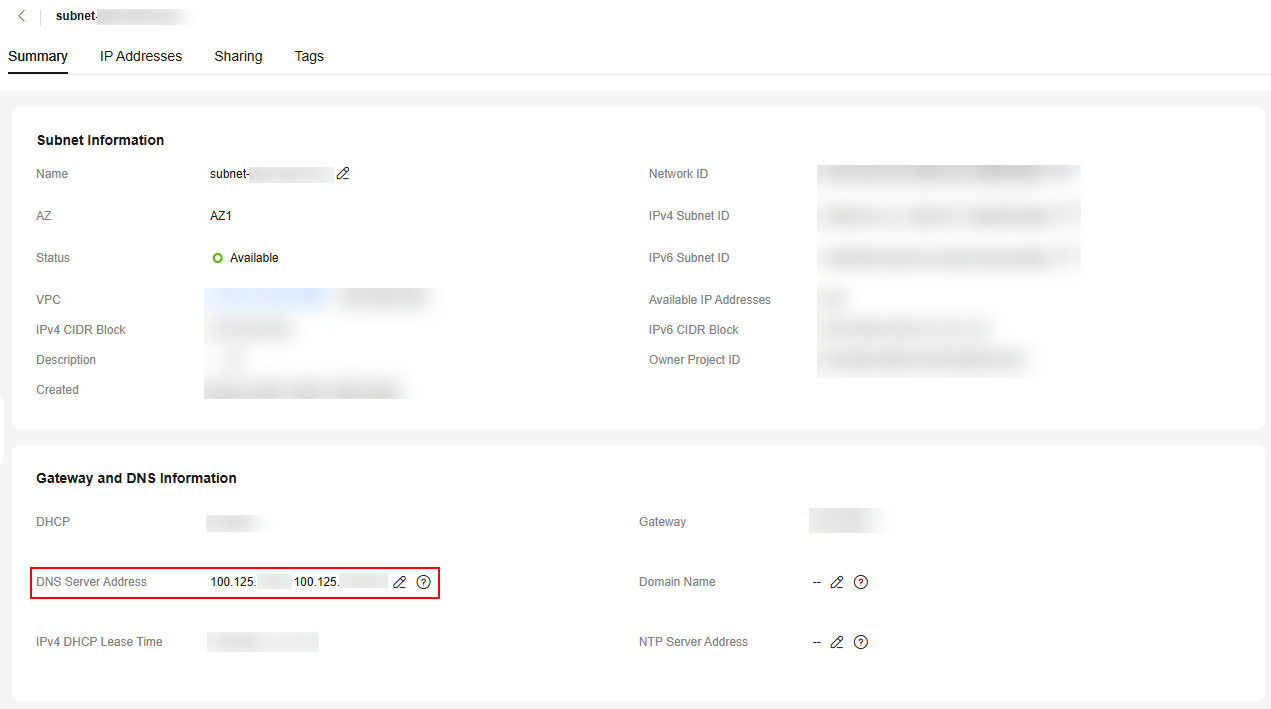
Changing the DNS Server Addresses for a VPC Subnet
If the DNS servers for the ECS are not provided by Huawei Cloud, replace them with Huawei Cloud private DNS servers that are in the same region as the ECS.
- Check addresses of the Huawei Cloud private DNS servers that are in the same region as the ECS by referring to What Are Huawei Cloud Private DNS Server Addresses?.
- In the Gateway and DNS Information area in step 5, click
 next to DNS Server Address.
next to DNS Server Address. - Change the DNS server addresses to private DNS server addresses.
Synchronizing the DNS Server Addresses for the ECS
New DNS server addresses will take effect after they are updated.
- Restart the OS. The ECS will then obtain the new DNS server addresses from the DHCP server.

Restarting the OS will interrupt services on the ECS. Perform this operation during off-peak hours.
Alternatively, wait for the DHCP lease to expire, which is 365 days by default. After the lease time expires, the DHCP server allocates another IP address and updates the DNS server addresses to the ECS.
- Manually change the DNS settings on the ECS.
If DHCP is disabled on the ECS, manually update DNS settings.
For example, if the ECS is running Linux, change the DNS configurations by editing the /etc/resolv.conf file.
For details about configuration examples, see How Do I Configure DNS for an ECS?
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






